Recombinant Mouse Selenoprotein P (Selenop)
-
中文名称:小鼠Selenop重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP021018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Selenop重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Selenop重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021018MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Selenop重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP021018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Selenop重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP021018MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Selenop
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Selenop; Selp; Sepp1; Selenoprotein P; SeP; Plasma selenoprotein P
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:20-380
-
氨基酸序列E SQGQSSACYK APEWYIGDQN PMLNSEGKVT VVALLQASUY LCLLQASRLE DLRIKLESQG YFNISYIVVN HQGSPSQLKH SHLKKQVSEH IAVYRQEEDG IDVWTLLNGN KDDFLIYDRC GRLVYHLGLP YSFLTFPYVE EAIKIAYCEE RCGNCNLTSL EDEDFCKTVT SATANKTAEP SEAHSHHKHH NKHGQEHLGS SKPSENQQPG PSETTLPPSG LHHHHRHRGQ HRQGHLESUD TTASEGLHLS LAQRKLURRG CINQLLCKLS KESEAAPSSC CCHCRHLIFE KSGSAIAUQC AENLPSLCSU QGLFAEEKVT ESCQCRSPPA AUQNQPMNPM EANPNUSUDN QTRKUKUHSN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Might be responsible for some of the extracellular antioxidant defense properties of selenium or might be involved in the transport of selenium. May supply selenium to tissues such as brain and testis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- In this study, the role of SeP in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury has been investigated. PMID: 29547524
- Results indicate a diversity of RNA elements conducting multiple occurrences of UGA redefinition to control the synthesis of full-length and truncated selenoprotein P (SELENOP) isoforms. PMID: 29069514
- Study suggests the 3' UTR structural elements (SECIS) in Sepp1 functions with site specificity and further illustrates how mRNA processing may produce transcripts with altered coding potential to produce diversity in selenoprotein isoforms. PMID: 27881738
- SeP causes exercise resistance through its muscle receptor low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1). SeP-deficient mice showed a 'super-endurance' phenotype after exercise training, as well as enhanced reactive oxygen species production, AMPK phosphorylation and Ppargc-1alpha expression in skeletal muscle. PMID: 28263310
- Through correlational analysis, it was determined that the effects of Se-supplement were closely related to SelP expression, inflammatory cytokines, and apoptosis molecule production. PMID: 27334433
- This study showed that Male mice lacking two key genes involved in Se metabolism (Scly(-/-)Sepp1(-/-) mice), selenoprotein P (Sepp1) and Sec lyase (Scly), develop severe neurological dysfunction, neurodegeneration, and audiogenic seizures. PMID: 26586820
- Results indicate that selenoprotein P (Sepp1) is important for this transport in selenium-replete mice but that glutathione peroxidase-3 (Gpx3) is not. PMID: 25068390
- Sepp1 haploinsufficiency or mutations that disrupt either the selenium transport or the enzymatic domain of SEPP1 exhibit increased colitis-associated carcinogenesis via increased genomic instability and promotion of a protumorigenic microenvironment PMID: 26053663
- data highlight SePP as the essential Se transporter to bones, and suggest a novel feedback mechanism for preferential uptake of Se in Se-deprived bones PMID: 24626785
- plasma Sepp1(UF) and small selenium-containing proteins are filtered by the glomerulus and taken up by PCT cells via megalin-mediated endocytosis. PMID: 24434121
- Tandem Sepp1-apoER2 interactions supply selenium for maintenance of brain neurons both at the blood-brain barrier and within the brain. Sepp1 inside the blood-brain barrier is taken up by neurons via apoER2, concentrating brain selenium in them. PMID: 24760755
- These findings provide the first in vivo evidence that Scly and Sepp1 work cooperatively to maintain selenoprotein function in the mammalian brain. PMID: 24519931
- longer isoforms of Sepp1 with high selenium content interact with a binding site distinct from the ligand-binding domain of apoER2 for selenium delivery PMID: 24532792
- metformin decreases binding of FoxO3a, a direct target of AMPK, to the SEPP1 promoter. PMID: 24257750
- Data indicate that uptake of Sepp1 and Gpx3 by d-13 visceral yolk sac was independent of apoER2 and megalin. PMID: 23651543
- results emphasize the importance of non-coding transcript variations as a regulatory means for Sepp1 expression in different tissues and stages of development; presence of a variant localized in the hippocampus and regulated by a microRNA may have implications for deficits in synaptic function caused by genetic deletion of Sepp1 PMID: 23064117
- study shows that pancreatic islets express relatively high levels of Sepp1 that may fulfill a function in antioxidant protection of beta-cells. Downregulation of Sepp1 expression by high glucose might thus contribute to glucotoxicity in beta-cells PMID: 23125459
- Sepp1(-/-) mice have impairments in fear extinction, latent inhibition, and sensorimotor gating, showing the important supporting role of Sepp1 on ApoER2-expressing parvalbumin interneurons. PMID: 22640876
- Sepp1 production by hepatocytes retains selenium in the organism and distributes it from the liver to peripheral tissues. PMID: 23038251
- the neurological phenotype caused by the absence of Sepp1 is exacerbated in male vs. female mice. PMID: 22487427
- apoER2-mediated uptake of long isoform Sepp1 is responsible for selenium distribution to tissues throughout the body. PMID: 22761431
- Deletion of Sepp1 (and presumably selenium deficiency in the brain) produce both neuronal and axonal degeneration as well as more moderate and potentially reversible neurite changes in the developing brain. PMID: 21636077
- Both genetic deletion and RNA interference-mediated knockdown of selenoprotein P improved systemic insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in mice. PMID: 21035759
- investigation of role of Sepp1 expression in adipocytes during adipogenesis and oxidative stress in models of obesity and insulin resistance PMID: 20959537
- Selenoprotein biosynthesis becomes redirected in hepatocytes during the acute-phase response at the expense of dispensable selenoproteins (e.g., SepP) and in favor of SepS expression, thereby causing declining serum selenium and improving liver function. PMID: 20370716
- Se-P from liver provides selenium to several tissues, especially testis and brain PMID: 12574155
- Selenoprotein P is required for development of functional spermatozoa and is an essential component of the selenium delivery pathway for developing germ cells. PMID: 15744015
- Brainstem axonal degeneration was found in mice with deletion of Sepp1. PMID: 16105800
- absence of selenoprotein P synthesis in the liver makes more selenium available for urinary metabolite synthesis, increasing loss of selenium from the organism and causing the decrease in whole-body selenium PMID: 17014962
- C terminus of Sepp1 is critical for the maintenance of selenium in brain and testis but not for the maintenance of whole body selenium PMID: 17311913
- Sepp1 is more important for maintaining selenium in the hippocampus than in other brain regions. PMID: 17311961
- Sertoli cell ApoER2 is a Sepp1 receptor and a component of the selenium delivery pathway to spermatogenic cells PMID: 17314095
- Thus, age represents another important modifier of the dynamic sex- and tissue-specific selenoprotein expression patterns. PMID: 17937617
- local Sepp expression is required to maintain selenium content in selenium-privileged tissues such as brain and testis during dietary selenium restriction PMID: 17961124
- Neurodegeneration in mice resulting from loss of functional selenoprotein P. PMID: 18172410
- kidney selenium homeostasis is mediated by a megalin-dependent Sepp1 uptake pathway in the proximal tubule PMID: 18174160
- Alternatively activated myeloid cells limit pathogenicity associated with African trypanosomiasis through the IL-10 inducible gene selenoprotein P. PMID: 18424738
- Spatiotemporal expression of the Se-P gene in postimplantational mouse embryos is reported. PMID: 18956332
- Data suggest that hepatic translation of Sepp1 mRNA is specifically impaired during the acute-phase response. PMID: 19136613
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Selenoprotein P family
-
组织特异性:In the kidney, expressed in the cortex with no expression observed in the medulla (at protein level). Expressed by the liver and secreted in plasma.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20363
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000081004
UniGene: Mm.392203
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
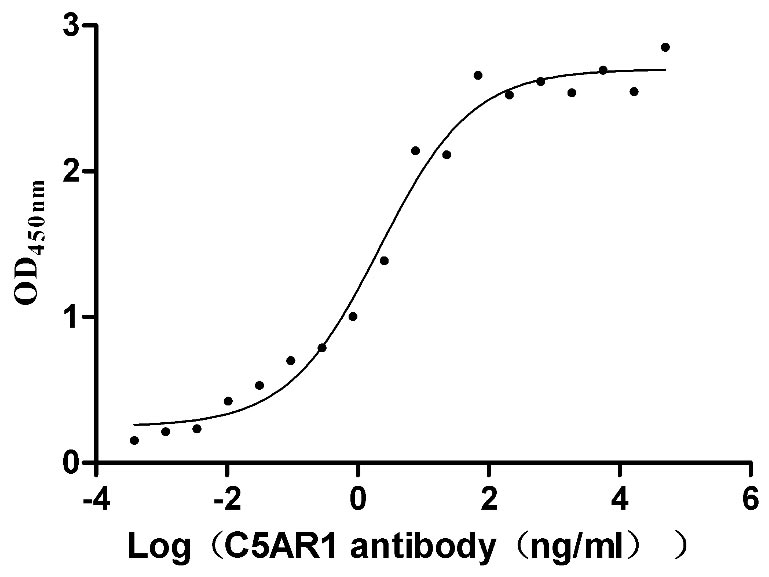
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
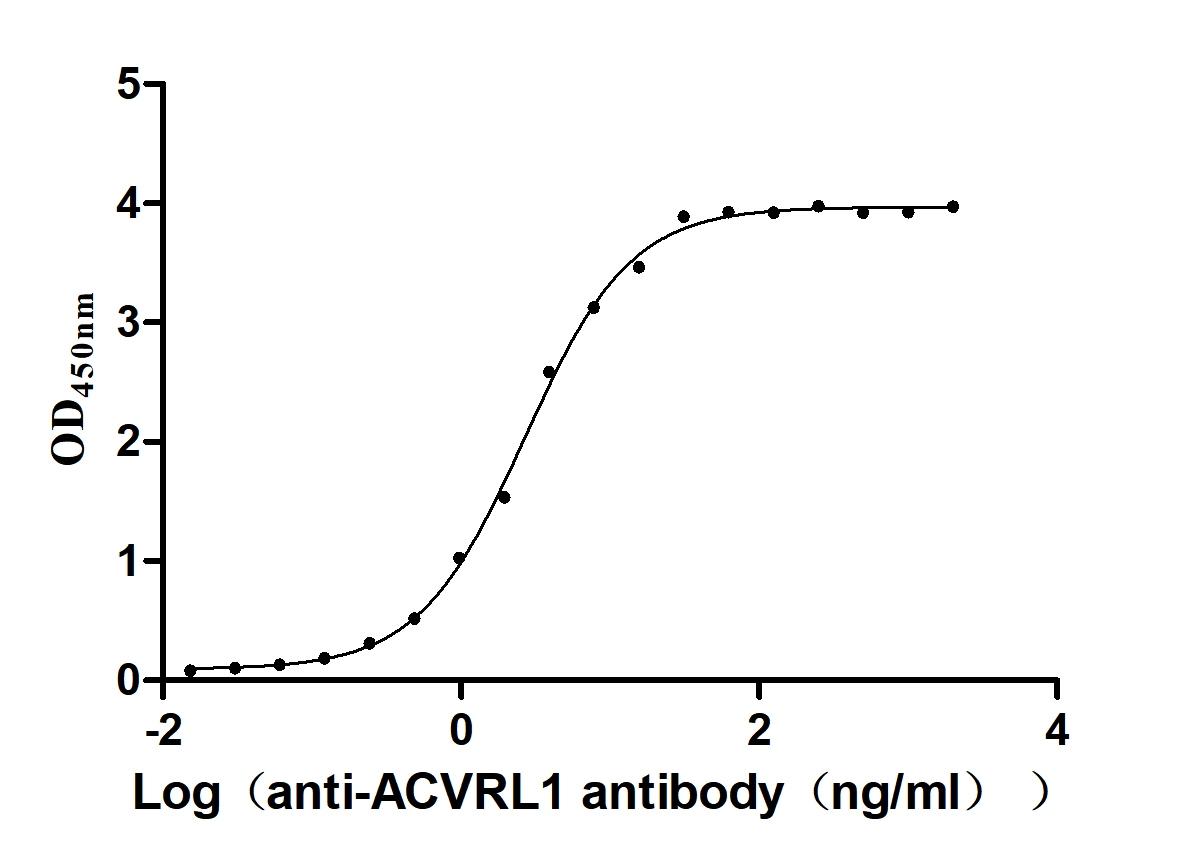
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
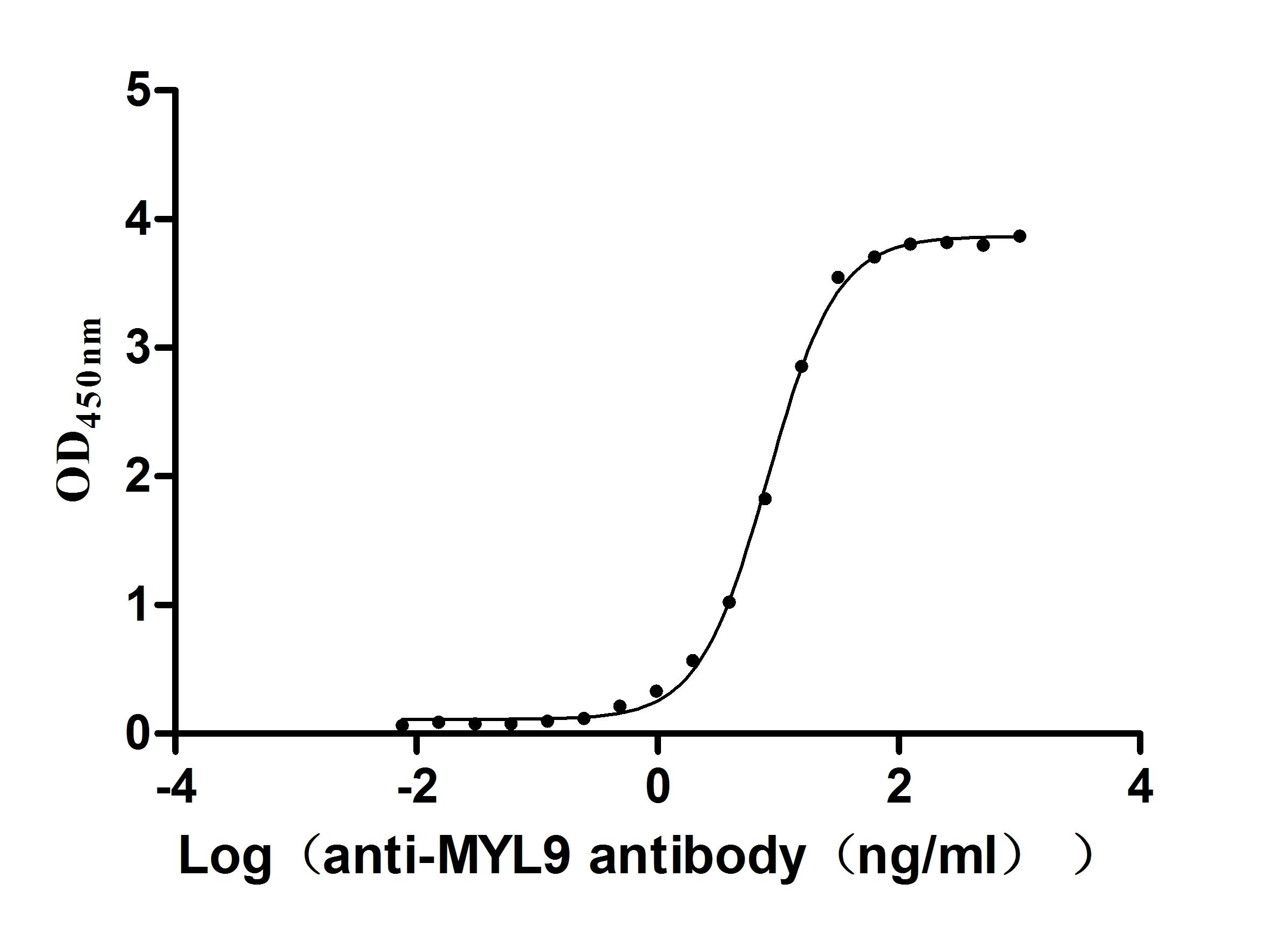
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)


-AC1.jpg)

-AC1.jpg)