Recombinant JC polyomavirus Major capsid protein VP1
-
货号:CSB-YP355946JAK
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP355946JAK
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP355946JAK-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP355946JAK
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP355946JAK
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
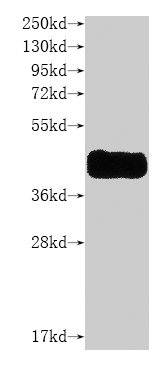
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:N/A
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:; Major capsid protein VP1; Major structural protein VP1
-
种属:JC polyomavirus (JCPyV) (JCV)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-354
-
氨基酸序列MAPTKRKGER KDPVQVPKLL IRGGVEVLEV KTGVDSITEV ECFLTPEMGD PDEHLRGFSK SISISDTFES DSPNRDMLPC YSVARIPLPN LNEDLTCGNI LMWEAVTLKT EVIGVTSLMN VHSNGQATHD NGAGKPVQGT SFHFFSVGGE ALELQGVLFN YRTKYPDGTI FPKNATVQSQ VMNTEHKAYL DKNKAYPVEC WVPDPTRNEN TRYFGTLTGG ENVPPVLHIT NTATTVLLDE FGVGPLCKGD NLYLSAVDVC GMFTNRSGSQ QWRGLSRYFK VQLRKRRVKN PYPISFLLTD LINRRTPRVD GQPMYGMDAQ VEEVRVFEGT EELPGDPDMM RYVDKYGQLQ TKML
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Forms an icosahedral capsid with a T=7 symmetry and a 40 nm diameter. The capsid is composed of 72 pentamers linked to each other by disulfide bonds and associated with VP2 or VP3 proteins. Interacts with a N-linked glycoprotein containing terminal alpha(2-6)-linked sialic acids on the cell surface to provide virion attachment to target cell. The serotonergic receptor 5HT2AR also acts as a cellular receptor for JCV on human glial cells. Once attached, the virions enter predominantly by a ligand-inducible clathrin-dependent pathway and traffic to the ER. Inside the endoplasmic reticulum, the protein folding machinery isomerizes VP1 interpentamer disulfide bonds, thereby triggering initial uncoating. Next, the virion uses the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation machinery to probably translocate in the cytosol before reaching the nucleus. Nuclear entry of the viral DNA involves the selective exposure and importin recognition of VP2/Vp3 nuclear localization signal. In late phase of infection, neo-synthesized VP1 encapsulates replicated genomic DNA at nuclear domains called promyelocytic leukemia (PML) bodies, and participates in rearranging nucleosomes around the viral DNA.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- All viral populations were characterized by rearrangements within the noncoding regulatory region (NCCR) and 1 point mutation, S267L in the VP1 gene, suggestive of neurotropic strains. One patient with Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) had a single neurotropic strain with rearranged noncoding regulatory region (NCCR), and 1 patient had a single strain with small NCCR alterations. PMID: 28453853
- found that deletion of nucleotides 376-396 results in decreased levels of viral DNA replication and a lack of VP1 expression. PMID: 25142442
- Synthetic antibodies and peptides recognizing progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy-specific point mutations in polyomavirus JC capsid viral protein 1. PMID: 25879139
- These data show that capsid proteins of Mad-1 and WT3 JC Polyomavirus can both engage alpha2,6-linked sialic acid on the lactoseries tetrasaccharide c as well as multiple sialylated gangliosides. PMID: 25855729
- This study demonstrated that the 5-fold VP1 pore is an important structural feature of JC polyomavirus and that minor modifications to this structure have significant impacts on infectious entry. PMID: 25609820
- C80 of JCV Vp1 is required for Vp1 stability and pentamer formation, and C247 is involved in capsid assembly in the nucleus PMID: 24130786
- These results demonstrate that viruses from progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy patients with single point mutations in VP1 disrupt binding to sialic acid motifs and render these viruses noninfectious. PMID: 23760462
- VP1 C terminus mutants were replication-competent and remains stable overtime in vitro. PMID: 21940415
- mutations of JCV VP1 might favor progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy onset; VP1 substitutions may favor JCV brain invasion by abrogation of sialic acid binding with peripheral cells while maintaining sialic acid-independent binding with brain cells PMID: 21628664
- model of the interaction between VP1 and the sialic acid component of the human JCV receptor PMID: 15347668
- frequent amino acid substitutions in the outer loops of VP1 of JCPyV associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PMID: 15958683
- A unique deletion was found in the C terminus may be instrumental in facilitating entry or replication of JCV into granule cell neurons. PMID: 16894191
- A possible role for merkel cells Polyomavirus as an etiologic agent in the carcinogenesis of merkel cell carcinoma. PMID: 18593898
- JCV VP1 loop mutations are associated with a favorable prognosis for PML PMID: 19043822
- several amino acids on surface of VP1 display accelerated evolution in viral sequences isolated from progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy patients but not healthy subjects; evidence that some mutations are involved in binding of sialic acid PMID: 19197354
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Virion. Host nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Polyomaviruses coat protein VP1 family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: vg:1489518
Most popular with customers
-
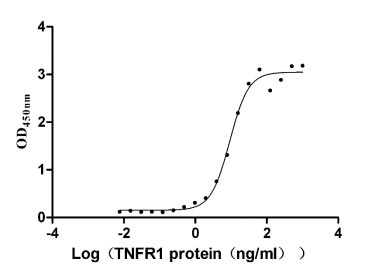
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
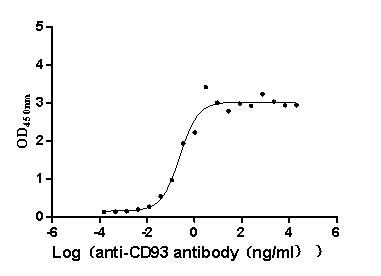
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
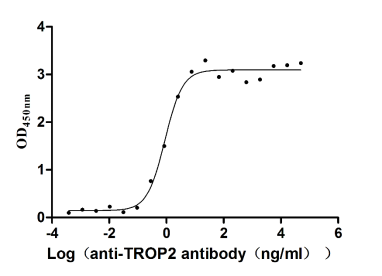
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
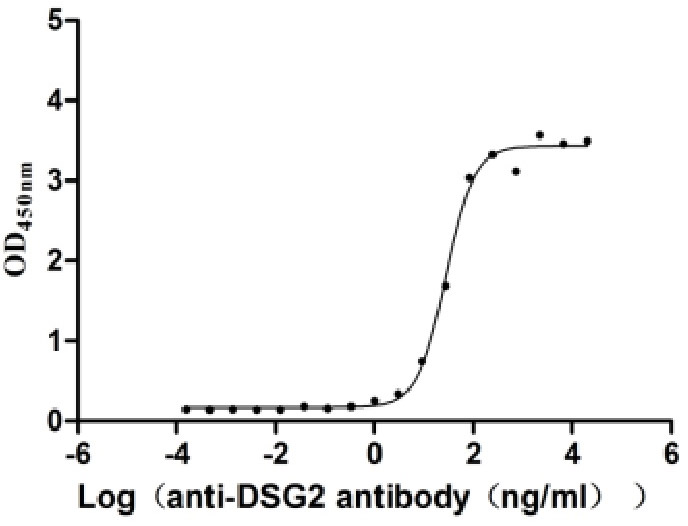
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
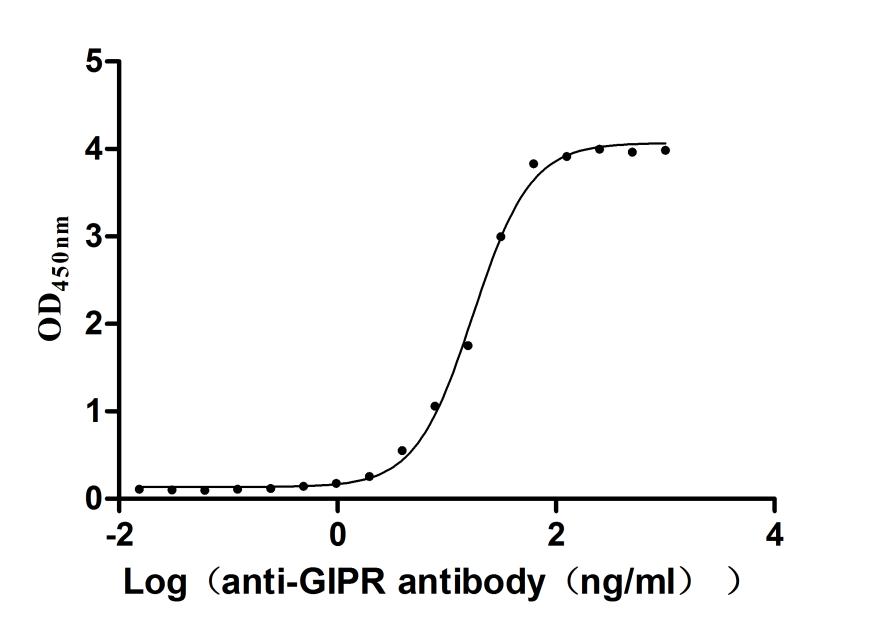
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)










