Recombinant Mouse Recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (Rbpj)
-
货号:CSB-YP019486MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP019486MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP019486MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP019486MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP019486MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Rbpj; Igkjrb1; Igkrsbp; Rbpsuh; Recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless; J kappa-recombination signal-binding protein; RBP-J kappa
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-526
-
氨基酸序列MPSGFPQSPR TSPRARPKTR ITGALPMDYS EGLSAEERPA HAPSAGKFGE RPPPKRLTRE AMRNYLKERG DQTVLILHAK VAQKSYGNEK RFFCPPPCVY LMGSGWKKKK EQMERDGCSE QESQPCAFIG IGNSDQEMQQ LNLEGKNYCT AKTLYISDSD KRKHFMLSVK MFYGNSDDIG VFLSKRIKVI SKPSKKKQSL KNADLCIASG TKVALFNRLR SQTVSTRYLH VEGGNFHASS QQWGAFYIHL LDDDESEGEE FTVRDGYIHY GQTVKLVCSV TGMALPRLII RKVDKQTALL DADDPVSQLH KCAFYLKDTE RMYLCLSQER IIQFQATPCP KEQNKEMIND GASWTIISTD KAEYTFYEGM GPVLAPVTPV PVVESLQLNG GGDVAMLELT GQNFTPNLRV WFGDVEAETM YRCGESMLCV VPDISAFREG WRWVRQPVQV PVTLVRNDGV IYSTSLTFTY TPEPGPRPHC SAAGAILRAN SSQVPSNESN TNSEGNYTNA STNSTSVTSS TATVVS
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional regulator that plays a central role in Notch signaling, a signaling pathway involved in cell-cell communication that regulates a broad spectrum of cell-fate determinations. Acts as a transcriptional repressor when it is not associated with Notch proteins. When associated with some NICD product of Notch proteins (Notch intracellular domain), it acts as a transcriptional activator that activates transcription of Notch target genes. Probably represses or activates transcription via the recruitment of chromatin remodeling complexes containing histone deacetylase or histone acetylase proteins, respectively. Specifically binds to the immunoglobulin kappa-type J segment recombination signal sequence. Binds specifically to methylated DNA. Binds to the oxygen responsive element of COX4I2 and activates its transcription under hypoxia conditions (4% oxygen). Negatively regulates the phagocyte oxidative burst in response to bacterial infection by repressing transcription of NADPH oxidase subunits.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- homoeostatic repressor of multiple pro-angiogenic and angiostatic factor genes in cardiomyocytes PMID: 27357444
- Early pancreatic islet fate and maturation is controlled through RBP-Jkappa. PMID: 27240887
- In this study, the s found that conditional disruption of RBP-J, the transcription factor of canonical Notch signaling, increased irradiation sensitivity in mice. PMID: 27188577
- Macrophage maturation is controlled by Notch ligand Dll1 expressed in vascular endothelial cells of arteries and requires macrophage canonical Notch signaling via Rbpj, which simultaneously suppresses an inflammatory macrophage fate. Conversely, conditional mutant mice lacking Dll1 or Rbpj show proliferation and transient accumulation of inflammatory macrophages, which antagonizes arteriogenesis and tissue repair. PMID: 29038527
- RBPJ binds and trans-activates the Il23r promoter and induces IL-23R expression and represses anti-inflammatory IL-10 production in Th17 cells. PMID: 27346359
- RBP-J deficiency drastically reduced dopamine release in the striatum and caused a subtle decrease in the number of dopaminergic neurons. These findings demonstrated that Notch/RBP-J signaling regulates dopamine responsiveness in the striatum, which may explain the mechanism whereby Notch/RBP-J signaling affects an individual's susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disease. PMID: 28267151
- RBP-J-mediated Notch signalling is critical for basophil-dependent immunoregulation. Deficiency of RBP-J influences the immunoregulatory functions of BA, which include activation of T cells and their differentiation into T helper cell subtypes. PMID: 28493549
- study uncovered a regulatory network, where miR-182 functions as an important new node that receives inputs from RBP-J and TNF-alpha signaling and positively regulates inflammatory osteoclastogenesis; suppression of miR-182 by RBP-J serves as an important mechanism that restrains TNF-alpha induced osteoclastogenesis PMID: 27183593
- structural and biophysical studies demonstrate that RITA binds RBP-J similarly to the RAM (RBP-J-associated molecule) domain of Notch, our biochemical and cellular assays suggest that RITA interacts with additional regions in RBP-J. PMID: 28487372
- RBP-J mediated by miR-133a probably contributed to the regulation of DCs maturation and activation in osteosarcoma PMID: 27794430
- Rbpj-kappa mediated Notch signaling plays a critical role in development of hypothalamic Kisspeptin neurons. PMID: 26318021
- Results reveal an essential role for canonical Notch/RBP-J signaling in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and suggest that role, at least in part, is mediated by the regulation of GABAergic signaling PMID: 25515406
- The bone marrow contains a progenitor that expresses renin throughout development and possesses a B-lymphocyte pedigree. This cell requires RBP-J to differentiate. PMID: 24549417
- functions as a transcriptional repressor on the promoter of the microRNA miR-155 PMID: 24996169
- DNA methylation-dependent binding of RBPJ to a GC repressor element can negatively regulate smooth muscl myosin heavy chain promoter activity and can inhibit marker gene expression in phenotypically modulated cells PMID: 25324571
- Rbpj directly regulates the expression of uterine matrix metalloproteinase in a Notch pathway-dependent manner, which is required for normal post-implantation decidual remodeling. PMID: 24971735
- RBP-J maintains the identity of the renin cell by not only activating genes characteristic of the myo-endocrine phenotype but also, preventing ectopic gene expression and adoption of an aberrant phenotype PMID: 24904090
- RBP-J-mediated Notch signaling is required for macrophages to promote hepatic fibrosis by up-regulation of NF-kappaB activation through CYLD. PMID: 25145286
- Environmental cues that regulate RBP-J expression/function potentially modulate the requirement for costimulatory signaling for osteoclast differentiation and bone remodeling. PMID: 25329696
- RBPJ in mouse Sertoli cells is required for proper regulation of the testis stem cell niche. PMID: 25406395
- Rbpj is required in postnatal endothelial cells to maintain proper artery, capillary and vein organization and to prevent abnormal arteriovenous shunting and malformation pathogenesis. PMID: 25209249
- we found that a fraction of RBPJ occupancy sites shifted between interphase and mitosis, suggesting that RBPJ can be retained on mitotic chromatin by sliding on DNA rather than disengaging from chromatin during mitotic chromatin condensation PMID: 24603501
- The CSL-KyoT2 corepressor complex is a negative regulator of Notch signaling. PMID: 24290140
- Disruption of the transcription factor RBP-J results in osteopenia attributable to attenuated osteoclast differentiation. PMID: 23224519
- RBP-J is essential for proper formation and maintenance of the kidney vasculature and glomeruli PMID: 24226518
- RBP-Jkappa-dependent Notch signaling is required for murine articular cartilage and joint maintenance. PMID: 23839930
- Data indicate the function of Rbpj is diversified and context dependent in the gliogenesis of somatosensory ganglia. PMID: 23826407
- Notch/Rbpjkappa signaling regulates progenitor maintenance and differentiation of hypothalamic arcuate neurons, which contribute to homeostatic regulation of body size. PMID: 23884446
- Notch negatively regulates chondrocyte differentiation in the axial skeleton by suppressing Sox9 transcription, and Rbpj-independent Notch signaling mechanisms may also contribute to axial skeletogenesis PMID: 22991339
- demonstrate dynamic binding of RBPJ in response to Notch activation at essentially all sites co-occupied by NICD PMID: 23651858
- RBP-J deficient dendritic cells exhibit attenuated cytoskeleton reorganization when contacting T cells. PMID: 23138187
- Data found that loss of RBPj in mature excitatory neurons was well tolerated, with no evidence for neurodegeneration or of learning and memory impairment in mice aged up to 18 months. PMID: 23110206
- Based on the transgenic mouse model, our data indicate that MZ B cells with certain BCR specificity can develop in a Notch-RBP-J independent manner PMID: 22719978
- The results defined a signaling network in which signaling via Notch-RBP-J and TLRs is integrated at the level of IRF8 synthesis. A mechanism was identified by which heterologous signaling pathways can regulate TLR-induced polarization of macrophages. PMID: 22610140
- Mice carrying a mesenchymal-specific deletion of CSL/RBP-Jkappa, a key Notch effector, exhibit spontaneous multifocal keratinocyte tumors that develop after dermal atrophy and inflammation. PMID: 22682244
- RBP-J-mediated Notch signaling in aortic valves may be critically involved in valve homeostasis and valve diseases as well. PMID: 21773950
- Mice harboring intestinal epithelial cell-specific deletion of Rbpj, a transcription factor that mediates signaling through Notch receptors, develop chronic colitis characterized by the accumulation of T helper (Th)17 cells in colonic lamina propria. PMID: 22279105
- data demonstrate that Notch regulation of chondrocyte maturation is solely mediated via the RBPj-kappa-dependent pathway, and the perichodrium or osteogenic lineage probably influences chondrocyte terminal maturation and turnover of the cartilage matrix PMID: 22354840
- RBP-J strongly suppresses tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone resorption, but has minimal effects on physiological bone remodeling. PMID: 22249448
- When HNF-6 loss is combined with RBP-J loss, a phenotype consisting of cholestasis, hepatic necrosis, and fibrosis is observed that is more severe than the phenotype seen with Notch signaling loss alone. PMID: 21898486
- The data of this study indicated that Rbpj-mediated canonical Notch signaling inhibits DRG neuronal differentiation. PMID: 21510873
- differentiating hair cells and supporting cells rapidly die in RBPjkappa mutants, suggesting a requirement of RBPjk for cell survival in this tissue. PMID: 21632926
- Notch signaling disruption via RBPJk heterozygous inactivation results in aortic valve disease. PMID: 21493891
- Study shows a novel RBP-J function that promotes INP differentiation. PMID: 21443869
- MINT forms a high affinity complex with CSL; the domains of MINT and CSL that are necessary and sufficient for complex formation are delineated PMID: 21372128
- roles for Rbpj and notch signaling in multiple aspects of inner ear development including prosensory cell maturation, cellular differentiation and survival PMID: 21420948
- RBP-J-mediated canonical Notch signaling governs retinal cell specification and differentiation, and maintains retinal lamination through the expression of beta-catenin. PMID: 20017954
- reduction in graft survival was associated with augmented alloantigen specific T-cell proliferation and increased number of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells in the RBP-J deficient recipient mice PMID: 21168915
- This study suggested RBP-J is not required for granule neuron progenitor development and medulloblastoma initiated by Hedgehog pathway activation in the external germinal layer PMID: 20950430
- Repression of p53 by RBP-Jkappa and activation of p53 by C/EBPbeta through differential binding of these two factors indicates a type of co-operative regulation in p53 expression. PMID: 20446924
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Su(H) family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:19664
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000040694
UniGene: Mm.209292
Most popular with customers
-
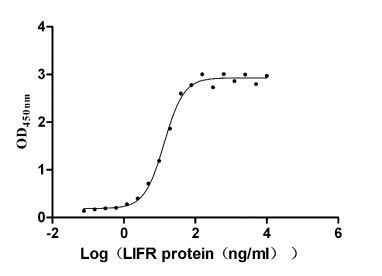
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
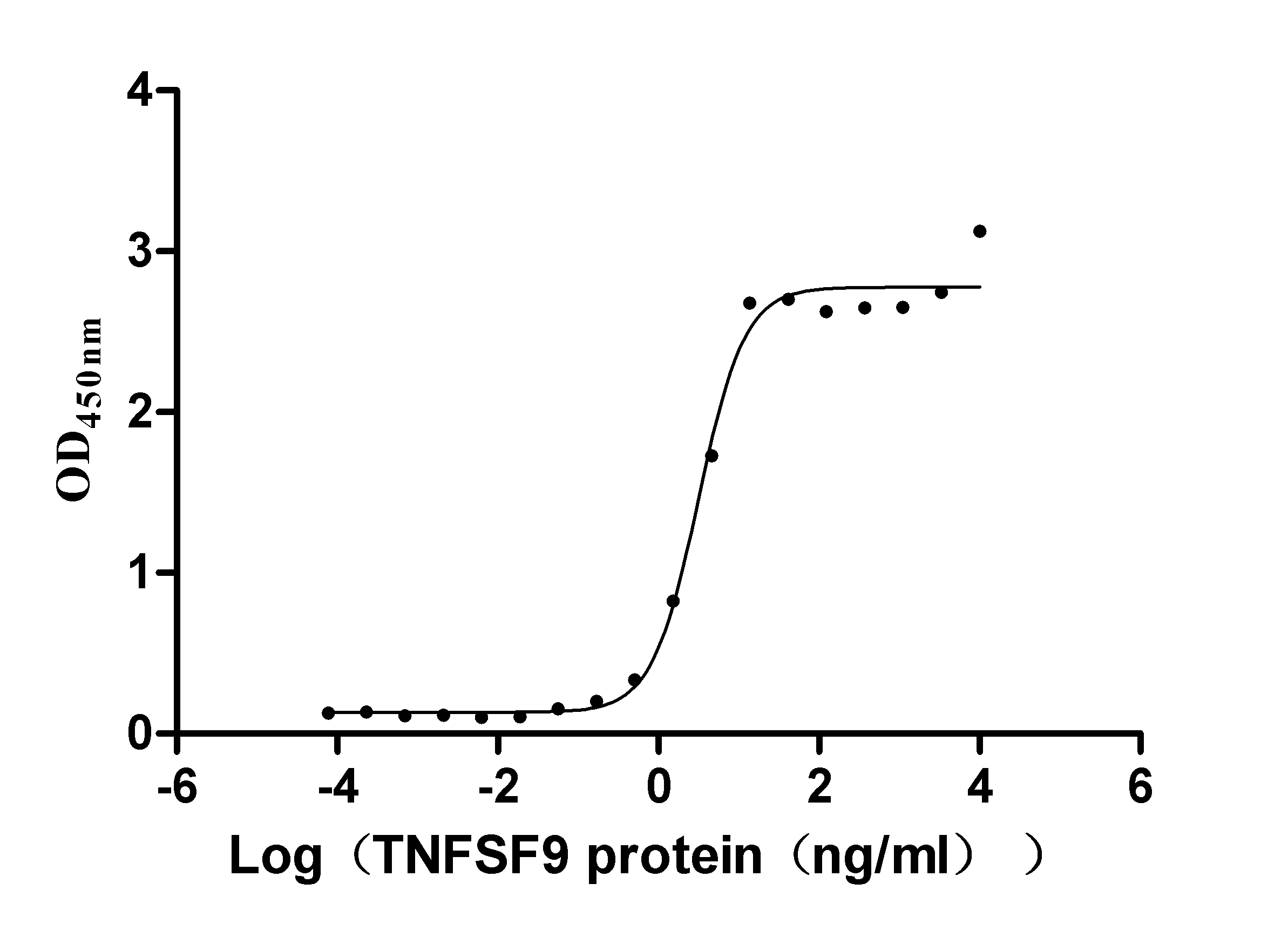
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9 (TNFSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
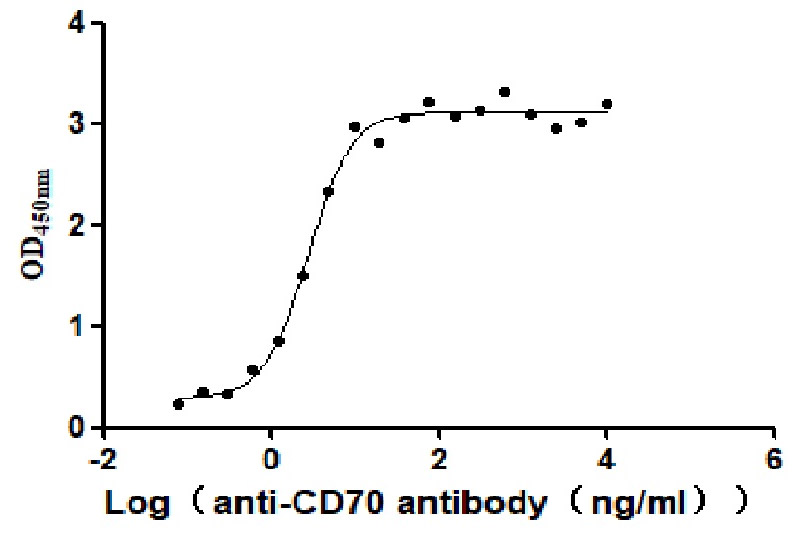
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)