Recombinant Mouse von Willebrand factor (Vwf), partial
In Stock-
中文名称:小鼠Vwf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP025960MO
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
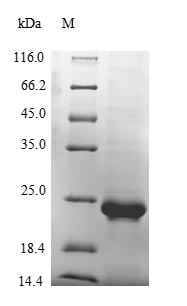
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Vwfvon Willebrand factor; vWF) [Cleaved into: von Willebrand antigen 2; von Willebrand antigen II)]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:23.9 kDa
-
表达区域:1498-1665aa
-
氨基酸序列DVVFVLEGSDEVGEANFNKSKEFVEEVIQRMDVSPDATRISVLQYSYTVTMEYAFNGAQSKEEVLRHVREIRYQGGNRTNTGQALQYLSEHSFSPSQGDRVEAPNLVYMVTGNPASDEIKRLPGDIQVVPIGVGPHANMQELERISRPIAPIFIRDFETLPREAPDLV
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:
The recombinant Mouse Vwf protein is encoded by the gene of Vwf (1498-1665aa). The gene of Vwf was cloned in a system (E.coli) that supported the expression of Vwf and translation of messenger RNA. Modification of Vwf by recombinant DNA technology could lead to the expression of the target protein. The protein was fused with N-terminal 10xHis tag & C-terminal Myc tag in the production. The purity is 85% determined by SDS-PAGE.
Vwf is a protein coding gene that encodes von Willebrand factor. According to some studies, Vwf may have the following features.
Assay of vWF-cleaving proteases based on decreased collagen-binding affinity of degraded vWF. Type 1 VWD is characterized by a partial quantitative deficiency of vWF. The full-length vWF cDNA encodes a highly repetitive protein that is much larger than the mature vWF subunit. The platelet-VWF complex is the preferred substrate for ADAMTS13 under fluid shear stress. Inhibition of the VWF-collagen interaction with an anti-human VWF monoclonal antibody resulted in abolished arterial platelet thrombus formation in baboons. The phenotype of VWF survival was found in a subgroup of patients with type 1 VWD. Low VWF levels may be associated with massive bleeding, mainly due to reduced VWF synthesis and/or constitutive secretion. -
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Important in the maintenance of hemostasis, it promotes adhesion of platelets to the sites of vascular injury by forming a molecular bridge between sub-endothelial collagen matrix and platelet-surface receptor complex GPIb-IX-V. Also acts as a chaperone for coagulation factor VIII, delivering it to the site of injury, stabilizing its heterodimeric structure and protecting it from premature clearance from plasma.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- is synthesized in megakaryocytes and endothelial cells (ECs) and has two main roles: to carry and protect coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) from degradation by forming VWF-FVIII complex; and to mediate platelet adhesion and aggregation at sites of vascular injury. PMID: 29392565
- this study shows that Von Willebrand factor protects against acute CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity through phospho-p38 MAPK signaling pathway inhibition PMID: 28868583
- the ADAMTS13-vWF axis is partially involved in the pathophysiology of kidney ischemic reperfusion injury. PMID: 27507004
- Type 2N von Willebrand disease variants were associated with decreased VWF secretion and impaired factor VIII binding/stability. PMID: 28581694
- identify a critical role for VWF in cerebral inflammation and blood-brain barrier damage after intracerebral haemorrhage PMID: 27782211
- Refrigeration-induced binding of VWF to platelets facilitates their rapid clearance by inducing GPIbalpha-mediated signaling. PMID: 29097365
- BLOC-2 subunit HPS6 deficiency affects the tubulation and secretion of von Willebrand factor from mouse endothelial cells PMID: 27889498
- A novel single-domain antibody against von Willebrand factor A1 domain that interferes with VWF-platelet interactions in vivo. By using this sdAb, show that the A1 domain is pertinent to the participation of VWF in the inflammatory response. PMID: 28642239
- These experiments delineate an unexpected pathway in which microbiota-triggered TLR2 signaling alters the synthesis of proadhesive VWF by the liver endothelium and favors platelet integrin-dependent thrombus growth. PMID: 28572286
- ADAMTS13 controls vascular remodeling by modifying VWF reactivity during stroke recovery. PMID: 28428179
- these novel findings support the hypothesis that conformation of the VWF A domains plays a critical role in modulating macrophage-mediated clearance of VWF in vivo. PMID: 27554083
- results revealed localized vascular expression of FVIII and von Willebrand factor and identified lymphatic endothelial cell as a major cellular source of FVIII in extrahepatic tissues. PMID: 27207787
- Endothelial cell derivedVWF is the major determinant that mediates VWF-dependent ischemic stroke by promoting postischemic thrombo-inflammation. PMID: 27444201
- VWF deficiency reduces the progression of liver fibrosis, suggesting a mechanistic role of elevated plasma VWF levels in cirrhosis PMID: 28527913
- von Willebrand factor exerts beneficial effects in a mouse sepsis model via recruitment of neutrophils to inflammatory sites. PMID: 26494840
- Staphylococcus lugdunensis binds directly to von Willebrand factor, which proved to be vital for withstanding shear forces and for its adhesion to the vessel wall and cardiac valves. PMID: 26743845
- Clinical experimental cerebral malaria progression was delayed, and overall survival was significantly prolonged in VWF(-/-) mice compared with WT controls. PMID: 26511133
- in stable compensated heart failure mice, disruptions in endothelial vWF expression and extrusion may reduce the incidence of endocardial thrombosis PMID: 26565707
- VWF is expressed in a mosaic pattern in the capillaries of many vascular beds and in the aorta. Hearts of VWF-null mice demonstrate an abnormal endothelial phenotype as well as cardiac dysfunction. PMID: 26744078
- SNAP23 Regulates Endothelial Exocytosis of von Willebrand Factor PMID: 26266817
- Both platelet-VWF and plasma-VWF are required for optimal platelet-derived FVIII gene therapy for hemophilia A in the presence of inhibitors. PMID: 25955153
- a genetic link between EGLN1 and VWF in a constitution specific manner which could modulate thrombosis/bleeding susceptibility and outcomes of hypoxia, is reported. PMID: 26047609
- novel findings demonstrate a specific and critical role for the R1205 residue in modulating macrophage-mediated clearance of VWF in vivo PMID: 25690668
- Clearance differences between blood group O and non-blood group O individuals may therefore be related to the blood group status of the individual rather than the ABH antigen loading on VWF itself. PMID: 25650553
- Certain VWD-type 2B mutations relieve the need for shear stress to induce LRP1 binding. Enhanced LRP1 binding coincides with a reduced survival of VWF/p.R1306Q and VWF/p.V1316M PMID: 25728415
- These data suggest that whereas platelet-derived VWF does not play a crucial role in hemostasis and arterial thrombosis, it aggravates thrombo-inflammatory diseases such as stroke via a GPIb-dependent mechanism. PMID: 26209660
- Platelet-endothelial interactions occur in early atherosclerosis. These interactions are in part caused by endothelial von Willebrand factor large multimers, which can be reversed with exogenous ADAMTS13. PMID: 26156014
- Data suggest that targeting platelet receptor glycoprotein Ibalpha (GPIbalpha)-von Willebrand factor VWF-A1 binding interface may offer a therapeutic approach to reducing platelet-driven thrombosis. PMID: 25293780
- Absence of vWF increases hematopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures and has a protective effect in irradiated lungs. PMID: 24982209
- VWF-binding protein contributes to vascular adhesion of S aureus through 2 independent mechanisms: shear-mediated binding to VWF and activation of prothrombin to form S aureus-fibrin-platelet aggregates. PMID: 24951431
- a delayed and markedly reduced thrombogenic response was still evident in VWF(-/-), GPVI, and alpha2beta1 blocked animals, suggesting that alternative primary hemostatic mechanisms can partially rescue the bleeding phenotype associated with these defects. PMID: 25051961
- a fragment containing only approximately 20% of the VWF sequence is sufficient to support FVIII stability in vivo PMID: 24850761
- Expression of VWF/p.S1494C-p.A1534C in mice triggers an acute onset of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. PMID: 24713928
- Following endothelial damage, platelet cross-linking during closure of the vessel lumen is mediated by GPIbalpha-VWF interactions. PMID: 24553181
- The results indicate that elevation of extracellular sodium within the physiological range raises vWF sufficiently to increase coagulability and risk of thrombosis. PMID: 24733925
- Galpha12 may play an important role in promoting membrane trafficking and exocytosis for basal and thrombin-induced vWF secretion, in a process involving SNAP, Galpha12/13 and Galphaq/11 PMID: 24081657
- Carboxyl terminus of ADAMTS13 directly inhibits platelet aggregation and ultra large von Willebrand factor string formation under flow in a free-thiol-dependent manner. PMID: 24357063
- VWF represents a promising target for the treatment of cutaneous inflammation, e.g., leukocytoclastic vasculitis. PMID: 23812299
- VWF has a role in leukocyte recruitment with chromatin decondensation by PAD4, which increases myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice PMID: 24200682
- Platelet aggregation, secretion, and spreading were diminished due to inhibition of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in platelets from mice expressing a vWD-type 2B-associated vWF (vWF/p.V1316M). PMID: 24270421
- a new function for VWF in vivo as regulator of bloodstream thrombopoiesis PMID: 23737952
- VWF type 2B binds to platelets, which is a signal for clearance by macrophages, possibly contributing to thrombocytopenia PMID: 23945153
- VWF deficiency confers partial preservation of blood brain barrier integrity after hypoxia/reoxygenation and seizures. PMID: 23825365
- Compared with wild-type mice (n=6), we found less bacteria in postcapillary (60+/-6 versus 32+/-5 bacteria) and collecting venules (48+/-5 versus 18+/-4 bacteria; P<0.05) of VWF knockout mice (n=5). PMID: 23720451
- Hypoxia is associated with a phenotypic shift which target regulation of VWD in lung endothelial cells. PMID: 23580145
- These findings implicate a role for intronic splicing in mediating lineage-specific expression of vWF in the endothelium. PMID: 23529929
- ADAMTS13 and VWF are causally involved in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. PMID: 22983446
- Provide new evidence for ADAMTS13 in reducing VWF-mediated acute cerebral inflammation following ischemic stroke. PMID: 22712744
- Endothelial cell (EC) VWF is sufficient to support hemostasis in VWF-/- mice, and VWF produced in megakaryocytes/platelets can also contribute to hemostasis in the absence of EC-derived VWF. PMID: 22642380
- study showed O-glycosylations are dispensable for normal VWF multimerization and biosynthesis; it appears that some O-glycosylation sites, particularly the T1255 and T1256 residues, are involved in maintenance of VWF plasma levels and are essential for normal haemostasis PMID: 22616016
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted. Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
-
组织特异性:Plasma. Expressed in liver.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:22371
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000001995
UniGene: Mm.22339
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
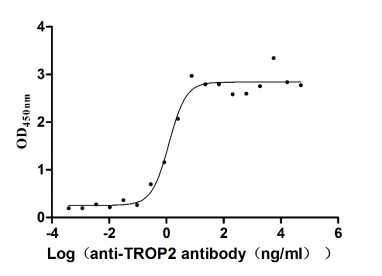
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
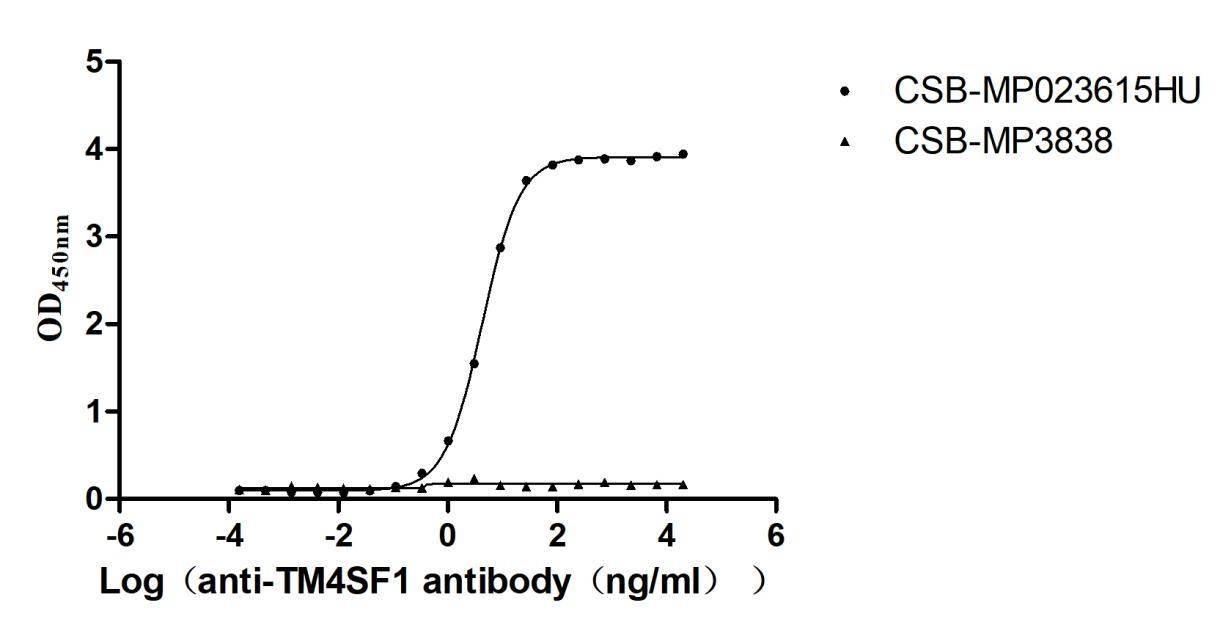
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)