Recombinant Mouse Ephrin-B2 (Efnb2), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Efnb2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP007466MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Efnb2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007466MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Efnb2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007466MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Efnb2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP007466MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Efnb2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP007466MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Efnb2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Efnb2; Elf2; Epl5; Eplg5; Htkl; Lerk5; Ephrin-B2; ELF-2; EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 5; LERK-5; HTK ligand; HTK-L
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cell surface transmembrane ligand for Eph receptors, a family of receptor tyrosine kinases which are crucial for migration, repulsion and adhesion during neuronal, vascular and epithelial development. Binds promiscuously Eph receptors residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Binds to receptor tyrosine kinase including EPHA4, EPHA3 and EPHB4. Together with EPHB4 plays a central role in heart morphogenesis and angiogenesis through regulation of cell adhesion and cell migration. EPHB4-mediated forward signaling controls cellular repulsion and segregation from EFNB2-expressing cells. May play a role in constraining the orientation of longitudinally projecting axons.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Production of inflammatory cytokines was inhibited by Ti particles through bidirectional signals. Addition of ephB4Fc inhibited the osteoclastmediated formation of Ti particles via bidirectional ephrinB2/ephB4 signaling. Activation of this bidirectional signaling pathway may be a potential clinical treatment for osteolysis surrounding prostheses. PMID: 30015911
- Results show that early but not late post conditioning hippocampal protein synthesis is necessary for the formation of remote memory and provide the first evidence of a possible involvement of EphrinB2 in neuronal plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex. PMID: 29444449
- GRIP1 binds to apoER2 and EphrinB2 to induce activity-dependent AMPA receptor insertion at the synapse. PMID: 28978486
- Results show that EfnB2 plays a previously unrecognized role as a principal regulator of hematopoiesis from the dorsal aorta and embryonic stem cells by controlling the emergence of hemogenic endothelial cells. During vascular development, EfnB2 is essential for the proper sorting of arterial and venous-fated endothelium into distinct arterial and venous vascular beds. PMID: 27250641
- Data reveal that ephrinB2 and ephrinB3 signaling is required to control progenitor identities in the ventral spinal cord. PMID: 28595615
- As endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs)derived from mouse bone marrow were cultured on substrates of increasing stiffness, the mRNA and protein levels of the specific arterial endothelial cell marker ephrinB2 were found to increase, while the expression of the venous marker EphB4 decreased PMID: 28732675
- Male Efnb2 knockout mice presented reduced blood pressure. Region from aa 313 to aa 331 of EFNB2 was essential for reverse signaling regulating VSMC contractility. PMID: 27530629
- Suggest role for ephrinB2/EphB4 signaling in the maintenance of neurovascular homeostasis and show that EphrinB2 activation promotes vascular repair mechanisms and reduces brain swelling after mild cerebral ischemia. PMID: 28254815
- The Eph/ephrin-B2-mediated heterotypic or homotypic cell interactions between thymocytes and thymic epithelial cells (TECs), or between TECs and themselves, contribute to the early maturation of MTS20(+) TECs. PMID: 27060907
- Control of abscission requires Eph kinase activity, and Src and citron kinase (CitK) are downstream effectors in the Eph-induced signal transduction cascade PMID: 27551053
- The Netrin-1 and ephrin-B2 synergistic growth cone responses involve the potentiation of Src family kinase signaling, a common effector of both pathways. PMID: 26633881
- in vivo study demonstrated, for the first time, that EFNB2 is essential for normal long bone growth and development PMID: 26980243
- the role of ephrin B2 in endochondral ossification using Osx1Cre-targeted gene deletion, was investigated. PMID: 26755702
- our study uncovered a novel cell autonomous role for ephrinB2 in lateral motor column motoneurons PMID: 26503288
- These data indicate that ephrinB2/EphB4 signaling within the osteoblast lineage is required for late stages of osteoblast differentiation. PMID: 23165727
- EfnB2 is an essential regulator of endothelial cell death and vessel pruning. This regulation depends upon phosphotyrosine-EfnB2 signaling repressing JNK3 activity via STAT1. PMID: 25807892
- disruption of cochlear signalling results in supporting cell translocation into hair cell layers PMID: 25923646
- Neural crest defects in ephrin-B2 mutant mice are non-autonomous and originate from defects in the vasculature. PMID: 26385750
- Mice bearing genetically altered cytoplasmic region of ephrinB2 have significantly altered EphB4-dependent forward signaling. PMID: 25865237
- ephrin-B2 signaling has an important role in the formation of pituitary stem/progenitor cell niches and in pituitary organogenesis. PMID: 25480420
- Efnb2 expression was attenuated in Pou3f4 hemizygous null mutants relative to control. PMID: 25299585
- Efnb2 conditional knockout mice were defective in acute arterial dilation. Vasodilation was impaired in cremaster arterioles in response to either increased flow or ACh, and in the carotid arteries in response to increased flow. PMID: 24673722
- cell-cell interactions with endothelial cells enforce quiescence and promote stem cell identity. Mechanistically, endothelial ephrinB2 and Jagged1 mediate these effects PMID: 25283993
- These results suggest that ephrin-B2 forward signaling through EphA4 is required for the precise control of cortical neuron migration. PMID: 24477991
- Data indicate that conditional inactivation of Efnb2 in early-stage embryonic ear tissues disrupted cell proliferation, cell survival, and epithelial folding at the origin of the endolymphatic epithelium. PMID: 24583262
- Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling mediates distal alveolar formation. PMID: 23742148
- ephrin-B2 is an important regulator of PDGFRbeta endocytosis and thereby acts as a molecular switch controlling the downstream signaling activity of this receptor PMID: 24298057
- EphB2 and EphB3 are involved in the control of thymic epithelial cells (TEC) survival and that the absence of these molecules causes increased apoptotic TEC. PMID: 23146940
- We confirmed that ephrin-B2 protein causes co-clustering of EphB2 and glutamate receptors in spinal cord neurons. PMID: 23623938
- B2 expressed on astrocytes inhibited axonal growth PMID: 23518227
- ephrin-B2 could be one of the promoters to upregulate gliosis following brain injury. PMID: 23106883
- These findings suggest the importance of these ephrin-b2 in establishing functional auditory circuits prior to experience. PMID: 23042409
- PDZ domain-dependent ephrinB2 reverse signaling protects against PTC rarefaction by regulating angiogenesis and vascular stability during kidney injury PMID: 23492730
- a role for ephrin-B2 in the development and healing of bone through activation of osteoblast-specific gene expression. PMID: 23129351
- Ephrin-B2(+) astrocytes therefore promote neuronal differentiation of adult NSCs through juxtacrine signaling. PMID: 22983209
- results suggest the involvement of EFNB2 in thymocyte development; however, heavy redundancy among Eph/EFN family members prevents the occurrence of detrimental phenotypes in the T cell compartment caused by T cell-specific EFNB2 gene null mutation PMID: 22673212
- The results of this study suggested that rapid accumulation of EphrinB2 in hippocampal CA1 neurons is involved in the behavioural and cellular modifications induced by contextual fear conditioning. PMID: 22101302
- Dorsal and ventral-temporal axons require ephrin-B2 reverse signalling. PMID: 21847105
- Both EphB2/EphB3 forward signaling and ephrin-B2 reverse signaling were shown to be required for midline fusion of the palate. PMID: 21539827
- These findings suggest the involvement of cell-cell EphA4 and ephrin-B2 signaling in establishing order in the developing inferior colliculus PMID: 20886601
- There may be a link between vascular ephrinB2 expression and the proinflammatory activation of monocytes that may contribute to the pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis. PMID: 21127290
- Data show that ephrinB4 can promote the growth of melanomas expressing the ephrin-B2 ligand by stimulating proliferation, survival and angiogenesis. PMID: 20649938
- Presynaptic ephrin-B2 expression plays an important role in regulating inflammatory pain through the regulation of synaptic plasticity in the dorsal horn and is also involved in the pathogenesis of some types of neuropathic pain. PMID: 21059214
- demonstrate that bath application of ephrin-B2 induces rapid and sustained growth cone collapse and axon retraction in ventrotemporal retinal ganglion cell axons PMID: 20629048
- These data suggest the relevance of a nonactivated EphB2 for regulating T cell progenitor migration and its modulation upon ephrin-B engagement. PMID: 20504947
- Result implies a NC-derived cell-specific role of EphB-ephrin-B2 interactions in the collective migration of the thymic rudiment during organogenesis. PMID: 20616004
- Results suggest that formation of arteriovenous malformations in Notch1 gain of function mutants and ephrinB/EphB pathway loss of function mutant embryos occurs by different mechanisms. PMID: 20101599
- EphB2-ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required to prevent the formation of ipsilateral VCN-MNTB projections and that this signaling operates non-cell autonomously. PMID: 20660266
- results show that full VEGFR3 signalling is coupled to receptor internalization; ephrin-B2 is a key regulator of this process and thereby controls angiogenic and lymphangiogenic growth PMID: 20445537
- ephrin-B2 reverse signalling involving PDZ interactions regulates endothelial tip cell guidance to control angiogenic sprouting and branching in physiological and pathological angiogenesis PMID: 20445540
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction, adherens junction.
-
蛋白家族:Ephrin family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in inner and outer pillar cells of the organ of Corti (at protein level). Expressed on lateral floor plate cells, specifically on commissural axon segments that have passed through the floor plate. Expressed in cells of the retinal ganglion cell
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:13642
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000001319
UniGene: Mm.209813
Most popular with customers
-
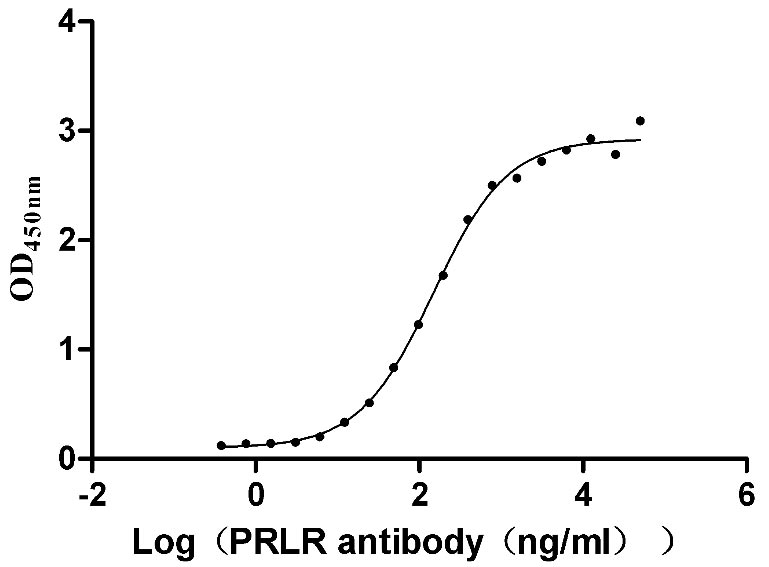
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
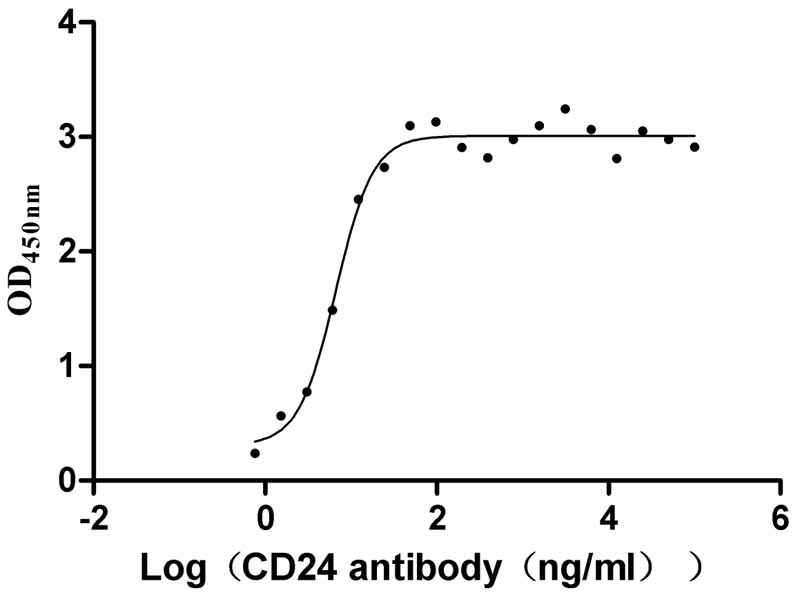
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
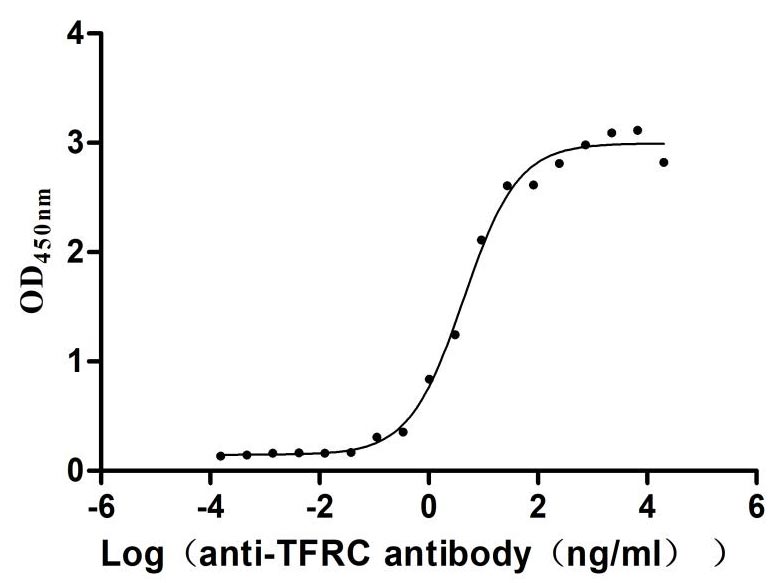
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
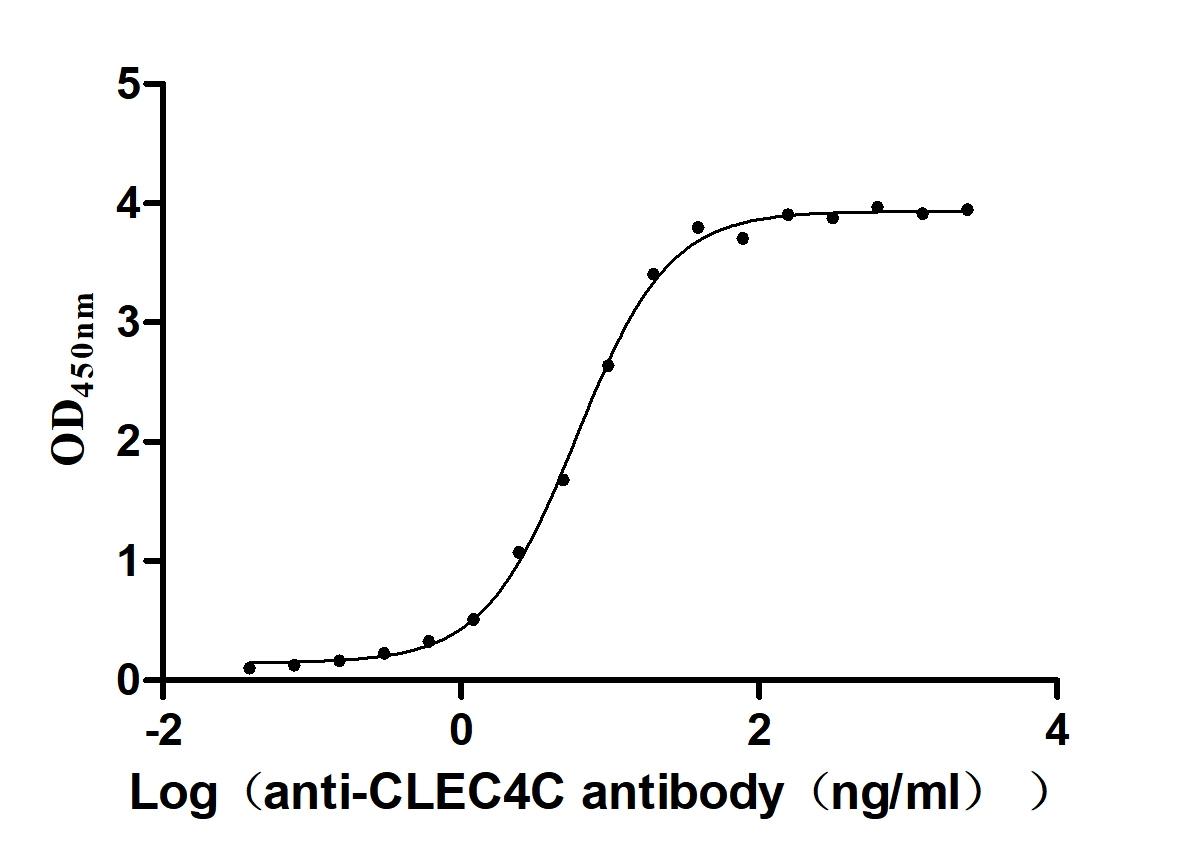
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)



-AC1.jpg)