Recombinant Mouse Dysferlin (Dysf), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Dysf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP884154MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dysf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP884154MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dysf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP884154MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dysf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP884154MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Dysf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP884154MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dysf; Fer1l1Dysferlin; Dystrophy-associated fer-1-like protein; Fer-1-like protein 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Key calcium ion sensor involved in the Ca(2+)-triggered synaptic vesicle-plasma membrane fusion. Plays a role in the sarcolemma repair mechanism of both skeletal muscle and cardiomyocytes that permits rapid resealing of membranes disrupted by mechanical stress.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our data suggest that dysferlin modulates SR Ca(2+) release in skeletal muscle, and that in its absence osmotic shock injury causes increased RyR1-mediated Ca(2+) leak from the SR into the cytoplasm. PMID: 28568606
- dysferlin has membrane tubulating capacity and that it shapes the T-tubule system. PMID: 28104817
- These results provide one mechanism by which the C57BL/6J background intensifies dysferlinopathy, giving rise to a more severe form of muscular dystrophy in the Dysf(B6) mouse model through increased membrane leak and inflammation. PMID: 27070822
- dysferlin-deficient cardiomyocytes showed slower Ca2+ re-sequestration. Dysferlin deficiency blunted the beta-adrenergic effect on relaxation and pumping function of ex vivo working hearts. PMID: 26415898
- Using both naturally occurring and genetically engineered dysferlin-deficient mice, the s demonstrated that loss of dysferlin confers increased susceptibility to coxsackievirus infection and myocardial damage. PMID: 26073173
- By targeting DYSF premRNA introns harbouring differentially defined 3' splice sites (3' SS), we found that target introns encoding weakly defined 3' SSs were trans-spliced successfully in vitro in human myoblasts also in vivo in skeletal muscle of mice. PMID: 25904108
- Dysferlin does not regulate cardiac voltage-dependent ion channels in cardiomyocytes. PMID: 26112643
- results show that dysferlin exerts protective effects on the fukutin(Hp/-) FCMD mouse model, and the (dysferlin(sjl/sjl): fukutin(Hp/-)) mice will be useful as a novel model for a recently proposed antisense oligonucleotide therapy for FCMD PMID: 25198651
- These novel observations of conspicuous intermyofibrillar lipid and progressive adipocyte replacement in dysferlin-deficient muscles. PMID: 24685690
- Laser-wounding induced rapid recruitment of local dysferlin-containing sarcolemma, formation of stable dysferlin accumulations surrounding lesions, endocytosis of dysferlin, and formation of large cytoplasmic vesicles from distal regions of the fiber. PMID: 24784578
- Dysferlin, a calcium-triggered exocytotic membrane repair protein, is required for the cytoprotective effects of TRAF2-mediated signaling after myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. PMID: 24572254
- Alternate splicing of the dysferlin C2A domain confers Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent binding for membrane repair. PMID: 24239457
- these findings demonstrate the importance of dysferlin and myoferlin for transverse tubule function and in the genesis of muscular dystrophy. PMID: 24177035
- Data indicate that bone marrow transplantation (BMT) improved functional and histological outcome in the A/J Dysfprmd mouse model. PMID: 23777246
- discovery of dysferlin as a t-tubule protein that stabilizes stress-induced Ca(2+) signaling offers a therapeutic avenue for limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B and Miyoshi myopathy patients. PMID: 24302765
- Dysferlin-peptides reallocate mutated dysferlin thereby restoring function PMID: 23185377
- The results suggest that decreased myotube fusion in dysferlin deficiency is attributable to intrinsic inflammatory activation and can be improved using anti-inflammatory mediators. PMID: 22560623
- Mice with dystrophin and dysferlin double mutations develop mixed sarcomas with variable penetrance and latency. PMID: 22682622
- C2 domains mediate high affinity self-association of dysferlin in a parallel homodimer PMID: 22110769
- We observed that dysferlin-deficient muscles recovered the tetanic force production to the same extent as their WT counterparts following a saponin exposure. Data suggest that dysferlin is unlikely involved in repairing saponin-induced membrane damage. PMID: 21941430
- Data suggest dysferlin has an important function in the internal membrane systems of skeletal muscle, involved in calcium homeostasis and excitation-contraction coupling. PMID: 22043020
- Data show that dysferlin is not only a membrane repair protein but also important for muscle membrane maintenance and integrity. PMID: 21079765
- Dysferlin function in intracellular vesicles and its implication in muscle membrane resealing. PMID: 21119217
- Using dysferlin-deficient mouse myocytes, demonstrate that membrane blebbing in skeletal muscle myotubes in response to hypotonic shock requires dysferlin. PMID: 20558759
- Dysf deficiency led to increased expression of complement factors in muscle, while muscle-specific transgenic expression of dysf normalized the expression of complement factors and eliminated the dystrophic phenotype present in dysf-null mice. PMID: 21060153
- loss of dysferlin in endothelial cells resulted in deficient adhesion followed by growth arrest and impaired angiogenic response PMID: 20724702
- Data show that components of the inflammasome pathway are specifically up-regulated and activated in dysferlin-deficient but not in dystrophin-deficient and normal muscle, and suggest that muscle cells can actively participate in inflammasome formation. PMID: 20413686
- Our goal was to define a functional signature for skeletal muscles that lack dysferlin PMID: 20544921
- In the absence of dysferlin, cardiomyocyte membrane damage occurs and is localized to the intercalated disk and sarcoplasm PMID: 19875504
- Dysferlin-null myofibers can survive contraction-induced injury for at least 3 days but are subsequently eliminated by necrosis and inflammation. Myogenesis to replace lost fibers does not appear to be significantly compromised in dysferlin-null mice. PMID: 19923419
- Data show that restoration of dysferlin in skeletal muscle fibers is sufficient to rescue Dysf-deficient mice, although its mild overexpression does not appear to functionally enhance membrane repair in other models of muscular dystrophy. PMID: 19834057
- SJL/J mice show spontaneous myopathy and have a mutation in the dysferlin gene, a gene which is also mutated in human limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B (LGMD2B) PMID: 11891182
- Calcium-sensitive phospholipid binding properties of normal and mutant ferlin C2 domains. PMID: 11959863
- Dysferlin-null mice maintain a functional dystrophin-glycoprotein complex but nevertheless develop a progressive muscular dystrophy PMID: 12736685
- dysferlin binds to annexins A1 and A2 and has a role in Ca2+-dependent repair of sarcolemmal injury through a process of vesicle fusion PMID: 14506282
- Data show that affixin is a dysferlin binding protein that colocalizes with dysferlin at the sarcolemma of normal skeletal muscle. PMID: 15835269
- Overexpression of CAR may lead to physiological dysfunction by impairing sarcolemmal repair (through dysferlin deficiency). PMID: 17148677
- Study examined the degradation of normal and mutant (L1341P) dysferlin; mutant dysferlin aggregates in the ER-stimulated autophagosome formation to engulf them via activation of ER stress-eIF2alpha phosphorylation pathway. PMID: 17331981
- dysferlin-mediated membrane repair is important for maintaining membrane integrity of cardiomyocytes, particularly under conditions of mechanical stress PMID: 17607357
- Dysf was detected immunohistochemically in wild type mice, but not knockout mice. PMID: 17612291
- These data suggest that disturbances in dysferlin as well as Z-line proteins and transcription factors particularly under mechanical stress cause cardiomyopathy. PMID: 17828519
- Caveolin-1 or Caveolin-3, but not specific caveolin mutants, inhibit endocytosis of dysferlin through a clathrin-independent pathway colocalizing with internalized glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. PMID: 18096699
- Data show that dysferlin-null muscles produce higher contractile torque, and are equally susceptible to initial injury but recover from injury more slowly. PMID: 18815587
- Gadofluorine M-enhanced MR imaging may be of value in monitoring dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy disease progression in this animal model and could prove to be a useful tool in following the course of chronic muscle diseases in humans. PMID: 19001151
- Results suggest that dysferlin functions as a membrane fusion protein in the wound healing system of plasma membrane, and that the defect in dysferlin causes insufficient membrane fusion resulting in accumulation of vesicles. PMID: 19218742
- Muscle regeneration is attenuated in a mouse model of dysferlinopathy. PMID: 19286669
- The presence or absence of dysferlin does not have any consequences for the triggering or effector phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PMID: 19301206
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Defects in Dysf are the cause of a slowly progressive muscular dystrophy observed in SJL mice. It affects primarily the proximal muscles and it is inherited as autosomal recessive trait.
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane, sarcolemma; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cell membrane.
-
蛋白家族:Ferlin family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscles (at protein level). Expressed in skeletal muscle and heart. Also found in brain, liver and kidney.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:26903
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000080579
UniGene: Mm.220982
Most popular with customers
-
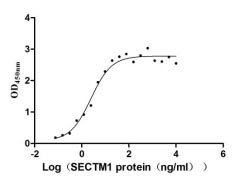
Recombinant Human Secreted and transmembrane protein 1 (SECTM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
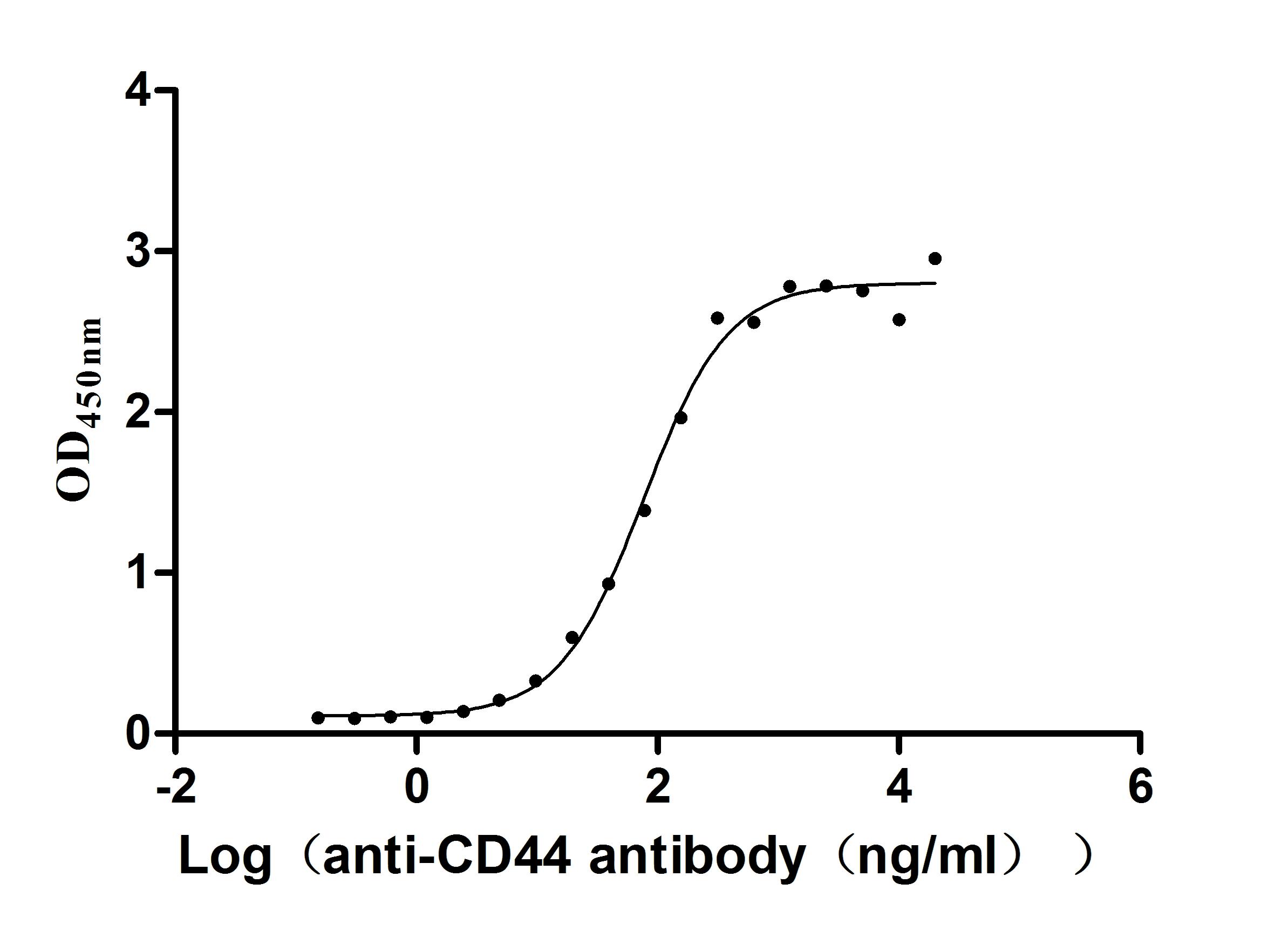
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
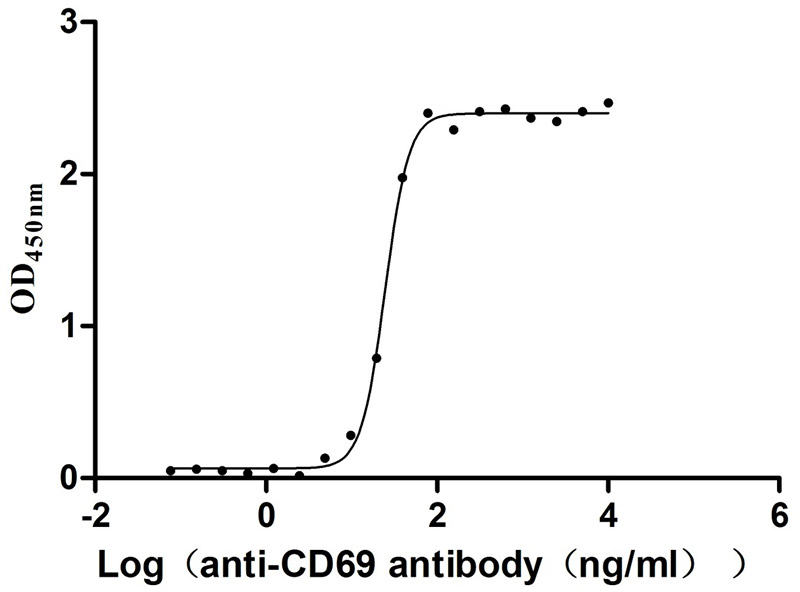
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
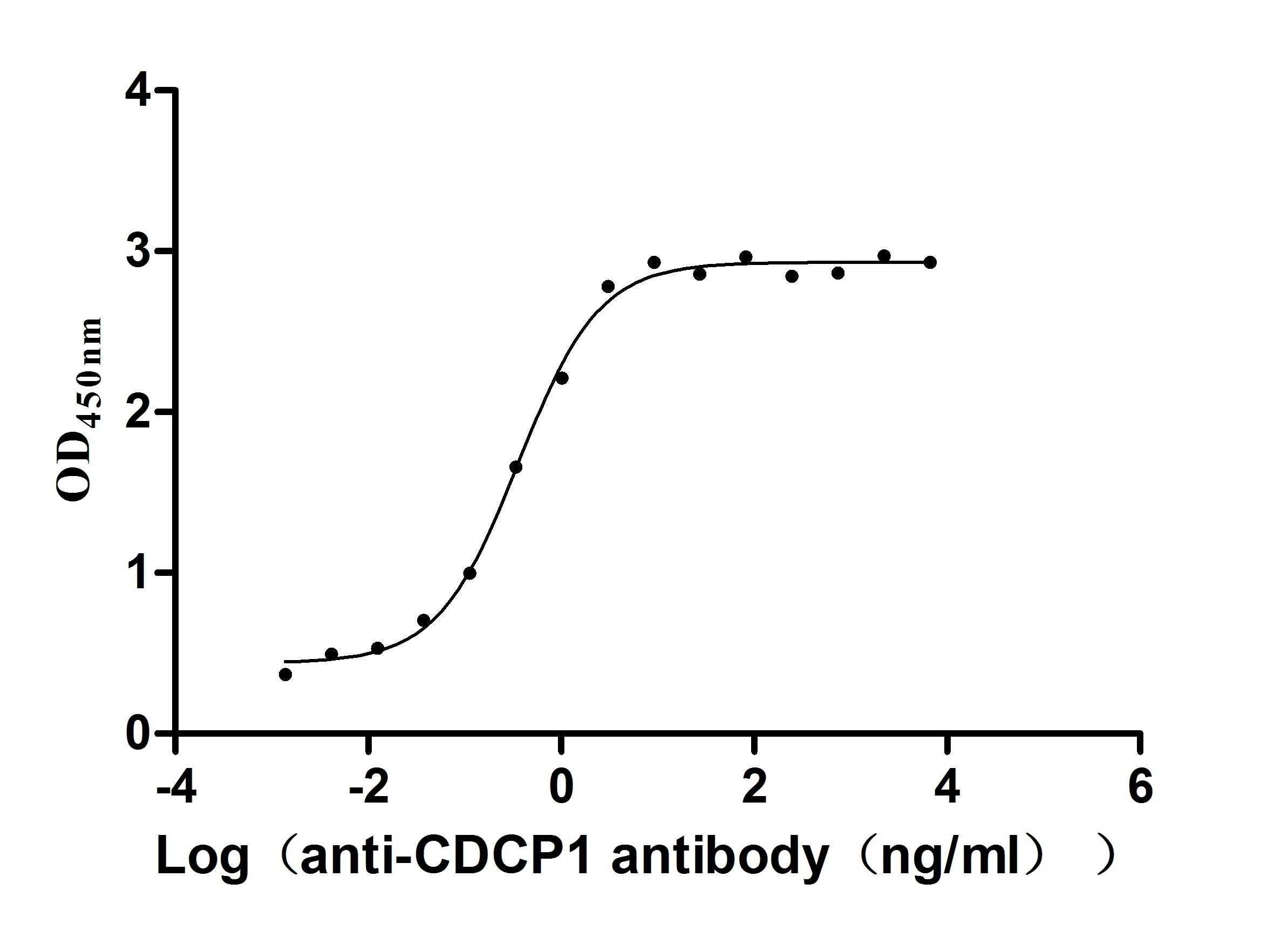
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
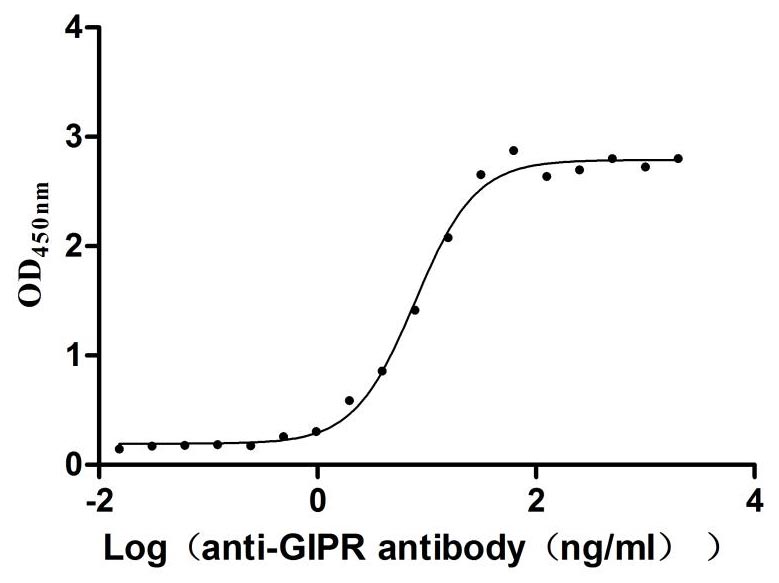
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
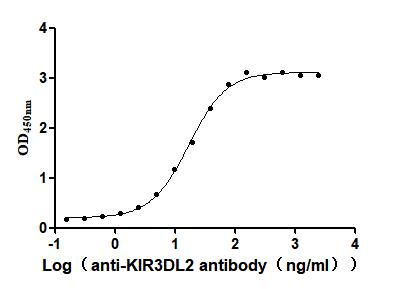
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
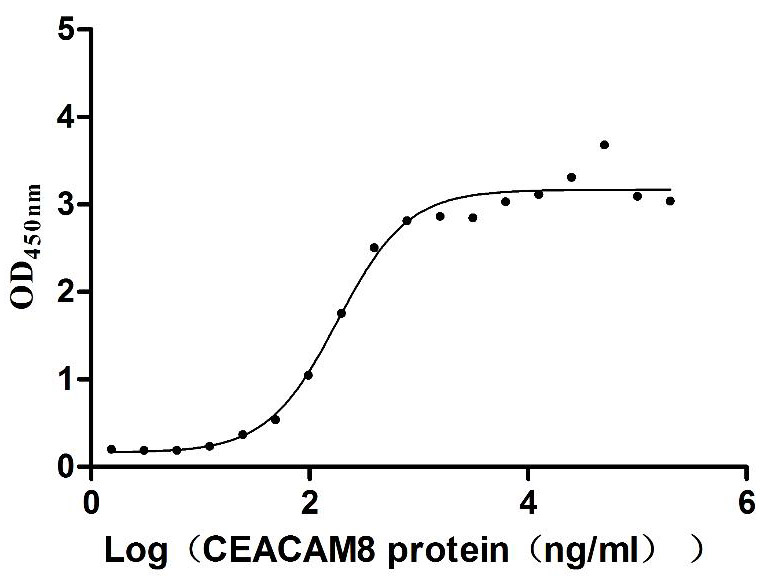
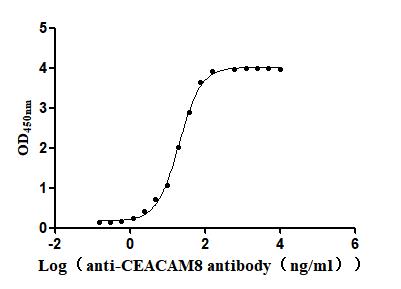
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)