Recombinant Mouse Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A (Pcyt1a)
-
中文名称:小鼠Pcyt1a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP017654MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pcyt1a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP017654MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pcyt1a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP017654MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pcyt1a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP017654MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pcyt1a重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP017654MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Pcyt1a
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Pcyt1a; Ctpct; Pcyt1; Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A; EC 2.7.7.15; CCT-alpha; CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase A; CCT A; CT A; Phosphorylcholine transferase A
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-367
-
氨基酸序列MDAQSSAKVN SRKRRKEAPG PNGATEEDGI PSKVQRCAVG LRQPAPFSDE IEVDFSKPYV RVTMEEACRG TPCERPVRVY ADGIFDLFHS GHARALMQAK NLFPNTYLIV GVCSDELTHN FKGFTVMNEN ERYDAVQHCR YVDEVVRNAP WTLTPEFLAE HRIDFVAHDD IPYSSAGSDD VYKHIKDAGM FAPTQRTEGI STSDIITRIV RDYDVYARRN LQRGYTAKEL NVSFINEKKY HLQERVDKVK KKVKDVEEKS KEFVQKVEEK SIDLIQKWEE KSREFIGSFL EMFGPEGALK HMLKEGKGRM LQAISPKQSP SSSPTHERSP SPSFRWPFSG KTSPSSSPAS LSRCRAVTCD ISEDEED
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Catalyzes the key rate-limiting step in the CDP-choline pathway for phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The findings reported herein indicate that palmitate-induced cisternal endoplasmic reticulum expansion is dependent on the activation of XBP-1/CCTalpha-mediated phospholipid accumulation in RAW 264.7 cells. PMID: 26174230
- Data suggest that CTalpha is an important factor in hepatocyte proliferation in vitro; however, liver regeneration, DNA synthesis, and phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis after partial hepatectomy are not impaired in CTalpha(-/-) knockout mice. PMID: 23074967
- CaMKI vies with CRM1/exportin 1 for access to a nuclear export signal, and assembly of a CaMKI-14-3-3 zeta-CCTalpha complex is a key effector mechanism that drives nuclear CCTalpha translocation. PMID: 22621903
- This study illustrates, for the first time, the connection between the acute accumulation of farnesylated prelamin A and involvement of CCT-alpha in generating an nucleoplasmic reticulum. PMID: 22223883
- 14-3-3zeta controls CCTalpha nuclear import in response to calcium signals, thereby regulating mammalian phospholipid synthesis. PMID: 20007511
- activation during the S phase of the cell cycle is mediated by the transcription factor Sp1 PMID: 12794070
- cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) phosphorylation of Sp1 activates CTalpha transcription during S phase. PMID: 15247247
- hepatic CTalpha has a role in regulating both hepatic and systemic lipid and lipoprotein metabolism PMID: 15331603
- ssion of CCTalpha increases surfactant PtdCho synthesis without affecting surfactant protein levels but disrupts glycogen metabolism in differentiating type II cells via its regulatory domain PMID: 15498769
- a physiologically relevant phosphorylation site and docking domain within CCTalpha serve as targets for ERKs, resulting in inhibition of surfactant synthesis PMID: 15788406
- CCTalpha expression is required for early embryonic development. PMID: 15798219
- SCD1 deficiency specifically increases CTP:choline cytidylyltransferase activity by promoting its translocation into membrane and enhances phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in liver PMID: 15829484
- CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CT) messenger RNA(mRNA) increased at S-M phase corresponding to an increase of Ets-1 protein mRNA and decrease of Net protein mRNA indicating that Net is an important endogenous repressor for CTalpha transcription PMID: 16157598
- These observations suggest a role for JNK kinases as negative regulators of phospholipid synthesis in murine lung epithelia. PMID: 16466687
- HDAC1 plays a critical role in CTalpha repression and that Sp1 and E2F may serve as key targets for HDAC1-mediated CTalpha repression in fibroblasts PMID: 16484221
- The studies demonstrate that developmental induction of surfactant phospholipid is due, at least in part, to transcriptional activation of the CCTalpha gene. PMID: 16645180
- CCTalpha was not required for the proliferation or differentiation of lung epithelia but was essential for the secretory component of phospholipid synthesis and critical for the proper formation of lamellar bodies and surfactant protein homeostasis. PMID: 17130238
- When knock-out hepatocytes were infected with an adenovirus expressing CTalpha, apoAI-dependent PC efflux returned partially, whereas cholesterol efflux and ABCA1 levels were not restored to normal levels. PMID: 18042552
- prostaglandin 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) inactivates CCTalpha by inducing generation of reactive oxidant species and the appearance of a cross-linked CCTalpha dimer in cells. PMID: 18614529
- CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase alpha is required for B-cell proliferation and class switch recombination. PMID: 19139091
- CCTalpha is monoubiquitinated at a molecular site (K(57)) juxtaposed near its nuclear localization signal, resulting in disruption of its interaction with importin-alpha, nuclear exclusion, and subsequent degradation within the lysosome. PMID: 19332566
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytosol. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Cytidylyltransferase family
-
组织特异性:Brain and liver (at protein level). Also found in heart, kidney, spleen, lung, skeletal muscle, ovary and testis.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:13026
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000078721
UniGene: Mm.98775
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
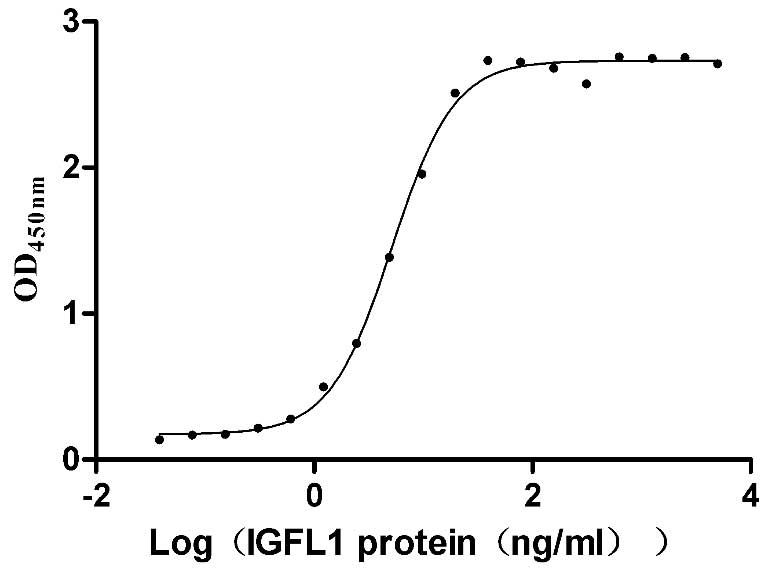
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Claudin-18 (Cldn18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
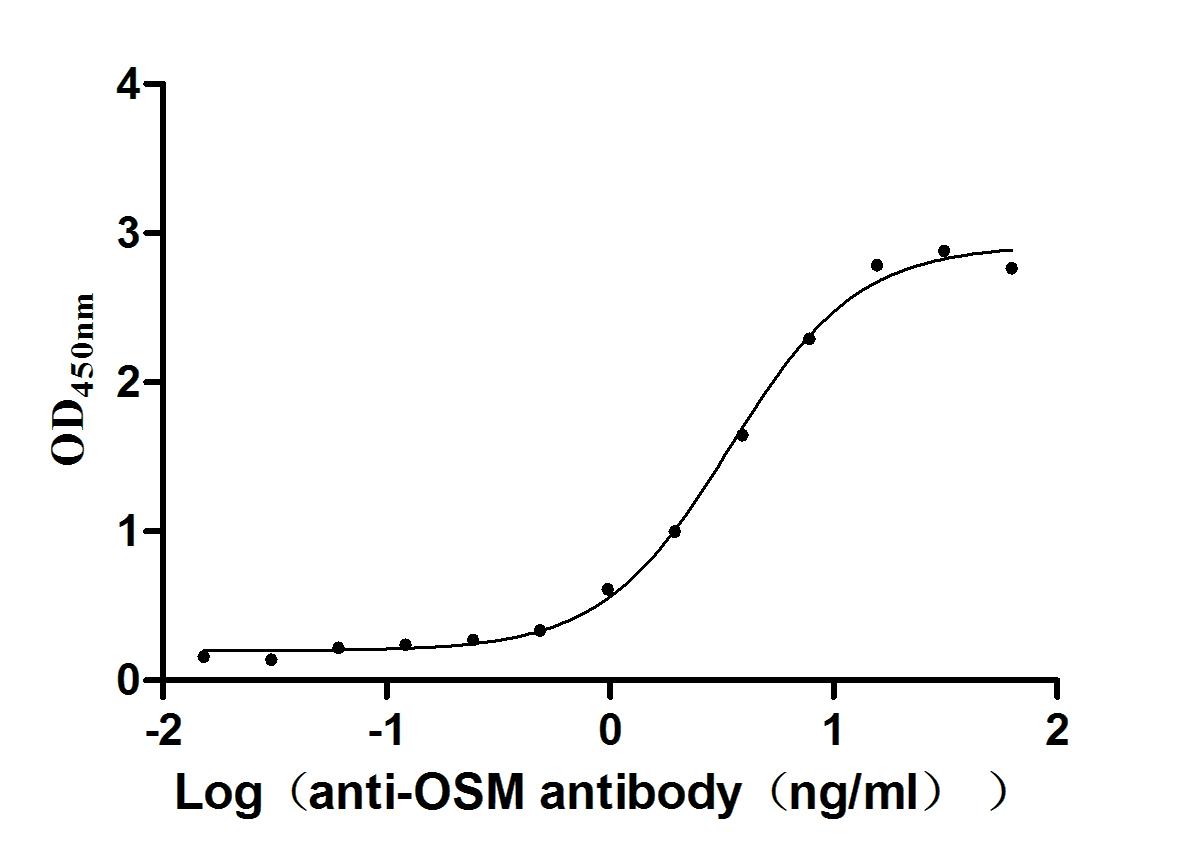
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
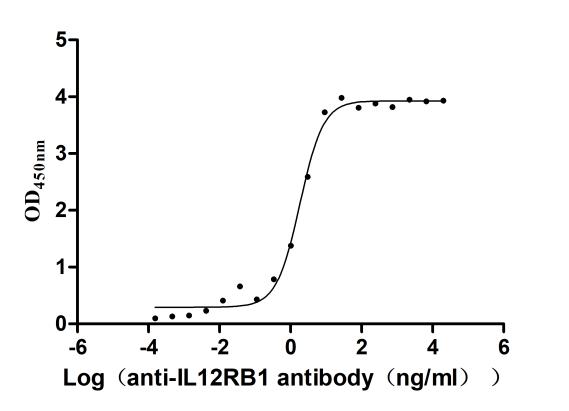
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
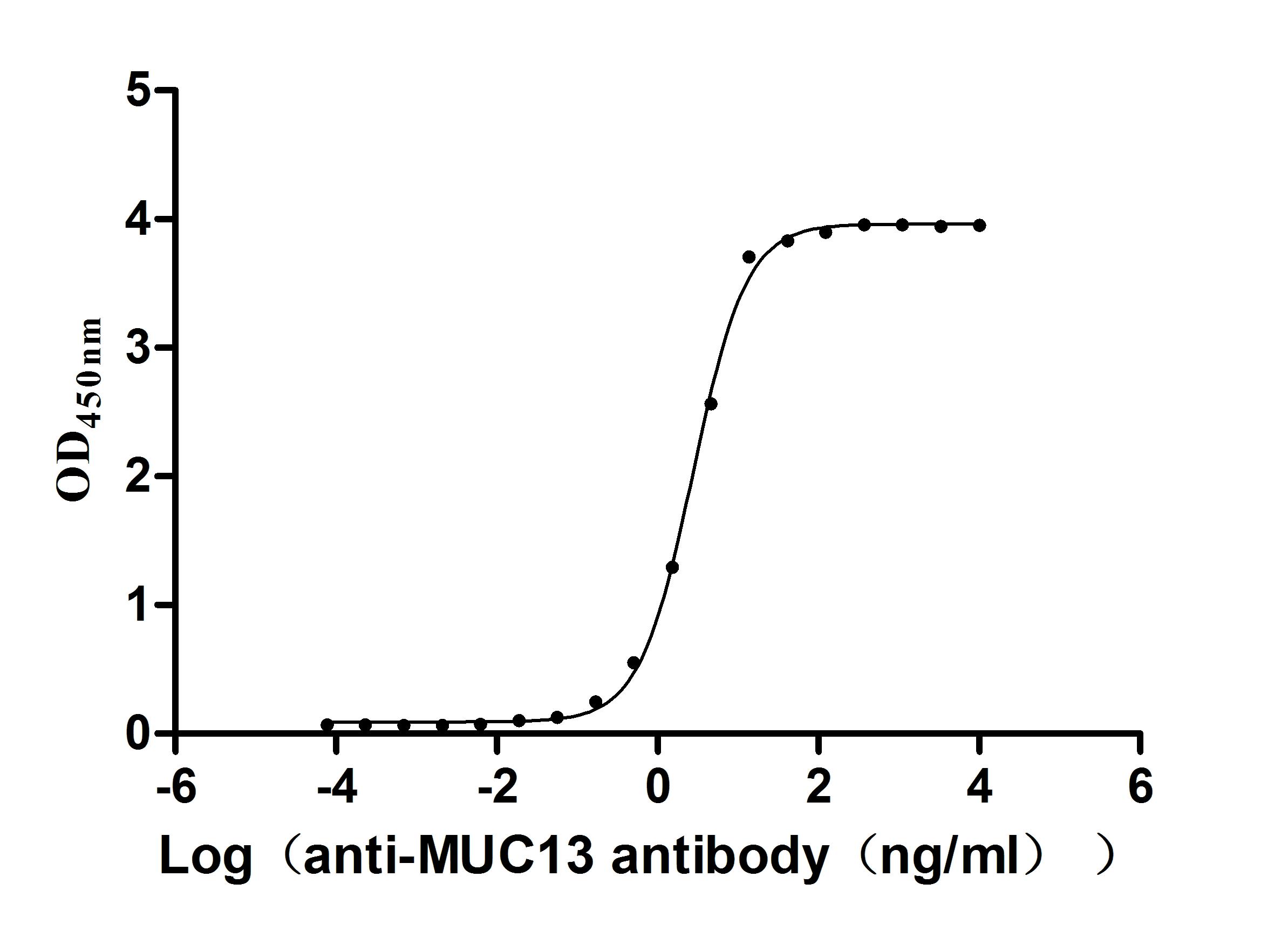
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)