Recombinant Rat Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein D (Sftpd)
-
中文名称:大鼠Sftpd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP021175RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Sftpd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021175RA
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Sftpd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021175RA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Sftpd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP021175RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Sftpd重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP021175RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Sftpd
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Sftpd; Sftp4; Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein D; PSP-D; SP-D; CP4; Lung surfactant protein D
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:20-374
-
氨基酸序列A EMKTLSQRSI TNTCTLVLCS PTENGLPGRD GRDGREGPRG EKGDPGLPGP MGLSGLPGPR GPVGPKGENG SAGEPGPKGE RGLVGPPGSP GISGPAGKEG PSGKQGNIGP QGKPGPKGEA GPKGEVGAPG MQGSAGAKGP AGPKGERGAP GEQGAPGNAG AAGPAGPAGP QGAPGSRGPP GLKGDRGAPG DRGIKGESGL PDSAALRQQM EALNGKLQRL EAAFSRYKKA ALFPDGQSVG DKIFRAANSE EPFEDAKEMC RQAGGQLASP RSATENAAVQ QLVTAHSKAA FLSMTDVGTE GKFTYPTGEA LVYSNWAPGE PNNNGGAENC VEIFTNGQWN DKACGEQRLV ICEF
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Contributes to the lung's defense against inhaled microorganisms, organic antigens and toxins. Interacts with compounds such as bacterial lipopolysaccharides, oligosaccharides and fatty acids and modulates leukocyte action in immune response. May participate in the extracellular reorganization or turnover of pulmonary surfactant. Binds strongly maltose residues and to a lesser extent other alpha-glucosyl moieties.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- in acute lung injury, serum level increased from day 5, peaked on day 10, and then gradually decreased until day 28 PMID: 27541374
- SPA binds dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine, the major surfactant lipid component, but not phosphatidylinositol; SPD exhibits the opposite preference. Data suggest flexibility in a key surface loop supports distinctive lipid binding of SPA; quadruple mutant SPA (E171D/P175E/R197N/K203D) that introduces SPD-like loop-stabilizing Ca2+ binding site in carbohydrate recognition domain exhibits ligand-binding preferences of SPD. PMID: 28719181
- In rat SP-D overexpressed mice, the lipopolysaccharide-induced levels of TNF-alpha and IL-10 in amniotic fluid and fetal serum and the expression of IL-10 in placenta and fetal membranes were significantly different from wild-type mice. PMID: 22892325
- Surfactant protein D modulated subpollen particle uptake in a cell type specific way (e.g. greater number of macrophages and epithelial cells, which participated in allergen particle uptake) and led to a decreased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. PMID: 22296755
- Silica exposure causes dynamic changes of SP-D and CC16 protein expression in lung tissue and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. PMID: 19080379
- An extended binding site for influenza A virus; calcium-dependent antiviral activity involves residues flanking the primary carbohydrate binding site as well as more remote residues displayed on the carbohydrate recognition domain surface. PMID: 20601494
- SP-D promotes attachment of allergen-containing subpollen particles to epithelial cells and may thus be involved in the inflammatory response to inhaled allergen. PMID: 20569420
- analysis of myeloperoxidase-dependent inactivation of surfactant protein D in vitro and in vivo PMID: 20228064
- Results suggest that SP-D-dependent processes regulating surfactant lipid homeostasis were disassociated from those mediating emphysema. PMID: 12163500
- Heterogeneous allele expression of SP-D mRNA in large intestine and other tissues. PMID: 12464693
- SP-A and SP-D are antimicrobial proteins that directly inhibit the proliferation of Gram-negative bacteria in a macrophage- and aggregation-independent manner by increasing the permeability of the microbial cell membrane PMID: 12750409
- SP-A and SP-D are antimicrobial proteins that directly inhibit the growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by increasing permeability of the organism PMID: 12857753
- SP-D interacts with chlamydial pathogens and enhance their phagocytosis into macrophages PMID: 15075250
- Degradation of pulmonary surfactant protein D by Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase abrogates innate immune function PMID: 15123664
- SP-A and SP-D enhance mannose receptor-mediated phagocytosis of M. avium by macrophages PMID: 15187139
- results indicated SP-A & SP-D have distinct functions in lung homeostasis & the function of the neck domain & carbohydrate recognition domain of SP-D is dependent on its own NH2-terminal & collagenous domains that cannot be complemented by those of SP-A PMID: 16500946
- The ligand binding of homologous human, rat, and mouse trimeric trimeric neck plus carbohydrate recognition domain (neck+CRD) fusion proteins, each with identical N-terminal tags remote from the ligand-binding surface, was compared. PMID: 16514117
- VEGF increased expression of SP-D mRNA in preterm rat lung. PMID: 17267143
- Interactions with the side chain of inner core heptoses provide a potential mechanism for the recognition of diverse types of lipopolysaccharides by SP-D. PMID: 18092821
- These results show that antiviral activities of surfactant protein-D can be reproduced without the N-terminal and collagen domains and that cross-linking of these domains is essential for anti-influenza A virus activity. PMID: 18302538
- After OVA challenge alveolar epithelial cells Type II (AEII) show a significantly higher expression of SP-A and SP-D leading also to higher amounts of both SPs in BALF, and macrophages gather predominantly SP-A. PMID: 18802356
- S-nitrosylation of SP-D causes quaternary structural alterations and a swtich to its inflammatory signaling role. PMID: 19007302
- Multimerization of surfactant protein D, but not its collagen domain, is required for antiviral and opsonic activities related to influenza virus. PMID: 19017984
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix. Secreted, extracellular space, surface film.
-
蛋白家族:SFTPD family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:25350
UniGene: Rn.11348
Most popular with customers
-
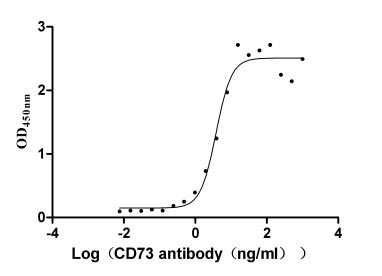
Recombinant Human 5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
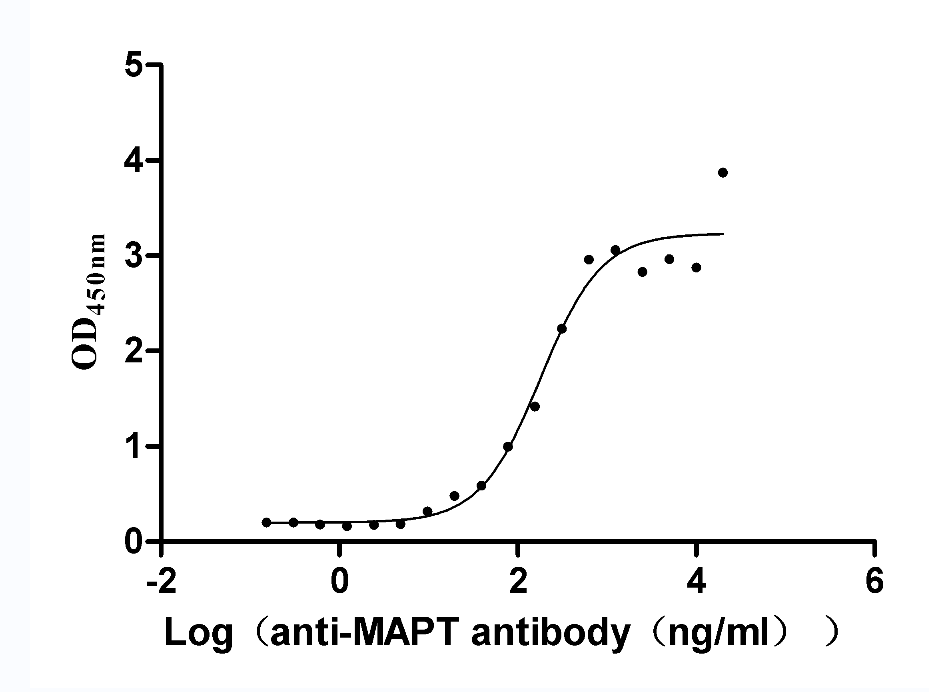
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
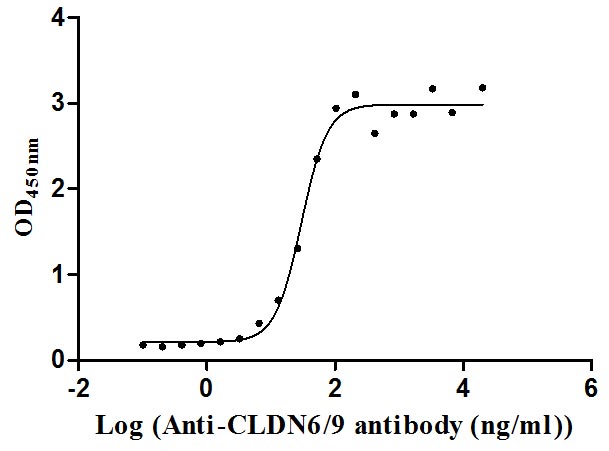
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
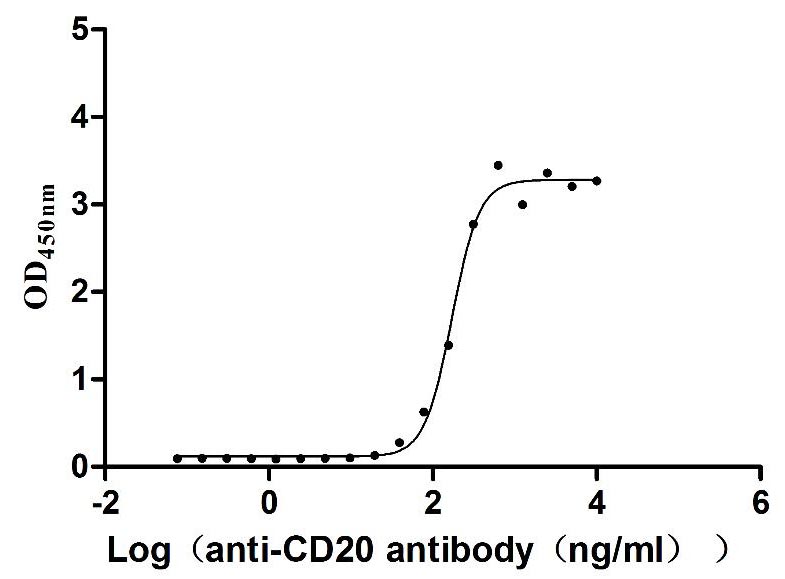
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)











