Recombinant Mouse 5-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 (Prkaa1), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Prkaa1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP707843MO1
-
规格:¥2,328
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
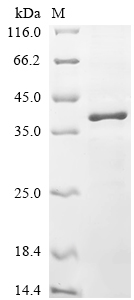
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus(Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:39.8 kDa
-
表达区域:1-312aa
-
氨基酸序列MRRLSSWRKMATAEKQKHDGRVKIGHYILGDTLGVGTFGKVKVGKHELTGHKVAVKILNRQKIRSLDVVGKIRREIQNLKLFRHPHIIKLYQVISTPSDIFMVMEYVSGGELFDYICKNGRLDEKESRRLFQQILSGVDYCHRHMVVHRDLKPENVLLDAHMNAKIADFGLSNMMSDGEFLRTSCGSPNYAAPEVISGRLYAGPEVDIWSSGVILYALLCGTLPFDDDHVPTLFKKICDGIFYTPQYLNPSVISLLKHMLQVDPMKRAAIKDIREHEWFKQDLPKYLFPEDPSYSSTMIDDEALKEVCEKFE
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose.
-
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism. In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation. AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators. Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton; probably by indirectly activating myosin. Regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating lipid metabolic enzymes such as ACACA, ACACB, GYS1, HMGCR and LIPE; regulates fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACACA and ACACB) and hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) enzymes, respectively. Regulates insulin-signaling and glycolysis by phosphorylating IRS1, PFKFB2 and PFKFB3. AMPK stimulates glucose uptake in muscle by increasing the translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, possibly by mediating phosphorylation of TBC1D4/AS160. Regulates transcription and chromatin structure by phosphorylating transcription regulators involved in energy metabolism such as CRTC2/TORC2, FOXO3, histone H2B, HDAC5, MEF2C, MLXIPL/ChREBP, EP300, HNF4A, p53/TP53, SREBF1, SREBF2 and PPARGC1A. Acts as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis in liver by phosphorylating CRTC2/TORC2, leading to CRTC2/TORC2 sequestration in the cytoplasm. In response to stress, phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of histone H2B (H2BS36ph), leading to promote transcription. Acts as a key regulator of cell growth and proliferation by phosphorylating TSC2, RPTOR and ATG1/ULK1: in response to nutrient limitation, negatively regulates the mTORC1 complex by phosphorylating RPTOR component of the mTORC1 complex and by phosphorylating and activating TSC2. In response to nutrient limitation, promotes autophagy by phosphorylating and activating ATG1/ULK1. In that process also activates WDR45. In response to nutrient limitation, phosphorylates transcription factor FOXO3 promoting FOXO3 mitochondrial import. AMPK also acts as a regulator of circadian rhythm by mediating phosphorylation of CRY1, leading to destabilize it. May regulate the Wnt signaling pathway by phosphorylating CTNNB1, leading to stabilize it. Also has tau-protein kinase activity: in response to amyloid beta A4 protein (APP) exposure, activated by CAMKK2, leading to phosphorylation of MAPT/TAU; however the relevance of such data remains unclear in vivo. Also phosphorylates CFTR, EEF2K, KLC1, NOS3 and SLC12A1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- AMPK may be a critical regulator of fibroblast activation through regulation of cytoskeleton dynamics and myocardin-related transcription factor-A nuclear translocation, promoting renal fibrosis. PMID: 28739141
- these findings identify a previously uncharacterized role of folate/DHFR/AMPKalpha axis in regulating oligodendrocyte survival and myelination. PMID: 28496133
- CNR1 modulates AMPKalpha to influence insulin resistance and endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by palmitate. PMID: 29909009
- Inhibiting the LTB4/BLT1 signaling pathway via AMPK activation is a potential treatment strategy for septic cardiac dysfunction because it efficiently attenuates cardiac apoptosis, which may occur via the inhibition of inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction. PMID: 28290498
- Thus, these findings suggest that AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2 activity in chondrocytes is important in maintaining joint homeostasis and osteoarthritis development. PMID: 28225087
- At molecular analysis, there was a time-dependent nuclear translocation of the active phosphorylated catalytic subunits AMPKalpha1/alpha2 and PGC-1alpha in young, but not in mature, mice after sepsis. PMID: 28974562
- Low AMPK expression is associated with Acute respiratory distress syndrome. PMID: 30171880
- AMPK stabilizes FOXO3 and suggest a role in the first initiation step of mitochondrial segregation in muscle cells. PMID: 29580989
- these results demonstrate that AMPK downregulation is not a triggering factor in fatty liver development but in contrast, establish the therapeutic impact of pharmacological AMPK re-activation in the treatment of fatty liver disease. PMID: 29343420
- Prkaa1 deletion activates skeletal muscle mTOR signalling, which has a central role in lipid metabolism and mitochondrial oxidation. Collectively, our study provides new insights into the role of Prkaa1 in skeletal muscle PMID: 29288408
- our findings suggest that the role of Cx43 in response to H2O2 stress is dependent on the activation of AMPK signaling pathways and regulates ROS production and cell necrosis. PMID: 29279848
- activation of AMPK at early stage of adipogenesis is involved in the anti-adipogenesis effect of Red Pepper Seed extract. PMID: 29316805
- Study indicate that the alpha 2 and alpha 1 subunits of AMPK have several functional differences, with alpha 2 conferring stronger osteogenic potential and a weaker ability to induce osteoblasts-associated osteoclastogenesis in MC3T3-E1 cells as well as conferring a lower adipogenic potential to 3T3-L1 cells. PMID: 27600021
- Over-expression of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) promoted the apoptosis of mesangial cells from the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) mice. PMID: 29268850
- AMPK-PGC-1a control of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulates Warburg metabolism. PMID: 28978464
- AMPKalpha1 has a critical role in maintaining the anticontractile actions of perivascular adipose tissue; an effect independent of the endothelium but likely mediated through altered adiponectin secretion or sensitivity. PMID: 27668984
- Ampk-/- mice displayed retardation of postnatal bone development, although bone deformity was not observed at birth. PMID: 29126229
- Cardiac SUR2A levels were significantly increased while Kir6.2 levels were not affected. Hypoxia did not induce phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) or protein kinase B (Akt), but triggered phosphorylation of AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK). AICAR, an activator of AMPK, increased the level of SUR2A in H9c2 cells. We conclude that oxygen increases SUR2A level by activating AMPK. PMID: 28121062
- This study provides new insights into the control of eEF2K by AMPK. PMID: 28502587
- These data indicate that a reduction in AMPK disrupts cellular metabolism in both progenitors and differentiated placental trophoblasts. PMID: 28335680
- Targeted activation of AMPK by GSK621 ameliorates H2O2-induced osteoblast cell injuries. PMID: 28060740
- Sestrin 1 targets at the AMPK/mTORC1/autophagy pathway to inhibit cardiac hypertrophy by interaction with AMPK which is responsible for autophagy regulation. Taken together, our data indicate that Sestrin 1 regulates AMPK/mTORC1/autophagy axis to attenuate cardiac hypertrophy. PMID: 28181410
- AMPK enhances intestinal barrier function and epithelial differentiation via promoting CDX2 expression, which is partially mediated by altered histone modifications in the Cdx2 promoter. PMID: 28234358
- our results elucidate a previously unrecognized role of AMPKalpha1 deletion in loss of contact inhibition of cellular proliferation and angiogenesis PMID: 27449088
- AMPK and Sirt2 control compensatory glucose uptake in metabolically arrested mitochondria. PMID: 27909079
- results indicate that liver AMPKalpha1alpha2 is required for maintaining glucose homeostasis during an acute bout of exercise. PMID: 29038293
- AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulates autophagy by phosphorylating BECN1 at Thr388 PMID: 27304906
- activation of AMPK might be a stress response of host cells to restrict virus production through promotion of autophagic degradation PMID: 27305174
- AMPK regulates T cell survival and function. Demonstrate AMPK-dependent and independent rolesof AICAR/Compound C in regulating T cell responses. PMID: 27177226
- AMPK was sufficient to stimulate osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 cells and inhibit adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through the AMPK-Gfi1-OPN axis. PMID: 27283242
- AMPK activation reduces the formation of atheromata-inducing macrophages in ApoE(-/-)-deficient mice by inhibiting expression of Ccr2, thereby preventing the Ccr2-mediated migration of Ly6C(hi) monocytes from the bone marrow. PMID: 28235712
- AMPK activation inhibited IL-1beta-stimulated CXCL10 secretion, associated with reduced interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase-4 (IRAK4) phosphorylation. PMID: 27840174
- Findings indicate that the energy-sensing LKB1-AMPK pathway regulates IGF1 secretion in mouse primary hepatocytes, which in turn regulates activation of the IGF1R-PKB pathway. PMID: 28500773
- These data suggest that nutrient availability dictates the mode of division and that LKB1-AMPK mediates this nutrient-driven effect on intestinal epithelial stem cell proliferation. PMID: 28766983
- Myeloid-Restricted AMPKalpha1 Promotes Host Immunity and Protects against IL-12/23p40-Dependent Lung Injury during Hookworm Infection PMID: 27183598
- Data suggest that Il4 (usually released from helper T-cells) induces Cox1 in macrophages at post-transcriptional level; activation of Ampk (catalytic subunit Prkaa1) by metformin blocks Il4-dependent induction of Cox1 and blocks macrophage polarization/activation. (Il4 = interleukin-4; Cox1 = cyclooxygenase 1; Ampk = AMP-activated protein kinase) PMID: 28684424
- The metformin-rescued P23H rhodopsin was still intrinsically unstable and led to increased structural instability of the rod outer segments. These data suggest that improving the traffic of misfolding rhodopsin mutants is unlikely to be a practical therapy, but also highlights the potential of altering translation through AMPK to improve protein function in other protein misfolding diseases PMID: 28065882
- Mechanistically, miR-499 directly targets Fnip1, an AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-interacting protein that negatively regulates AMPK, a known activator of PGC-1alpha. This miR-499/Fnip1/AMPK circuit can serve as a mechanism to couple muscle fiber type and mitochondrial function. PMID: 27506764
- dopamine is coupled to AMPK activation, which provides a substantial anti-inflammatory and bioenergetic advantage and reduces the severity of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. PMID: 27733575
- AMPKalpha1 deficiency suppresses brown adipogenesis in favor of fibrogenesis during brown adipose tissue development. PMID: 28668388
- AMPK-dependent metabolic repair mechanisms are important for mitigating lung injury. PMID: 28085510
- these data demonstrated that LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway activation improved the survival of diabetic mice complicated with endotoxemia. Thus, LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway may serve as a potentially useful therapeutic target for severe infection in diabetic patients. PMID: 28628912
- We confirmed that procyanidins suppressed acute hyperglycemia with an oral glucose tolerance test in a dose-dependent manner.procyanidins, especially cinnamtannin A2, significantly ameliorate postprandial hyperglycemia at least in part by promoting GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane by activating both insulin- and AMPK-signaling pathways. PMID: 27598258
- These findings demonstrate that the AMPK-TBC1D1 signaling nexus interacts with the PKB-mTOR pathway via IGF1 secretion, which consequently controls expression of lipogenic genes in the adipose tissue PMID: 27307439
- AMPKa1 deficiency impairs autophagy-mediated monocyte differentiation and decreases monocyte/macrophage survival PMID: 28330873
- The s identified lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as a new functional target of AMPKalpha1. PMID: 28515121
- AMPKalpha1 knockout (KO) mice exhibit normal renal sodium handling and a moderate antidiuretic state. This is accompanied by higher urinary aldosterone excretion rates and reduced blood pressure. Plasma volume, however, was found to be increased compared with wild-type mice. PMID: 28179232
- AMPK in adipocytes is vital for maintaining mitochondrial integrity. PMID: 27411013
- Study demonstrated that adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase alpha 1 (AMPKalpha1) is imperative for maintaining normal nociception, and mice deficient for AMPKalpha1 exhibit mechanical allodynia. PMID: 27058143
- The data suggest that AMPK is not required for the regulation of the intermediate filament interaction with CPT-I during exercise. PMID: 27941154
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=In response to stress, recruited by p53/TP53 to specific promoters.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family, SNF1 subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:105787
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000063166
UniGene: Mm.207004
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)










