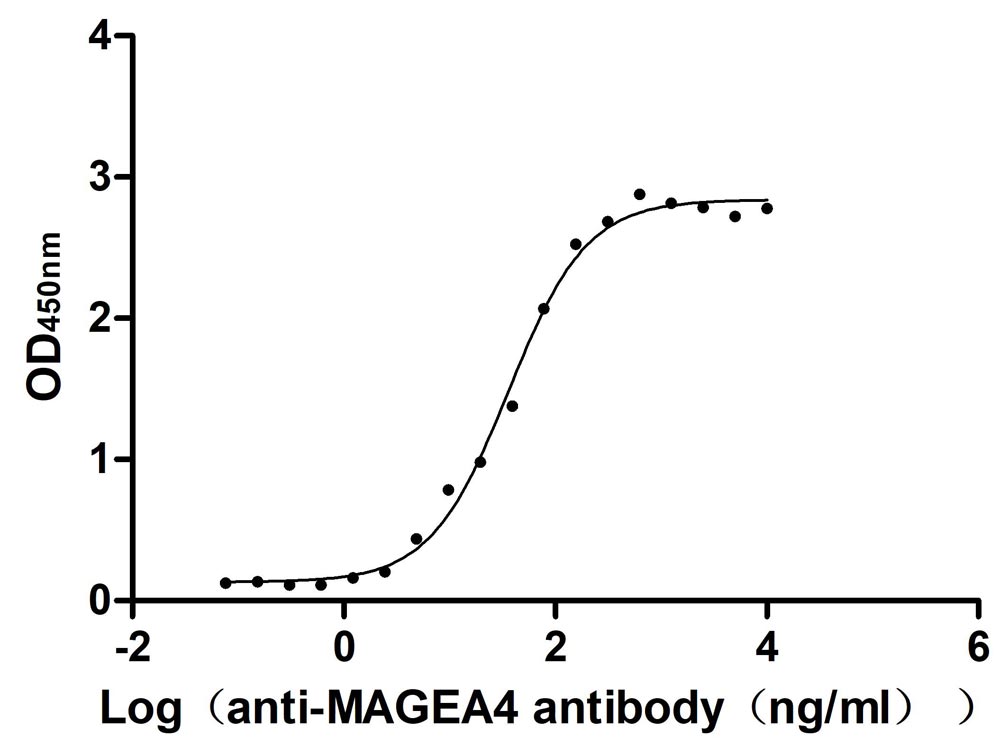
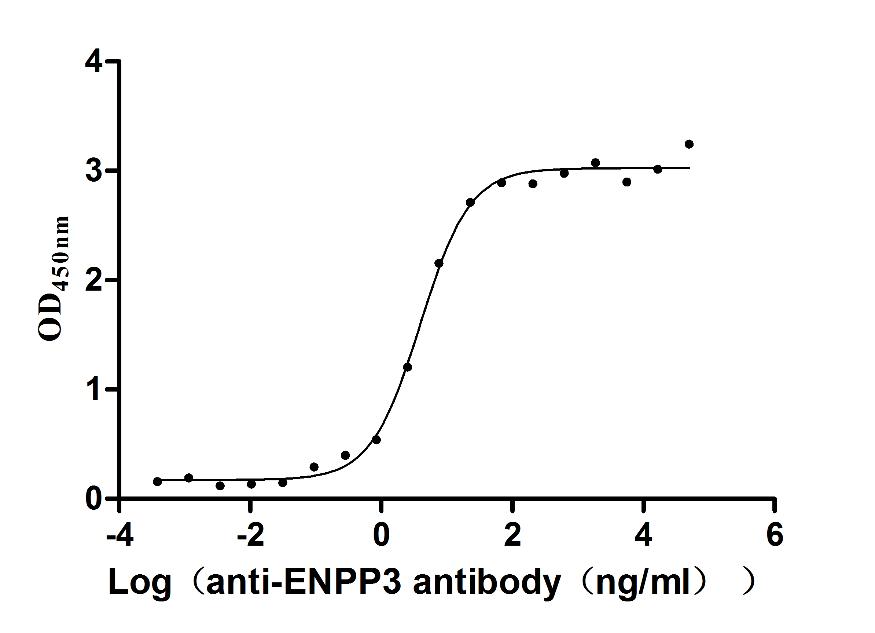
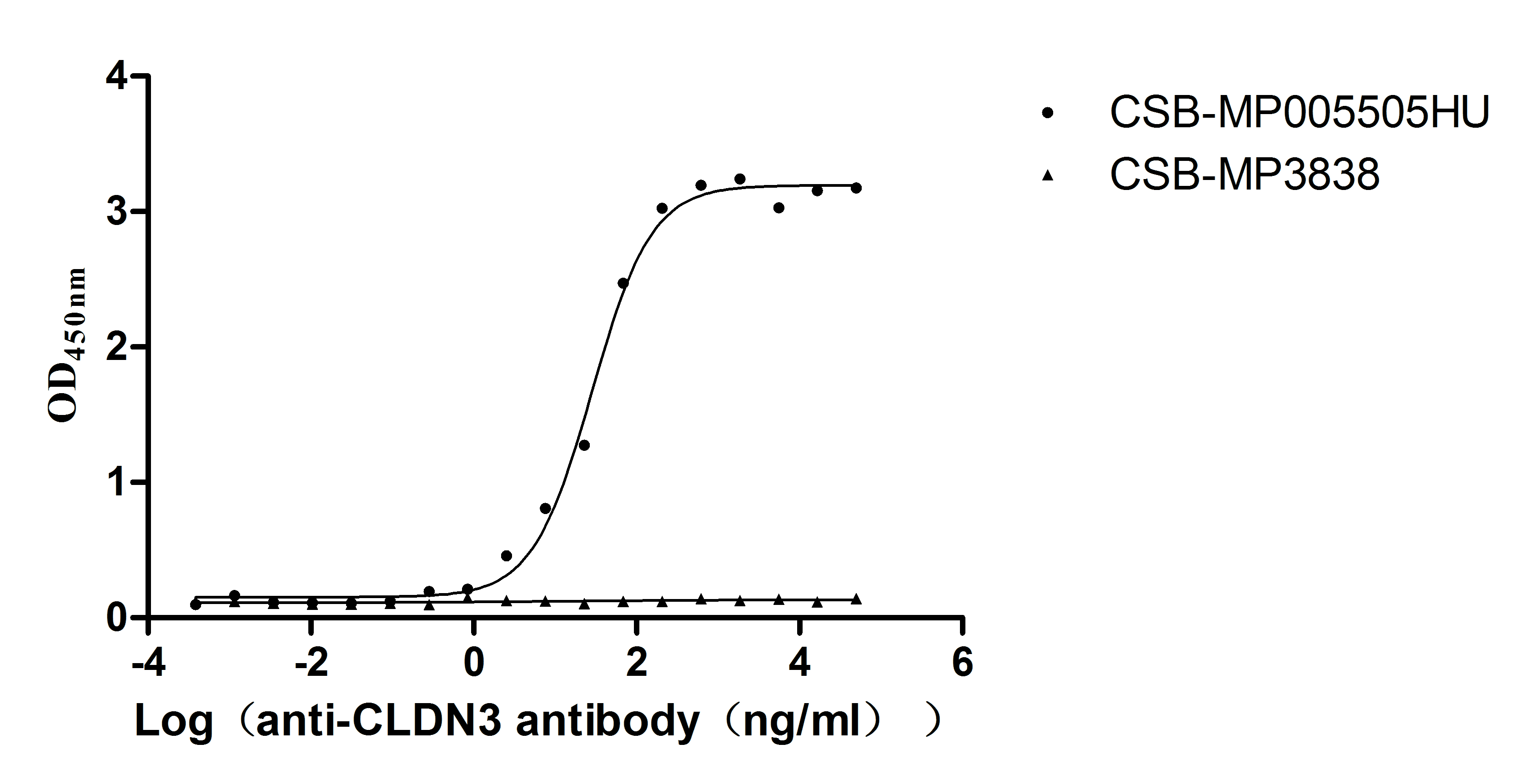
Recombinant Mouse Interferon regulatory factor 5 (Irf5)
-
中文名称:小鼠Irf5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP011820MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Irf5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP011820MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Irf5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP011820MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Irf5重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP011820MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Irf5Interferon regulatory factor 5; IRF-5
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-497
-
氨基酸序列MNHSAPGIPP PPRRVRLKPW LVAQVNSCQY PGLQWVNGEK KLFYIPWRHA TRHGPSQDGD NTIFKAWAKE TGKYTEGVDE ADPAKWKANL RCALNKSRDF QLFYDGPRDM PPQPYKIYEV CSNGPAPTES QPTDDYVLGE EEEEEEEELQ RMLPGLSITE PALPGPPNAP YSLPKEDTKW PPALQPPVGL GPPVPDPNLL APPSGNPAGF RQLLPEVLEP GPLASSQPPT EPLLPDLLIS PHMLPLTDLE IKFQYRGRAP RTLTISNPQG CRLFYSQLEA TQEQVELFGP VTLEQVRFPS PEDIPSDKQR FYTNQLLDVL DRGLILQLQG QDLYAIRLCQ CKVFWSGPCA LAHGSCPNPI QREVKTKLFS LEQFLNELIL FQKGQTNTPP PFEIFFCFGE EWPDVKPREK KLITVQVVPV AARLLLEMFS GELSWSADSI RLQISNPDLK DHMVEQFKEL HHLWQSQQQL QPMVQAPPVA GLDASQGPWP MHPVGMQ
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that plays a critical role in innate immunity by activating expression of type I interferon (IFN) IFNA and INFB and inflammatory cytokines downstream of endolysosomal toll-like receptors TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9. Regulates the transcription of type I IFN genes (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) and IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) by binding to an interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) in their promoters. Can efficiently activate both the IFN-beta (IFNB) and the IFN-alpha (IFNA) genes and mediate their induction downstream of the TLR-acti...显示更多
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Scavenger receptor class A is regulated by pathogens and suppresses IRF5 nuclear translocation by direct interaction. Reduced abundance of nuclear IRF5 shifts macrophage polarization from M1 towards M2, which subsequently switches T-helper responses from type 1 to type 2. PMID: 28695899
- Aged mice expressed higher IRF5 levels in the ischemic brains, suggesting that aging has a significant influence on stroke outcomes in mice, which is probably mediated by age-specific inflammatory responses. PMID: 28905935
- this study shows a critical role for IRF5 in regulating allergic airway inflammation PMID: 27759022
- IRF5 and IRF5 disease-risk variants increase glycolysis and human m1 macrophage polarization by regulating proximal signaling and Akt2 activation. PMID: 27545875
- these results reveal a role for Lyn as a specific suppressor of the TLR-MyD88-IRF5 pathway and illustrate the importance of fine-tuning IRF5 activity for the maintenance of immune homeostasis PMID: 27521268
- IRF5 siRNA reverses pancreatitis-induced activation of lung macrophages from M1 phenotype to M2 phenotype in severe acute pancreatitis associated with acute lung injury. PMID: 27895424
- Our data show that miR-146b targets IRF5, resulting in the regulation of macrophage activation. Furthermore, miR-146b deficient mice developed intestinal inflammation with enhanced M1 macrophage polarization. PMID: 27825654
- data suggest that IRF5 plays a causal role in inflammation, fibrosis and impaired vascular EC function in Tsk/+ mice PMID: 27050551
- Collectively, these results indicate a key role for IRF-5 in modulating the host antiviral response in peripheral organs that controls bunyavirus neuroinvasion in mice. PMID: 26468541
- studies extend prior ones suggesting that inhibiting IRF5 might be useful for chronic macrophage-induced inflammation and suggest that IRF5 blockade would ameliorate more acute forms of inflammation, including lung injury PMID: 26283380
- IRF5 plays an important role in the development of disease in the MRL/lpr mouse model of lupus in the absence of the DOCK2 mutation and that IRF5 is required for the transition from mature B cells to plasma cells. PMID: 25076492
- IRF5 expression in microglia is regulated by IRF8. IRF5 directly upregulates P2RX4 expression on microglia in peripheral nerve injury, and may play a role in neuropathic pain. PMID: 24818655
- PAR1 suppression of IRF5 and IL-12/23 secretion by macrophages provides a novel mechanism by which the host suppresses the mucosal Th1 and Th17 response to H. pylori infection. PMID: 24866378
- This study uncovers a new function for IRF5 in controlling the relative mass of different adipose tissue depots and thus insulin sensitivity in obesity. PMID: 25939064
- IKKbeta is an IRF5 kinase that instigates inflammation PMID: 25326420
- our results reveal a protective role for IRF5 in lupus-associated atherosclerosis that is mediated through the effects of IRF5 in both immune and nonimmune cells. PMID: 25595782
- IRF5 has a critical role in shaping the early innate immune response towards West Nile virus in the draining lymph node, which impacts the spread of virus infection, optimal B cell immunity, and disease pathogenesis. PMID: 25031348
- The IRF5 deficiency reduces IFN-alpha, IFN-beta and IL-6 production by Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)- and TLR7-stimulated DCs and reduces TLR7- and TLR9-induced IL-6 production by B cells PMID: 23291967
- establish the species-invariant role of IRF5 in controlling the inflammatory macrophage phenotype both in vitro and in in vivo PMID: 24453413
- These proteins were upregulated in Irf5(-/-) mice. PMID: 23912454
- Reduction of IRF5 expression, a factor that regulates macrophage polarization, reduced expression of inflammatory M1 macrophage markers, supported resolution of inflammation, accelerated cutaneous and infarct healing PMID: 24361318
- IRF5 levels in Tsk(-/+) hearts were similar to control. PMID: 23251680
- Our results establish IRF-3, -5, and -7 as the key transcription factors responsible for mediating the type I IFN and IFN stimulated gene response in myeloid dendritic cells during WNV infection and suggest a novel signaling link between MAVS and IRF-5. PMID: 23300459
- Our results show that IRF5 is a crucial driver of lupus development in mice. PMID: 21305501
- Irf5-deficient monocytes are defective in their response to peritoneal lavage of pristane-injected mice; pristane-induced Ly6C(hi) antigen-producing monocyte recruitment to the peritoneal cavity is impaired in Irf5-deficient mice. PMID: 22933628
- these results identify the IRF-5-Ikaros axis as a critical modulator of IgG2a/c class switching. PMID: 22535200
- overexpression of IRF5 in blood cells of systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE) patients may contribute to disease pathogenesis. PMID: 22678902
- uncovered a new, IFN-I-independent role of IRF5 in regulating chemokines involved in the homing of pDCs and certain lymphocyte subsets. PMID: 22422888
- A spontaneous genomic duplication and frameshift mutation in the guanine exchange factor dedicator of cytokinesis 2 (Dock2) that has arisen in at least a subset of circulating Irf5(-/-) mice and inadvertently been bred to homozygosity. PMID: 22431588
- the IRF5/Blimp-1 axis differentially regulates the expression of Nba2 lupus susceptibility genes, and they suggest an important role for the IRF5/Blimp-1/p202 axis in murine lupus susceptibility. PMID: 22116829
- The s show that the myxoma virus-induced innate immune response requires TLR9 and its adaptor MyD88, transcription factors IRF5 and IRF7, and the type I interferon positive-feedback loop mediated by IFNAR1. PMID: 21835795
- Levels of Irf5 mRNA and protein were higher in females than in age-matched males. PMID: 20802013
- Demonstrate a requirement for IRF5 in the development of SLE via its role in B cells. Antinuclear autoantibodies and Ig glomerular deposits, hallmarks of SLE, are absent in Irf5(-/-) mice challenged to develop SLE by pristane injection. PMID: 20479222
- Data show the role of IRF-5 in the B-cell terminal differentiation. PMID: 20176957
- IRF5 plays an essential role in lupus pathogenesis in murine models and this is mediated through pathways beyond that of type I IFN production PMID: 20007534
- study identifies IRF-5 as a new, principal downstream regulator of the TLR-MyD88 signalling pathway and a potential target of therapeutic intervention to control harmful immune responses PMID: 15665823
- we also provide evidence that this TLR synergy is mediated, at least in part, by activation of the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5). PMID: 17275788
- IRF5 is critical for antiviral immunity and for the induction of apoptosis, but not cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage, and acts as a tumor suppressor on a pathway that may be distinct from that for p53. PMID: 17360658
- IRF5 plays a critical role in interferon (IFN)-alpha and IFN-beta production induced not only by RNA-containing immune complexes but also by conventional Toll-like receptor (TLR)7 and TLR9 ligands. PMID: 17513736
- reveal a cell-type-specific function for IRF5 in the complex regulatory mechanism of death-receptor-induced apoptosis PMID: 18268344
- reveal the cell type-specific importance of IRF-5 in MyD88-mediated antiviral pathways and the widespread role of IRF-5 in the regulation of inflammatory cytokines PMID: 18332133
- Data show that IRF-5, which is activated via the MyD88 pathway, is subjected to TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination, which is important for IRF-5 nuclear translocation and target gene regulation. PMID: 18824541
- The functional characterization of the novel IRF-5 mutant in transformed B and T cell lines and in ATL and CLL patients may lead to a better understanding of the role of these transcriptional regulators in hematopoietic malignancies. PMID: 19430534
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:IRF family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:27056
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000004392
UniGene: Mm.6479


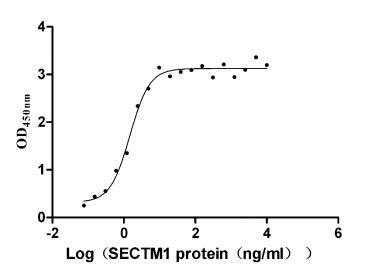
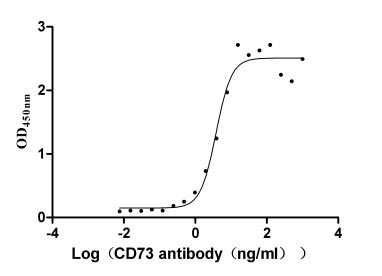
-AC1.jpg)