Recombinant Escherichia coli Outer membrane protein A (ompA)
In Stock-
中文名称:大肠杆菌ompA重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-CF364256ENV(A4)
-
规格:¥9720
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:ompA
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ompA; con; tolG; tut; b0957; JW0940; Outer membrane protein A; OmpA; Outer membrane porin A; Outer membrane protein 3A; Outer membrane protein B; Outer membrane protein II*; Outer membrane protein d
-
种属:Escherichia coli (strain K12)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
分子量:38.0 kDa
-
表达区域:22-346aa
-
氨基酸序列APKDNTWYTGAKLGWSQYHDTGFINNNGPTHENQLGAGAFGGYQVNPYVGFEMGYDWLGRMPYKGSVENGAYKAQGVQLTAKLGYPITDDLDIYTRLGGMVWRADTKSNVYGKNHDTGVSPVFAGGVEYAITPEIATRLEYQWTNNIGDAHTIGTRPDNGMLSLGVSYRFGQGEAAPVVAPAPAPAPEVQTKHFTLKSDVLFNFNKATLKPEGQAALDQLYSQLSNLDPKDGSVVVLGYTDRIGSDAYNQGLSERRAQSVVDYLISKGIPADKISARGMGESNPVTGNTCDNVKQRAALIDCLAPDRRVEIEVKGIKDVVTQPQA
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:With TolR probably plays a role in maintaining the position of the peptidoglycan cell wall in the periplasm (Probable). Plays a role in resistance to environmental stress, and a role in outer membrane functionality and cell shape. Non-covalently binds peptidoglycan (Probable). Acts as a porin with low permeability that allows slow penetration of small solutes. A very abundant protein, there can be up to 210,000 OmpA molecules per cell. Reconstitution in unilamellar lipid vesicles shows only about 3% of the protein is in an open conformation, which allows diffusion of L-arabinose at a rate comparable to that of OmpF porin; the pores interconvert very rarely. Native and reconstituted protein forms ion channels with 2 conductance states of (50-80 pS) and (260-320 pS); the states are interconvertible in this study. Interconversion requires refolding of the periplasmic domain. Small pores are converted into large pores by increasing temperature; in this model the C-terminal periplasmic domain forms 8 more beta sheets to form a larger pore. The center of the isolated beta-barrel is polar and has a central gate (involving Glu-73, Lys-103, Glu-149 and Arg-159, sandwiched between Tyr-29, Phe-40 and Tyr-94), with no obvious passage for water or ions (Probable). Gating involves the Glu-73-Arg-159 salt bridge; gate opening probably involves formation of alternate salt bridges Glu-149-Arg-159 and Glu-73-Lys-103. Modeling suggests that non-covalent binding of OmpA (from the outer membrane) and TolR (from the inner membrane) to peptidoglycan maintains the position of the cell wall in the periplasm, holding it approximately equidistant from both the inner and outer membranes. Trimeric Lpp controls the width of the periplasm, adjusts its tilt angle to accommodate to the available space, and can compensate in part for an absence of OmpA (Probable).; Required for F plasmid cell conjugation; purified protein plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhibits conjugation in a concentration-dependent manner. OmpA probably acts as the receptor on recipient cells (Probable). Required for the stabilization of mating aggregates during F plasmid conjugative transfer, may interact with F plasmid-encoded TraN, but not with TraN from plasmid R100-1. All 4 external, surface-exposed loops are required for F plasmid conjugation.; (Microbial infection) Mutants with decreased or altered protein are resistant to bacteriophage TuII*. Mutants which have no or greatly reduced protein levels are resistant to a number of bacteriophages, including K3, K4, K5, Ox2, Ox3, Ox4, Ox5, Ml, and Ac3 (Probable). Mutations in this protein render the bacteria partially or completely susceptible to a number of bacteriophages for which is it probably the receptor. All but the last external, surface-exposed loops are required for phage K3 infection.; (Microbial infection) A mutation in this locus (called tolG) renders the cell tolerant to bacteriocin JF246 but does not affect its sensitivity to colicins A, C, El, E2, E3, K, Ia, or Ib. Mutations in this protein render the bacteria partially or completely susceptible to colicin K or colicin L, for which is it probably the receptor.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data indicate the possibility of concatemers of outer membrane protein A (OmpA) either folding directly or forming domain swaps under folding conditions, which can either unfold back to the denatured state or fold directly to the native concatemeric state. PMID: 27973779
- Data suggest a multistep folding mechanism for outer membrane protein A (OmpA) that includes unstructured surface-adsorbed states converting through a partially inserted state with substantial beta-sheet structure to the final natively inserted barrel. PMID: 28001375
- The results suggest that the periplasmic domain slows down the rate, while improves the efficiency, of OmpA folding and membrane insertion under the crowding condition. PMID: 23225740
- The contribution of lipid solvation of tryptophans to the stability of OmpA is evaluated by calculating the difference in unfolding free energy. PMID: 23763479
- In vitro, OmpA+ Escherichia coli infection selectively upregulates Ecgp96 and TLR2 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC), whereas OmpA- E. coli upregulates TLR4 in these cells. PMID: 22963587
- OmpA periplasmic domain exists as an independent folding unit with a free energy of folding equal to -6.2 (+/-0.1) kcal mol(-1) at 25 degrees C. PMID: 21782315
- The stability of ompA mRNA was reduced in the presence of glucose. PMID: 21840983
- Cellular invasion was shown to require activation of host cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2alpha) by Loops1 and 2 but not 3 of Escherichia coli OmpA. PMID: 21148506
- Data show that disulfide bond formation and temperature play decisive roles in folding OmpA into its native large-pore. configuration. PMID: 21069910
- Mutation in loops 1, 2, and 4 resulted in significant inhibition of E. coli K1 invasion in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. PMID: 20851887
- single-mutants S163 and S167 of OmpA, which still contain cOHB on one serine of the sorting signal, form narrow pores in planar lipid bilayers at room temperature with lower and more irregular conductance than wild-type OmpA PMID: 20004640
- the structure of the SecB/OmpA complex was visualized by electron microscopy. The binding pattern between SecB tetramer and OmpA is asymmetric. PMID: 20170640
- Stable E. coli mRNAs as lpp and ompA were drastically destabilized immediately after phage T4 infection. PMID: 15476881
- evidence for convergent evolution; results indicate that large quantities of OmpA are secreted into the medium during all phases of growth, where it is present both in secreted vesicles and as a soluble secreted protein PMID: 15595387
- Results indicate that the two-domain structure of OmpA is a partially folded intermediate that is kinetically stable at lower temperatures and that mature fully folded OmpA is a large pore. PMID: 15850404
- results indicate that distinct regulatory circuits are responsible for growth phase- and growth rate-dependent control of the ompA mRNA stability PMID: 16313626
- controlled post-transcriptionally by RnaseR PMID: 16556233
- Bacteriophage sensitivity testing indicated an association between bacteriophage resistance and isolates having the novel ompA allele PMID: 16980421
- the beta-barrel platform (BBP) and BBP plus the EF motif in dihexanoylphosphatidylcholine micelles are eight-stranded antiparallel beta-barrels PMID: 17260943
- can function as an adhesin and invasin, participate in biofilm formation, act as both an immune target and evasin, and serves as a receptor for several bacteriophages. PMID: 17559395
- polarity analysis of the secretory protein proOmpA and protein-conducting channel SecYEG PMID: 17699162
- Data show that Stat3 activation and its interaction with Ec-gp96, which in turn interacts with E. coli outer membrane protein A, are critical for E. coli invasion. PMID: 18662321
- while bound to Skp, the beta-barrel domain of OmpA is maintained in an unfolded state, whereas the periplasmic domain is folded in its native conformation, allowig the transport of beta-barrels across the periplasm in an unfolded state PMID: 19181847
- Negatively charged lipopolysaccharide binds to OmpA-seventeen kDa protein (Skp) complexes, leading to a partial release of OmpA from the complex. The turn regions of OmpA remain bound to Skp. PMID: 19382746
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell outer membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:OmpA family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: ecj:JW0940
STRING: 316385.ECDH10B_1027
Most popular with customers
-
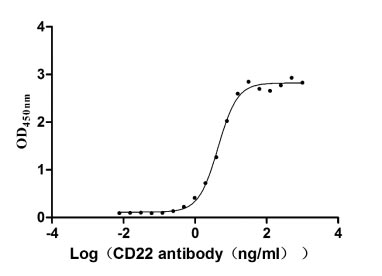
Recombinant Human B-cell receptor CD22 (CD22), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
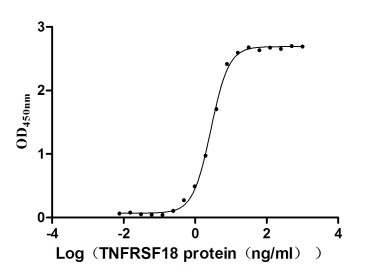
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
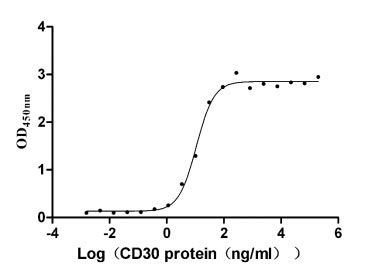
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
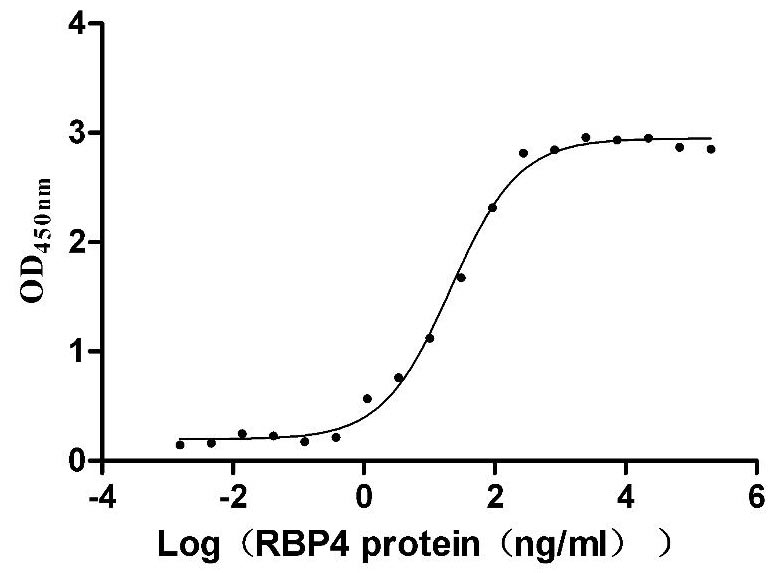
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
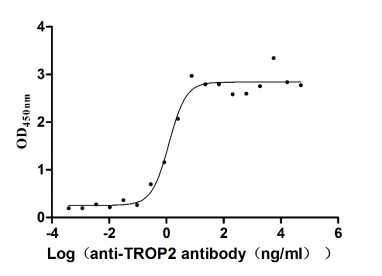
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
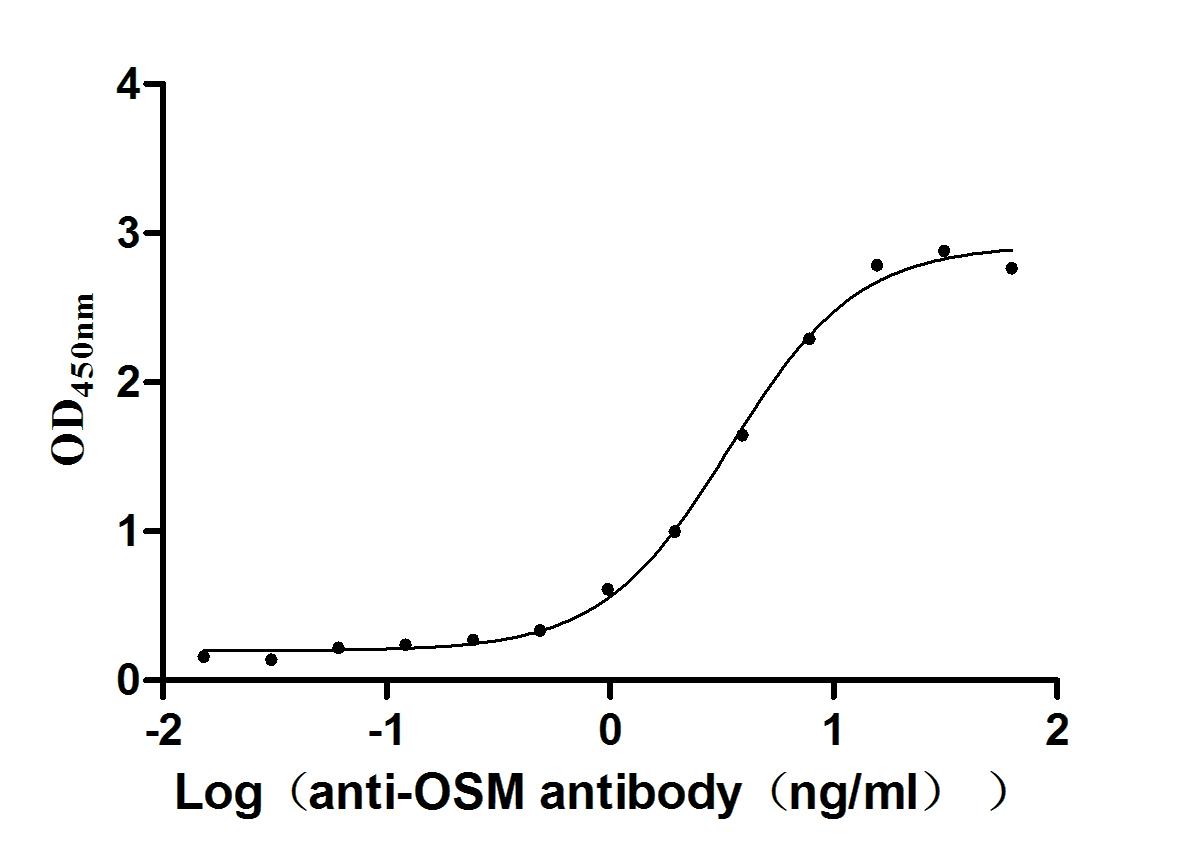
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
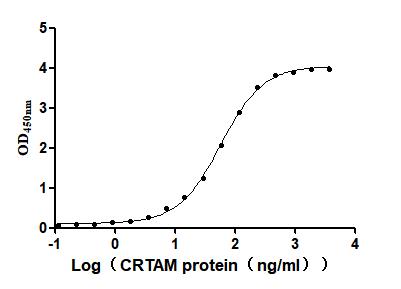
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

-SDS.jpg)