Recombinant Mouse Neuromedin-U (Nmu), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Nmu重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP889555MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Nmu重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP889555MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Nmu重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP889555MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Nmu重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP889555MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Nmu重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP889555MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Nmu
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:NmuNeuromedin-U [Cleaved into: Neuromedin precursor-related peptide 36; NURP36); Neuromedin precursor-related peptide 33; NURP33); Neuromedin-U-23; NmU-23)]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
表达区域:144-166
-
氨基酸序列FKAEYQS PSVGQSKGYF LFRPRN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Ligand for receptors NMUR1 and NMUR2. Stimulates muscle contractions of specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract.; Does not function as a ligand for either NMUR1 or NMUR2. Indirectly induces prolactin release although its potency is much lower than that of neuromedin precursor-related peptide 36.; Does not function as a ligand for either NMUR1 or NMUR2. Indirectly induces prolactin release from lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland, probably via the hypothalamic dopaminergic system.; Stimulates muscle contractions of specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data indicate a novel role for the peripheral NMU system, providing new insights into the pathogenesis of NAFLD/NASH. PMID: 29017855
- Loss of NMU-NMUR1 signalling reduced ILC2 frequency and effector function, and altered transcriptional programs following allergen challenge in vivo. Thus, NMUR1 signalling promotes inflammatory ILC2 responses, highlighting the importance of neuro-immune crosstalk in allergic inflammation at mucosal surfaces. PMID: 28902842
- data indicate that the NMU-NMUR1 neuronal signaling circuit provides a selective mechanism through which the enteric nervous system and innate immune system integrate to promote rapid type 2 cytokine responses that can induce anti-microbial, inflammatory and tissue-protective type 2 responses at mucosal sites PMID: 28869965
- NMU treatment in vivo resulted in immediate protective type 2 responses; accordingly, group 2 innate lymphoid cells -autonomous ablation of Nmur1 led to impaired type 2 responses and poor control of worm infection PMID: 28869974
- These results suggested that NMU can act directly on beta cells through NMUR1 in an autocrine or paracrine fashion to suppress insulin secretion. Collectively, our results highlight the crucial role of NMU in suppressing pancreatic insulin secretion, and may improve our understanding of glucose homeostasis. PMID: 28864416
- These results suggest that NMU and NMS are involved in thermoregulation via the prostaglandin E2 and beta3 adrenergic receptors, but that endogenous NMS might play a more predominant role than NMU. PMID: 26826380
- the anorectic effect of the lipidated NMU is partly mediated by a decrease in gastric emptying which is subject to tachyphylaxis after continuous dosing. PMID: 25895852
- Beta-adrenergic and cholinergic mechanisms are involved in the anxiolytic action of neuromedin-U. PMID: 23892031
- Data show that neuromedin U (NMU)-deficient mice developed less severe arthritis than control mice. PMID: 22314006
- investigation of neuromedin U effects on factors associated with obesity/diabetes: NMU reduced food consumption/body weight; NMU increased body temperature/metabolic rate; NMU improved glucose tolerance; these effects seem to be mediated by NMUR1 PMID: 21586559
- Analysis of NMU expression in ob/ob mice revealed elevated NMU mRNA levels in the dorsomedial hypothalamic (DMH) nucleus of ob/ob mice compared to lean litter-mates. NMU mRNA levels were elevated in the DMH of mice fasted for 24 h relative to controls PMID: 14622096
- results suggest that endogenous NMU may be involved in reflexes and adaptation to environmental stimuli PMID: 15369794
- NMU plays an important role in the regulation of feeding behavior and energy metabolism independent of the leptin signaling pathway. PMID: 15448684
- NMU receptor antagonists could be novel targets for pharmacological inhibition of allergic inflammatory diseases, including asthma. PMID: 16373672
- data suggest that LPS-induced IL-6 expression is partly dependent on autocrine/paracrine activation of the NMU-NMU-R1 signals in macrophages PMID: 16466693
- A study evaluating smooth muscle contraction in NMU1 receptor knockout mouse was used to determine which receptor subtype mediates the contractile responses generated by neuromedin in the mouse.[NMU1 receptor] PMID: 16474416
- results indicate that NMU suppresses gonadotropin secretion and regulates the onset of puberty PMID: 16716306
- Central control of bone remodeling by Nmu is reported. PMID: 17873881
- negative regulator of bone formation through the molecular clock PMID: 18761104
- proNMU(104-136) is a novel modulator of energy balance and may contribute to the phenotype exhibited by NMU knockout mice. PMID: 19531638
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:NmU family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:56183
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000031146
UniGene: Mm.154879
Most popular with customers
-
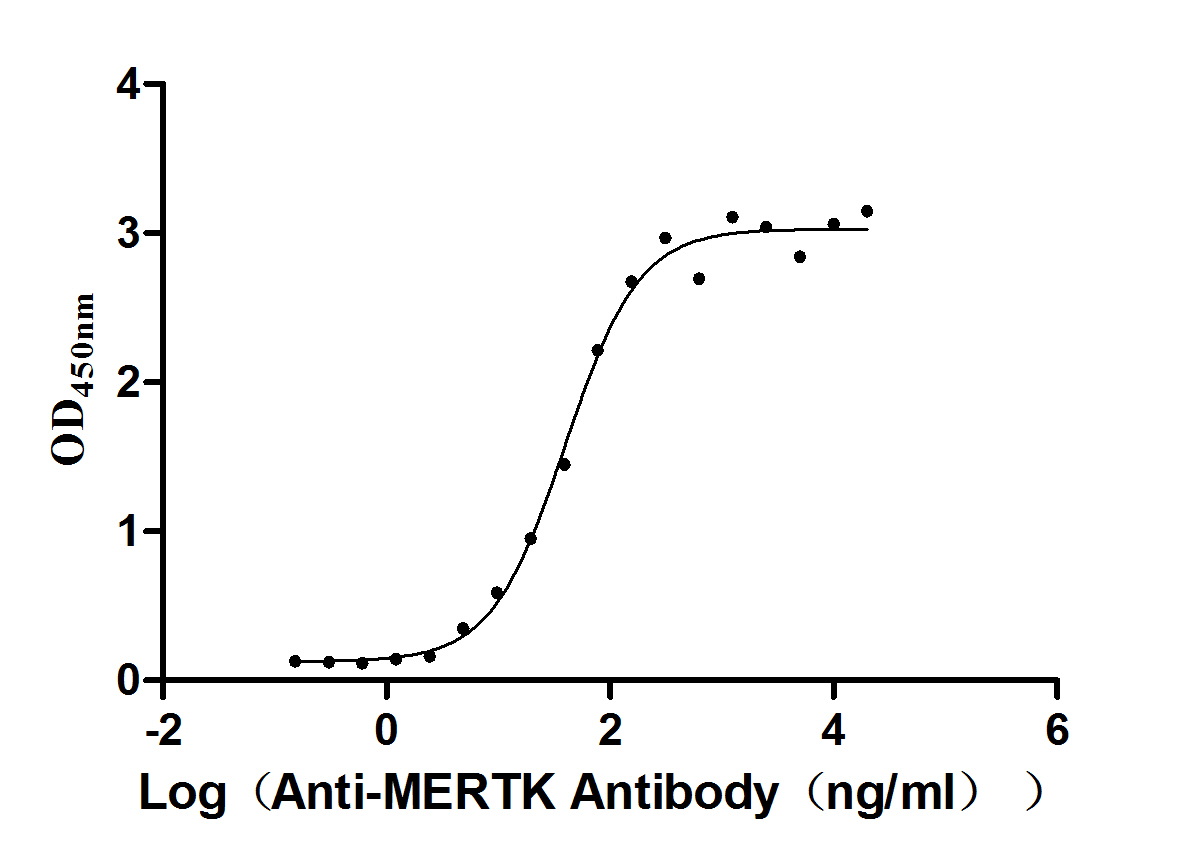
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
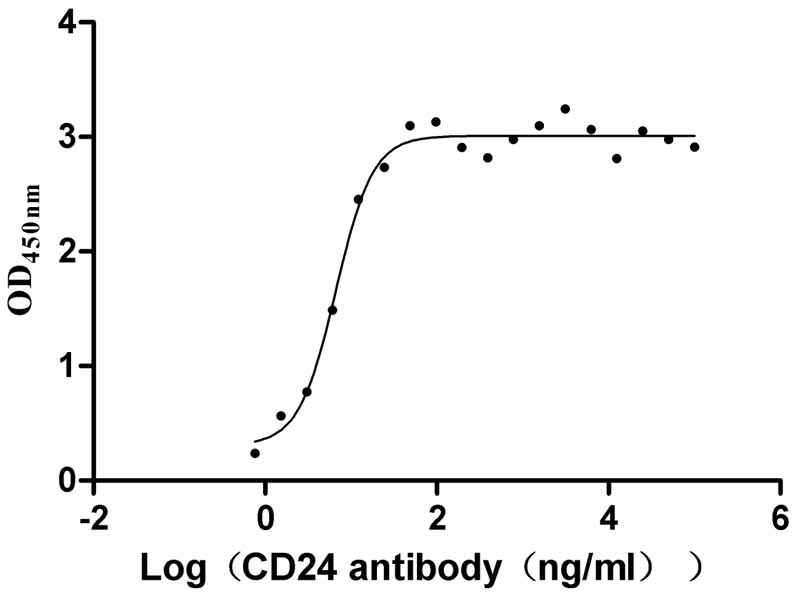
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
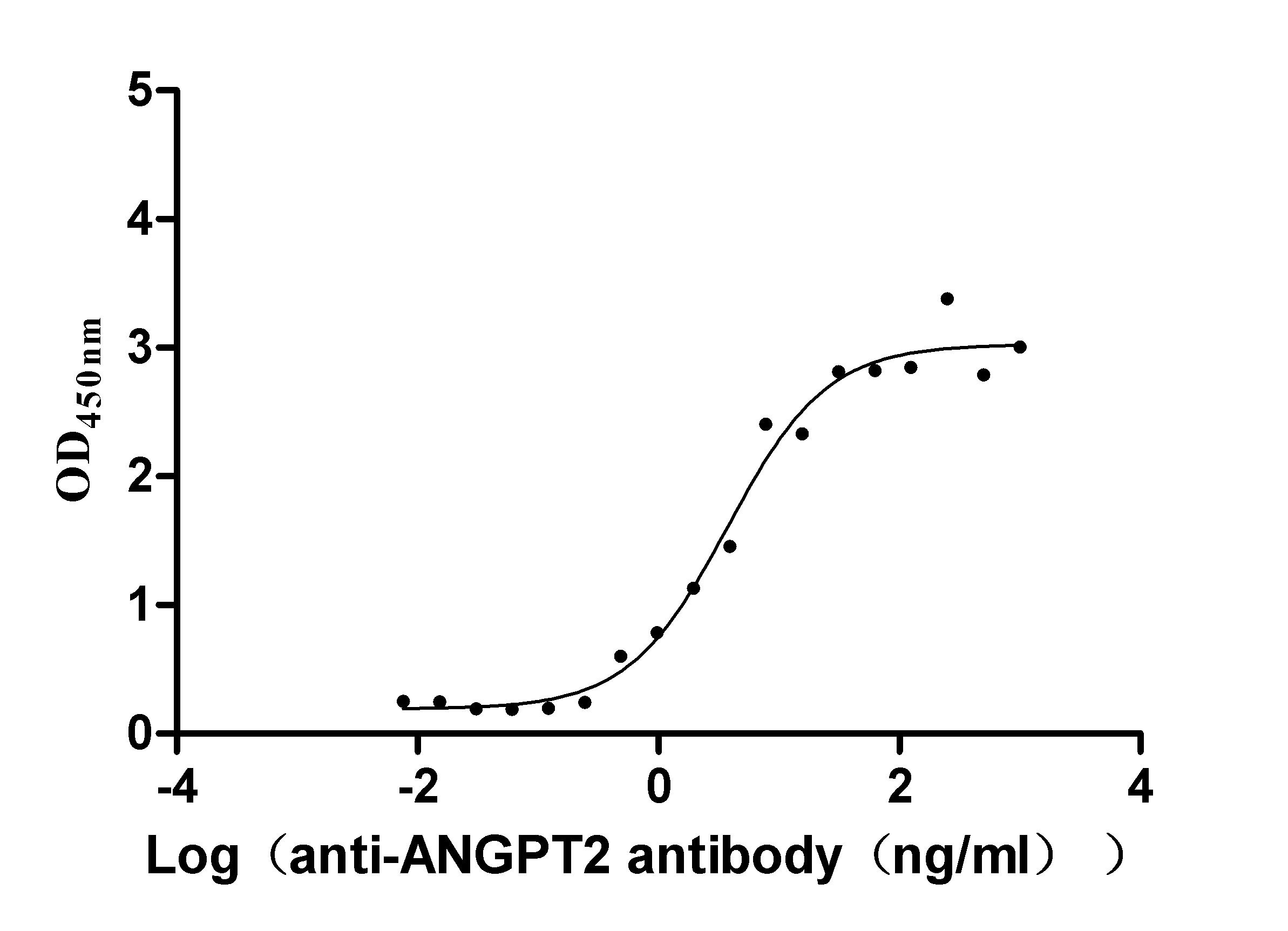
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
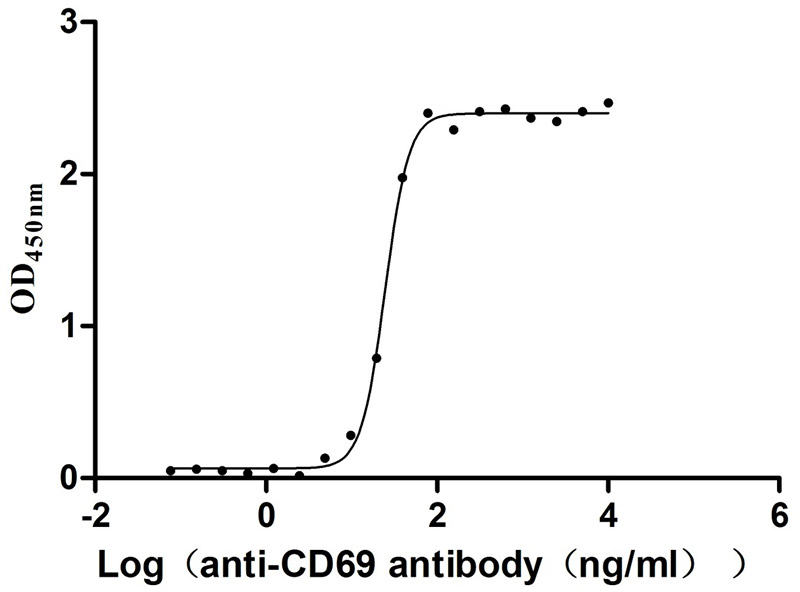
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)