Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (Cebpa)
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(Cebpa),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP005180MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(Cebpa),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP005180MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(Cebpa),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP005180MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(Cebpa),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP005180MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha(Cebpa),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP005180MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Cebpa
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cebpa; Cebp; CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; C/EBP alpha
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-359
-
氨基酸序列MESADFYEVE PRPPMSSHLQ SPPHAPSNAA FGFPRGAGPA PPPAPPAAPE PLGGICEHET SIDISAYIDP AAFNDEFLAD LFQHSRQQEK AKAAAGPAGG GGDFDYPGAP AGPGGAVMSA GAHGPPPGYG CAAAGYLDGR LEPLYERVGA PALRPLVIKQ EPREEDEAKQ LALAGLFPYQ PPPPPPPPHP HASPAHLAAP HLQFQIAHCG QTTMHLQPGH PTPPPTPVPS PHAAPALGAA GLPGPGSALK GLAGAHPDLR TGGGGGGSGA GAGKAKKSVD KNSNEYRVRR ERNNIAVRKS RDKAKQRNVE TQQKVLELTS DNDRLRKRVE QLSRELDTLR GIFRQLPESS LVKAMGNCA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that coordinates proliferation arrest and the differentiation of myeloid progenitors, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and cells of the lung and the placenta. Binds directly to the consensus DNA sequence 5'-TCan act as dominant-negative. Binds DNA and have transctivation activity, even if much less efficiently than isoform 2. Does not inhibit cell proliferation.; Directly and specifically enhances ribosomal DNA transcription interacting with RNA polymerase I-specific cofactors and inducing histone acetylation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- findings indicate that C/EBPalpha is a stronger inducer of osteoclast differentiation than c-Fos, partly via C/EBPalpha regulation by the RANK (535)IVVY(538) motif PMID: 29122885
- The earliest steps of adult hepatocellular arcinoma and aggressive pediatric liver cancer have identical features that include conversion of the tumor suppressor C/EBPalpha into an oncogenic isoform, which further creates preneoplastic foci where hepatocytes dedifferentiate into cancer cells, giving rise to liver cancer PMID: 29159818
- C/EBP-alpha mediates anti-inflammatory effects in podocytes PMID: 27644413
- the extracts dramatically attenuated the levels of adipogenic transcriptional factors, including CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPa), CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPb), and gamma receptors by peroxisome proliferators (PPARg), during adipogenesis PMID: 28604636
- shown that ectopic miR-155 expression and loss of C/EBPA expression in myeloid progenitor cells cooperate in transformation of HSPCs toward AML in the absence of FLT3-ITD PMID: 27363282
- Data demonstrate the importance of a controlled balance between C/EBPalpha and miR-182 for the maintenance of healthy granulopoiesis. PMID: 28663557
- Functional characterization of C/EBPa and C/EBPb proteomes suggests they can regulate novel pathways. PMID: 27746211
- results indicate that JMJD2B regulates PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha during adipogenesis PMID: 28060835
- A single +42-kb enhancer is essential for CEBPA expression in myeloid cells only. PMID: 26966090
- these data indicate that CycC activates adipogenesis in part by stimulating the transcriptional activity of C/EBPalpha. PMID: 28351837
- Taken together, these findings demonstrate that artesunate inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipoytes through the reduced expression and/or phosphorylation levels of C/EBP-alpha, PPAR-gamma, FAS, perilipin A, and STAT-3. PMID: 27109481
- we show that SIX1 binds to adipogenic and brown marker genes and interacts with C/EBPa, C/EBPb and EBF2, suggesting their functional cooperation during adipogenesis. PMID: 27923061
- these results indicate that C/EBPalpha functions throughout osteoclastogenesis as well as in Osteoclast function. This study provides additional understanding of the roles of C/EBPalpha in Osteoclast biology. PMID: 27129246
- the DNA sequences to which EVI1 binds at +35 and +37 kb and show that mutation of one of these releases Cebpa from EVI1-induced suppression. PMID: 27129260
- The efficient repression of E2F dependent S-phase genes and the activation of differentiation genes reside in the balanced DNA binding capacity of C/EBP alpha. PMID: 27131901
- Cebpa enhancers and silencers in a transcriptional model have roles in hematopoietic lineage specification PMID: 26945717
- Data show that CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein-alpha (C/EBPalpha) directly regulates Kruppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) expression and increasing the levels of histone demethylase Lsd1 and transcription factor Brd4 in B cell. PMID: 26974661
- The findings demonstrate a critical role for the +37 kb Cebpa enhancer for hematopoietic-specific Cebpa expression, with enhancer deletion leading to impaired myelopoiesis and potentially preleukemic progenitor expansion. PMID: 26937964
- Data indicate that miR-25 is a novel negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation and it suppressed 3T3-L1 adipogenesis by targeting KLF4 and C/EBPalpha, which provides novel insights into the molecular mechanism of miRNA-mediated cellular differentiation. PMID: 25923408
- MYB and C/EBPalpha activities are inter-dependent in controlling Flt3 expression to influence lineage commitment of multipotential progenitors. PMID: 26382271
- Data indicate that white adipose tissue from IgE receptor FcR1-deficient Fcer1a(-/-) mice showed an increased expression of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein-alpha (C-EBPalpha) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). PMID: 26295369
- miR-223 regulates adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation through a novel C/EBPs/miR-223/FGFR2 regulatory feedback loop. PMID: 25641499
- Data (including data from studies in transgenic/mutant mice) suggest Cebpa (CCAAT-enhancer binding protein alpha) in myeloid cells is down-regulated in type 2 diabetes resulting in poor maturation of Gr-1+ (chemokine receptor) myeloid cells. PMID: 26324181
- C/EBPalpha is required for the increased lipogenesis. C/EBPalpha plays a role in mediating the lipogenic effects of hepatic Trib1 deletion. PMID: 26348894
- IRF8 not only bestows monocyte and DC differentiation potential upon mononuclear phagocyte progenitors but also restrains these progenitors from differentiating into neutrophils in a process involving C-EBPalpha PMID: 25236377
- Endogenous prostaglandin E2 potentiates anti-inflammatory phenotype of macrophage through the CREB-C/EBP-beta cascade. PMID: 26118414
- CEBPA, CEBPB and CEBPD regulate proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes. PMID: 25749148
- Cebpa is a key regulator within the apoptotic network activated in pancreatic beta cells during insulitis, and Arl6ip5, Tnfrsf10b, Traf2, and Ubc are key executioners of this program. PMID: 24943845
- results suggest that dysregulation of Egr-1/C/EBPa on glucagon stimulation may provide an alternative mechanistic explanation for type 2 diabetes PMID: 25438063
- The structural differences between C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta that may account for the difference in binding 5hmC in the 8-mer TGAC|GCAA are explored. PMID: 25779641
- HDAC1 suppresses glucocorticoid receptor-potentiated preadipocyte differentiation by decreasing CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha and Ppargamma expression levels at the onset of differentiation. PMID: 25203139
- The expression of C/EBPalpha in liver was found to be affected by sex-dependent growth hormone secretion. PMID: 25451687
- Our study thus demonstrates that C/EBPalpha restricts IFN-gamma expression in T cells to allow proper class switching by B cells. PMID: 25398328
- Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides suppressed the mRNA expressions of SREBP-1c, C/EBPa and PPARg in mice. PMID: 24847504
- effect of C/EBPalpha on mast cells PMID: 25447519
- data shows that the substitution of C/EBPalpha serine 248 to alanine favors the selection of the megakaryocytic/erythroid lineage over the monocytic/granulocytic compartment PMID: 22715416
- These findings indicate that Suv39h1 enhances AP-2alpha-mediated transcriptional repression of C/EBPalpha in an epigenetic manner and further inhibits adipocyte differentiation. PMID: 24732798
- results suggest a previously unidentified role for C/EBPalpha in maintaining the proliferation required for Hoxa9/Meis1-mediated leukemogenesis PMID: 24958854
- C/EBPalpha promotes immunosenescence and efficiently discard the potential of using C/EBPalpha as a target for the alleviation of ageing/cancer associated immunosenescence. PMID: 24404186
- Nonparenchymal cell development, including bile and vascular systems, requires normal maturation of the liver parenchyma through C/EBPa expression in hepatocytes PMID: 23864446
- C/EBPalpha is required for macrophage activation, which plays an important role in maintaining skeletal muscle energy metabolism. PMID: 24691027
- our results show that C/EBPalpha is a key regulator of HSC biology, which influences the epigenetic landscape of HSCs in order to balance different cell fate options. PMID: 24415956
- we identify the contribution of dysregulated C/EBPalpha and E2F1 to elevated Trib2 expression and leukemic cell survival PMID: 24516045
- Plasma leptin level correlates to increased C/EBP-alpha and VCAM-1 production in chondrocytes from obese mice. PMID: 24582795
- This is associated with extensive C/EBPalpha-mediated reprogramming of PPARgamma binding. PMID: 24379442
- Data indicate that age-associated alterations of C-EBPalpha and C-EBPbeta proteins cause severe liver injury after CCl4 treatments. PMID: 24273171
- Data indicate that downregulation of ATF5 inhibits adipogenesis through C/EBPalpha by impairing the interaction with p300-C/EBPbeta. PMID: 24216764
- Anti-adipogenesis via modulation of mouse CEBPalpha and SREBP1C gene expression by 2',6'-O-acetylsalicortin, extracted from Salix pseudo-lasiogyne twigs. PMID: 23999723
- The expression level of adipocyte regulator C/EBPalpha is significantly upregulated in Dexamethasone-induced osteoporotic bone marrow stromal cells. PMID: 24091675
- Deletion of Cebpa rendered murine hematopoietic progenitors completely resistant to MLL-ENL-induced leukemic transformation, whereas C/EBPalpha was dispensable in already established AMLs. PMID: 24367003
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.; [Isoform 4]: Nucleus, nucleolus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, C/EBP subfamily
-
组织特异性:Isoform 2 and isoform 3 are expressed in adipose tissue and liver (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:12606
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000096129
UniGene: Mm.349667
Most popular with customers
-
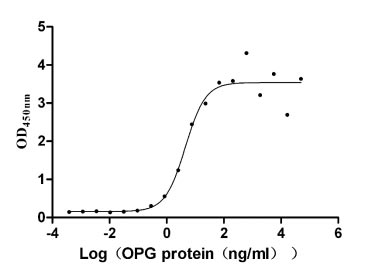
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
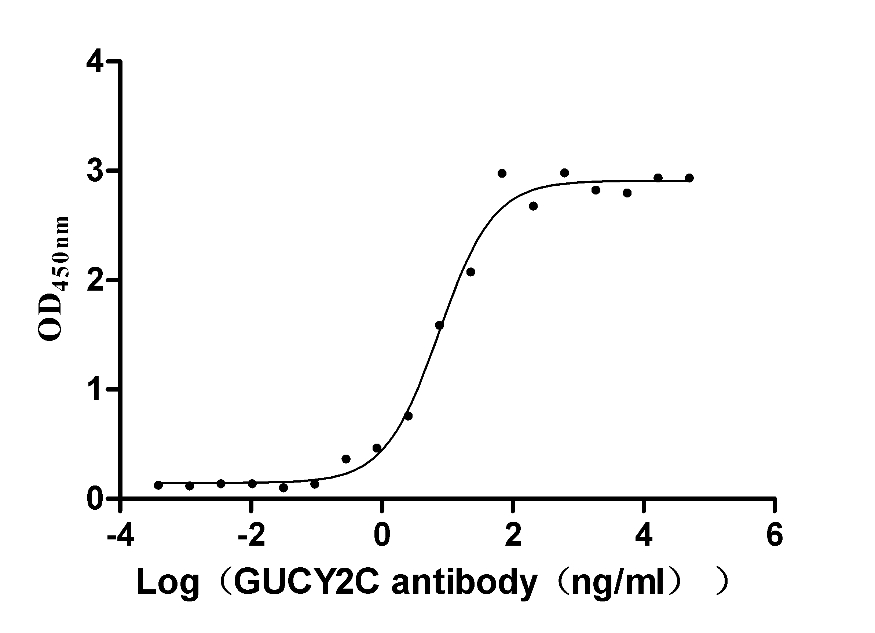
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
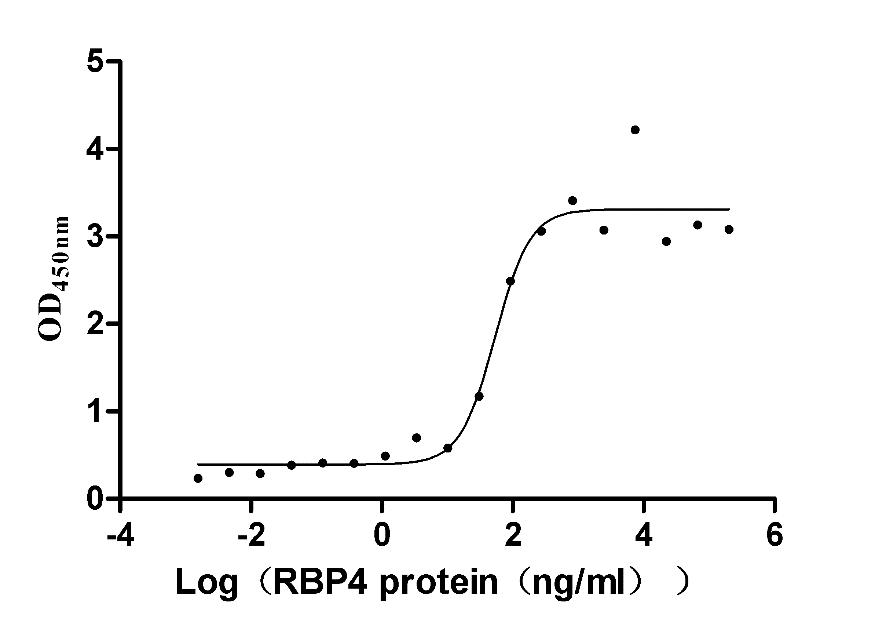
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)