Recombinant Mouse Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (Tfpi)
-
中文名称:小鼠Tfpi重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP023437MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tfpi重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP023437MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tfpi重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP023437MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tfpi重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP023437MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Tfpi重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP023437MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Tfpi; Tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TFPI; Extrinsic pathway inhibitor; EPI; Lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor; LACI
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:29-306
-
氨基酸序列LS EEADDTDSEL GSMKPLHTFC AMKADDGPCK AMIRSYFFNM YTHQCEEFIY GGCEGNENRF DTLEECKKTC IPGYEKTAVK AASGAERPDF CFLEEDPGLC RGYMKRYLYN NQTKQCERFV YGGCLGNRNN FETLDECKKI CENPVHSPSP VNEVQMSDYV TDGNTVTDRS TVNNIVVPQS PKVPRRRDYR GRPWCLQPAD SGLCKASERR FYYNSATGKC HRFNYTGCGG NNNNFTTRRR CLRSCKTGLI KNKSKGVVKI QRRKAPFVKV VYESIN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Inhibits factor X (X(a)) directly and, in a Xa-dependent way, inhibits VIIa/tissue factor activity, presumably by forming a quaternary Xa/LACI/VIIa/TF complex. It possesses an antithrombotic action and also the ability to associate with lipoproteins in plasma.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- endogenous TFPI from vascular smooth muscle cells inhibited ferric chloride-induced arterial thrombosis without causing hemostatic effects PMID: 28550640
- TFPI-1 interacts with AMOT, which led to a decrease in the phosphorylation of YAP and further increased the genes expression of the proliferation and migration involved. Our results further confirmed that atherosclerosis was a localized disease. PMID: 27875740
- Results suggest that endothelial cell-anchored TFPI controls lung tumor metastasis, and does so largely through the inhibition of local TF-induced thrombin generation and the regulation of the lung microenvironment in mice. PMID: 25945811
- Data argue against an important role for endogenous TFPI in the antibacterial, inflammatory and procoagulant response during pneumococcal pneumonia. PMID: 25832548
- Results demonstrate that TFPI physiologically modulates thrombin-dependent platelet activation in a manner that is required for successful embryonic development PMID: 25954015
- Tissue factor plays a hitherto unreported role in the generation of macrophage migratory inhibitory factor by vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis-prone ApoE(-/-) mice. PMID: 25677604
- The increased plasmin generation during the early stages of sepsis could cleave/inactivate TFPI and thus lead to thrombotic complications. PMID: 23106863
- structural features within residues of the 39-loop contribute to the resistance of FIXa to inhibition by plasma inhibitors ZPI and TFPI. PMID: 23530052
- PAK1 negatively regulates the expression of TFPI and additionally contributes to increased TF activity. PMID: 23038262
- Murine models of combined TFPI and factor VIII deficiency were used to examine the impact of TFPI deficiency on bleeding and clotting in hemophilia PMID: 22355108
- Data demonstrate an inhibitory role for TFPI in angiogenesis that is, in part, mediated through peptides within its carboxyl terminus. PMID: 22223730
- TFPI present within platelets functions to limit intravascular thrombus growth, likely through inhibition of the procoagulant activity of blood borne tissue factor. PMID: 21233452
- Data reveal distinct roles for endothelial- and myelomonocytic-derived TFPI. PMID: 20516367
- overexpression of TFPI results in improved hemodynamic performance and reduced pulmonary vascular remodeling in a murine model of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension PMID: 19648471
- inhibits metastasis in an experimental model of lung metastasis of B16 melanoma PMID: 12083498
- the correct balance between TF and TFPI in different organs is required to maintain hemostasis during embryonic development and in adult mice. PMID: 15598816
- both in humans and mice, there are temporal variations in TFPI activity PMID: 15604416
- platelets TFPI is also released in microvesicles or as a soluble protein PMID: 17082321
- partial TFPI deficiency interacts with decreased Thbd function in an organ selective manner to produce fibrin deposition in liver, brain, and placenta vascular beds. PMID: 17973652
- TFPIgamma is a third alternatively spliced form of TFPI that is widely expressed in mouse tissues but not made by human tissues. It contains the first two Kunitz domains and is a secreted, rather than a cell surface-associated, protein. PMID: 18503630
- TFPIalpha cDNA was cloned from pig aortic endothelial cells and found to encode a 279-residue mature protein with 79% overall identity to human TFPIalpha PMID: 18611227
- Pregnancy causes a decrease in APC resistance in mice, which can be explained by the elevation of protein S levels and increased TFPI activity in plasma. PMID: 19036061
- data demonstrate that alternatively spliced isoforms of TFPI are temporally expressed in mouse tissues at the level of protein production PMID: 19422457
- Vascular-directed tissue factor pathway inhibitor overexpression regulates plasma cholesterol and reduces atherosclerotic plaque development. PMID: 19713537
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
组织特异性:Isoform alpha is expressed in heart and spleen; isoform beta in heart and lung.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:21788
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000028487
UniGene: Mm.124316
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
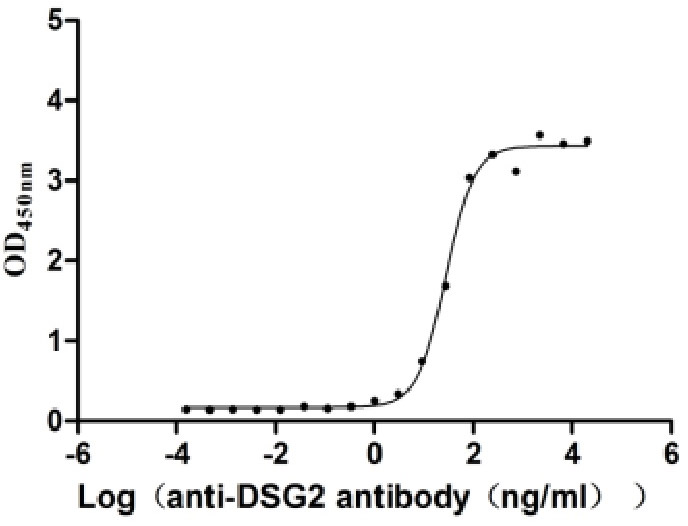
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
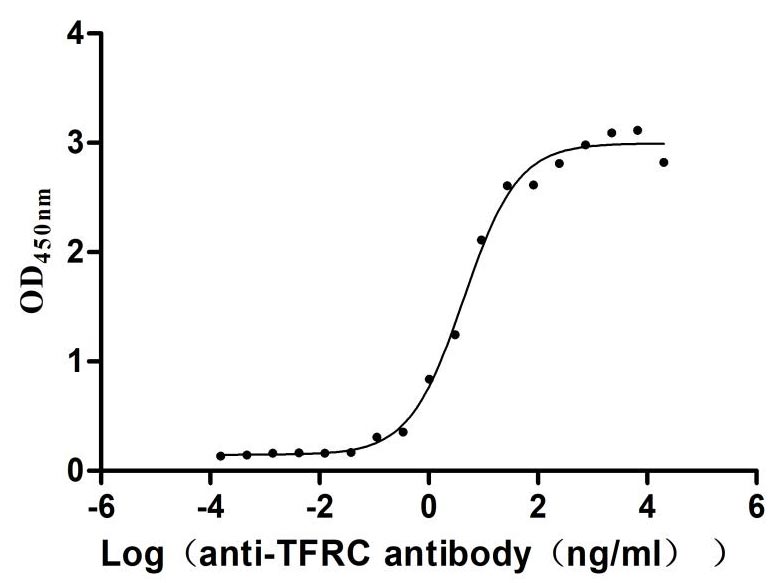
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
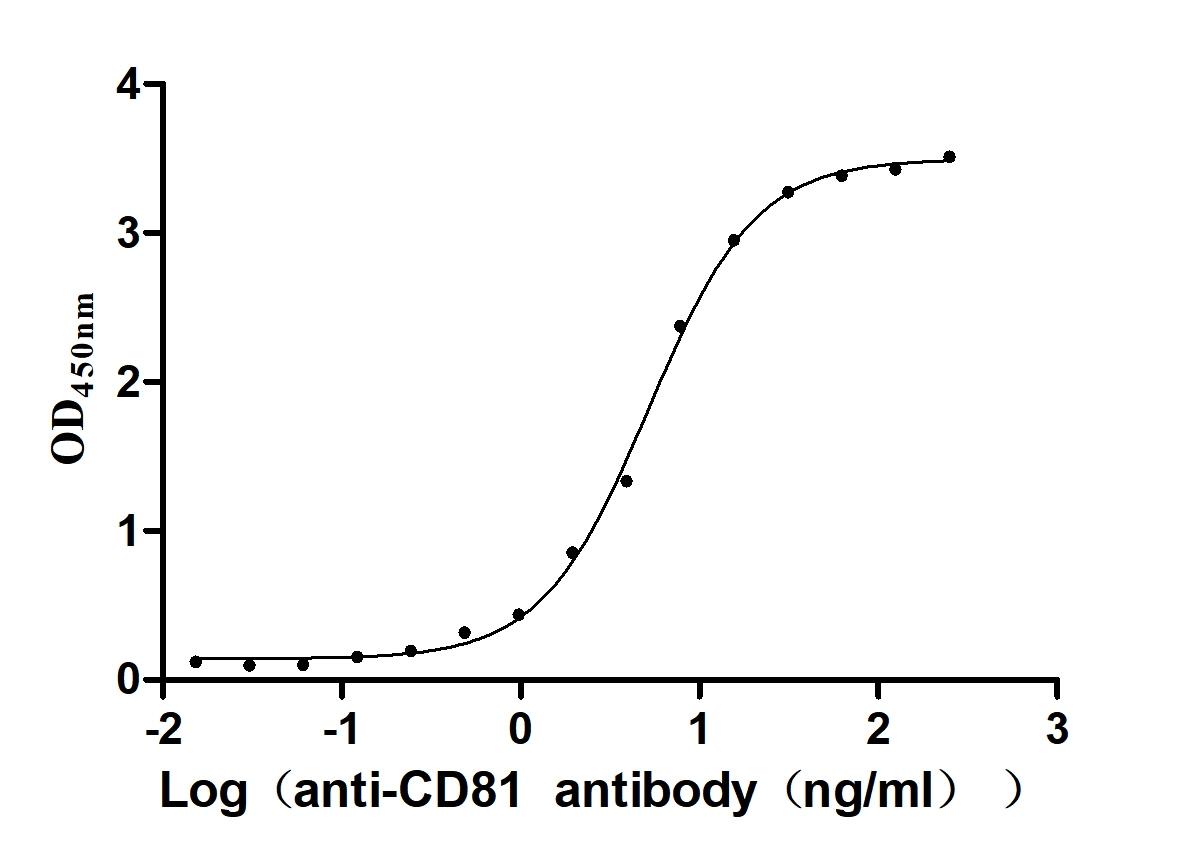
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
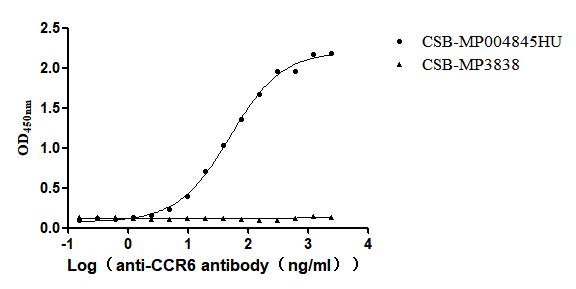
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)