Recombinant Human Syncytin-1 (ERVW-1), partial
-
中文名称:人ERVW-1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP891578HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人ERVW-1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP891578HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人ERVW-1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP891578HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Name:ERVW-1Synonyms:ERVWE1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ERVW-1; ERVWE1; Syncytin-1; Endogenous retrovirus group W member 1; Env-W; Envelope polyprotein gPr73; Enverin; HERV-7q Envelope protein; HERV-W envelope protein; HERV-W_7q21.2 provirus ancestral Env polyprotein; Syncytin) [Cleaved into: Surface protein; SU; gp50); Transmembrane protein; TM; gp24)]
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:This endogenous retroviral envelope protein has retained its original fusogenic properties and participates in trophoblast fusion and the formation of a syncytium during placenta morphogenesis. May induce fusion through binding of SLC1A4 and SLC1A5.; Endogenous envelope proteins may have kept, lost or modified their original function during evolution. Retroviral envelope proteins mediate receptor recognition and membrane fusion during early infection. The surface protein (SU) mediates receptor recognition, while the transmembrane protein (TM) acts as a class I viral fusion protein. The protein may have at least 3 conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and target cell membrane fusion, the coiled coil regions (heptad repeats) assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of membranes.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data revealed that human endogenous retrovirus W env might contribute to increase nitric oxide production and microglial migration ability in neuropsychological disorders by regulating the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. PMID: 28656540
- CD47 seems to mediate fusion mostly through broad contact surfaces between the partners' cell membrane while syncytin-1 mediate fusion through phagocytic-cup like structure. PMID: 27714815
- HERV-W was expressed in demyelinated lesions from multiple sclerosis brains, which were all positive for this endogenous pathogenic protein. Pronounced HERV-W immunoreactivity in active multiple sclerosis lesions was intimately associated with areas of active demyelination throughout the successive stages of lesion evolution in multiple sclerosis brains. PMID: 27456869
- ERVWE1, ERVFRDE1 and ERV3 transcription was down-regulated in hydatidiform moles and gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. PMID: 26992684
- Study found no associations between embroynal ERVW-1 polymorphisms and preeclampsia. PMID: 27546366
- Identification of the two CpG dinucleotides around transcription start site as key epigenetic elements has provided valuable information for further studies on the epigenetic regulation of syncytin-1 in pancreatic cancer cells PMID: 26230721
- Positive associations were observed between HERV-w methylation and dietary intakes of beta-carotene and carotenoids in a population of obese subjects. PMID: 25340371
- Syncytin-1 and ASCT-2 is localized at the acrosomal region and equatorial segment of the spermatozoa. PMID: 24687878
- Data show that Multiple Sclerosis-Associated Retrovirus (MSRV) is predominantly expressed over ERWVE1 in astrocyte-derived U-87 glioblastoma cell line. PMID: 24814867
- The effect of ETS1 on syncytialization of trophoblasts likely results, at least in part, from inhibition of syncytin expression. PMID: 25651508
- These results indicated that aberrant hypermethylation is involved in downregulation of syncytin-1, and epigenetic alterations may play a significant role in the development of preeclampsia PMID: 23888950
- Exosomes from cultured primary villous cytotrophoblasts and sera of pregnant women have syncytin-1 on their surfaces. It acts on cellular binding and uptake of exosomes. PMID: 24812088
- Increased trophoblast apoptosis and altered expression levels of syncytin-1, calpain 1, and AIF is observed in preeclamptic placentas. PMID: 24413738
- Syncytin-1 overexpression may be an indicator of urothelial cell carcinoma risk. PMID: 24013223
- Insertionally polymorphic HERV-K113 and HERV-K115 are not associated with HIV infections. PMID: 24204983
- Influenza A virus infection transactivated ERVWE1 by increasing the transcription of GCM1. PMID: 24478419
- Overexpression of HERV-W envelope gene elevated the levels of SK3 channel in neuroblastoma cells. PMID: 23727510
- Syncytin-1 knockdown significantly inhibited BeWo cell growth and DNA synthesis and Syncytin-1 could promote the G1/S transition through p15 and CDK4. PMID: 23333240
- In discordant monozygotic twins, HERVWE1 expression is higher in smaller fetuses and lower in larger counterparts. Methylation of the HERVWE1 gene promoter region may participate in gene regulation. PMID: 23290063
- This study linked decreased Syncytin-1 expression to an epigenetic hypermethylation of the entire promoter of ERVW-1. PMID: 23457515
- HERV-W env transcription was found to be elevated in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia subjects compared to controls. Molecular sequence characteristics may represent distinct features of the genome of patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. PMID: 23212585
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone did not influence the differentiation of isolated trophoblasts into functional syncytium as determined by beta-hCG secretion, albeit inducing syncytin-1 expression. PMID: 22971074
- Data suggest that sorting of syncytin-1 into placental exosomes represents mechanism allowing syncytin-1 to reach and interact with target cells of maternal immune system to execute its immune-modulatory roles during pregnancy. PMID: 22999499
- proposed that Syncytin-1 is regulated by PPARgamma/RXRalpha signaling during placentogenesis to drive multinuclear syncytiotrophoblast layer formation and maintenance. PMID: 22573555
- The role of syncytin-1 and Pb1 in cell-cell fusion was studied using lentiviral vectors that express short hairpin RNAs for stable knockdown of both genes. PMID: 22573740
- The findings suggested that syncytin 1 is shed from the placenta into the maternal circulation in association with placental microvesicles, and modulates immune cell activation and the responses of immune cells to lipopolysaccharide stimulation. PMID: 22348442
- Data show that beta-catenin/BCL9-Like (BCL9L)/T-cell factor 4 (TCF4) signalling directly targets the GCM1/syncytin pathway and thereby regulates the fusion of human choriocarcinoma cells. PMID: 22109522
- results further highlighted the existence of a correlation between the extent of the decrease in the expression levels of both syncytins 1 and 2 fusogenic proteins and the degree of severity of preeclampsia symptoms PMID: 21493955
- HERV-W env triggers brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) production in human U251 glioma cells. PMID: 20100784
- Analysis of non-spliced ERVWE1 mRNAs and env mRNAs detected efficient splicing of endogenously expressed RNAs in trophoblastic but not in non-placental cells. PMID: 21771862
- CD9 increases GCM1 expression via the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway, resulting in the increase in ERVWE1 expression. PMID: 19692500
- HERV-W syncytin expression apparently does not play role in endometriosis. However, it may possibly influence development of endometriosis because of increased expression in normal endometrium in endometriosis patients. PMID: 19903052
- contributor to normal placental architecture, especially in the fusion processes of cytotrophoblasts to syncytiotrophoblasts. the gene expression of syncytin may be altered in cases with placental dysfunction such as preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome. PMID: 11854637
- mRNA abundance for syncytin showed stimulation by forskolin in BeWo cells PMID: 12175968
- syncytin-mediated trophoblastic fusion in human cells is regulated by GCMa PMID: 12397062
- Syncytin gene activation is highest in term placenta PMID: 12620933
- Hypoxia alters expression and function of syncytin and its receptor during trophoblast cell fusion of human placental BeWo cells: implications for impaired trophoblast syncytialisation in pre-eclampsia. PMID: 12757936
- Syncytin gene expression is down-regulated by hypoxia, which strengthens the hypothesis that syncytin is reduced in disturbed pregnancies in the course of placental hypoxia. PMID: 14520239
- syncytin promoter is located in the 5' long terminal repeat (LTR) of the HERV-W gene and that binding sites for CBF and Oct in the proximal promoter are critical for transcriptional regulation of the gene in trophoblast cells. PMID: 14613893
- relative L1 and HERV-W expression levels are elevated in representative samples of malignant vs. non-malignant ovarian tissues PMID: 15109395
- Cytoplasmic domain of syncytin is not essential for syncytin-mediated fusion but may play regulatory role. Intramolecular interaction between two heptad repeat regions (HRA and B) is involved in fusion process. PMID: 15269105
- Syncytin's proinflammatory properties in the nervous system demonstrate a novel role for an endogenous retrovirus protein, which may be a target for therapeutic intervention. PMID: 15452578
- The 146-bp region of the 5'-flanking region (nt-294/-148) of the human syncytin gene acts as a placenta-specific enhancer. PMID: 15888734
- GCMa-driven syncytin expression is the key mechanism for syncytiotrophoblast formation PMID: 16004993
- Syncytin transcripts were found in first-trimester trophoblast cells with both villous and extravillous phenotypes and also in the JAR and JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cell lines. PMID: 16760410
- evaluation of the interaction of the HERV-W envelope with the hASCT2 receptor; a region consisting of the N-terminal 124 amino acids of the mature glycoprotein surface subunit was determined as the minimal receptor-binding domain PMID: 16820059
- Syncytin is expressed by human cancer cells and is involved in cancer-endothelial cell fusions PMID: 16871371
- Median viral RNA levels for syncytin-1 were higher in brains of MS patients relative to non-MS patients and median syncytin-1 DNA levels in MS brains were higher than non-MS brain tissue. PMID: 17209768
- Transcripts from the HERV-W element on chromosome 7q21.2 encoding syncytin and from the SOD1 gene were detected at elevated levels in biopsies from the most affected muscles from MND patients compared to biopsies from control individuals. PMID: 17453631
- present evidence in support of the direct role for syncytin-A in mouse trophoblast stem cell fusion and differentiation involved in placental dev. PMID: 17762178
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Surface protein]: Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein.; [Transmembrane protein]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Syncytin-1]: Virion.
-
蛋白家族:Gamma type-C retroviral envelope protein family, HERV class-I W env subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed at higher level in placental syncytiotrophoblast. Expressed at intermediate level in testis. Seems also to be found at low level in adrenal tissue, bone marrow, breast, colon, kidney, ovary, prostate, skin, spleen, thymus, thyroid, brain and tra
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 13525
OMIM: 604659
KEGG: hsa:30816
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000419945
Most popular with customers
-
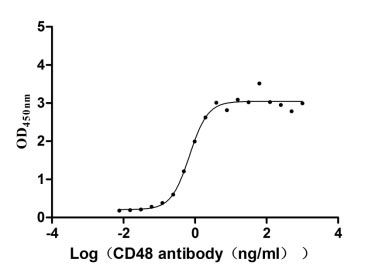
Recombinant Human CD48 antigen (CD48) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
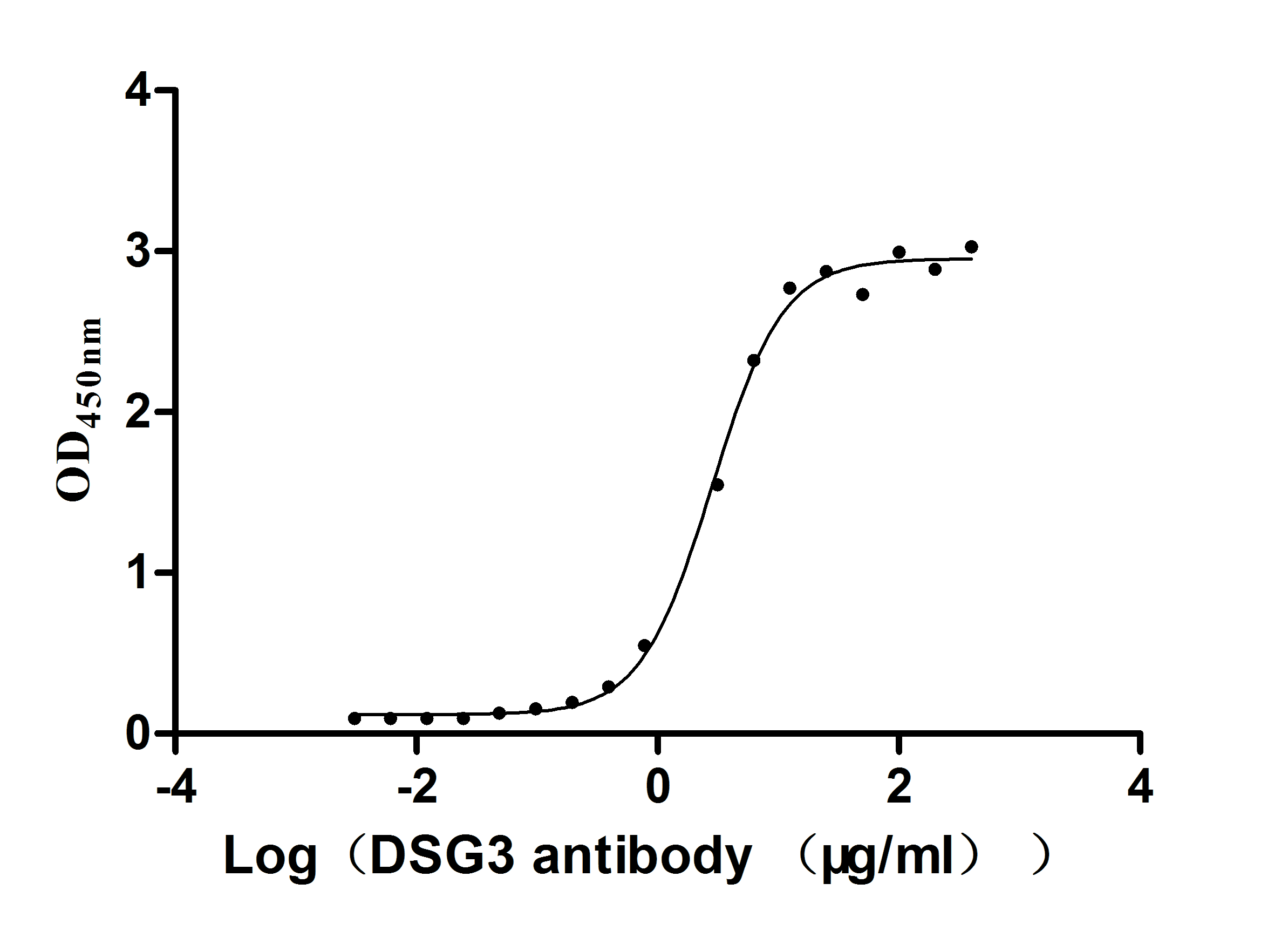
Recombinant Mouse Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
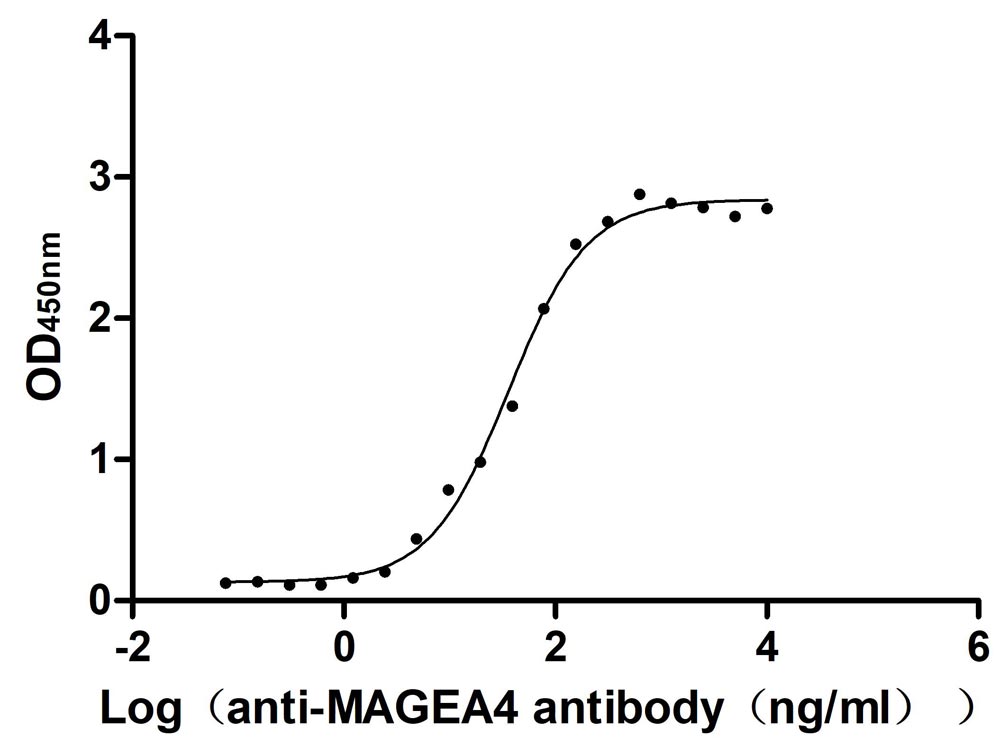
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
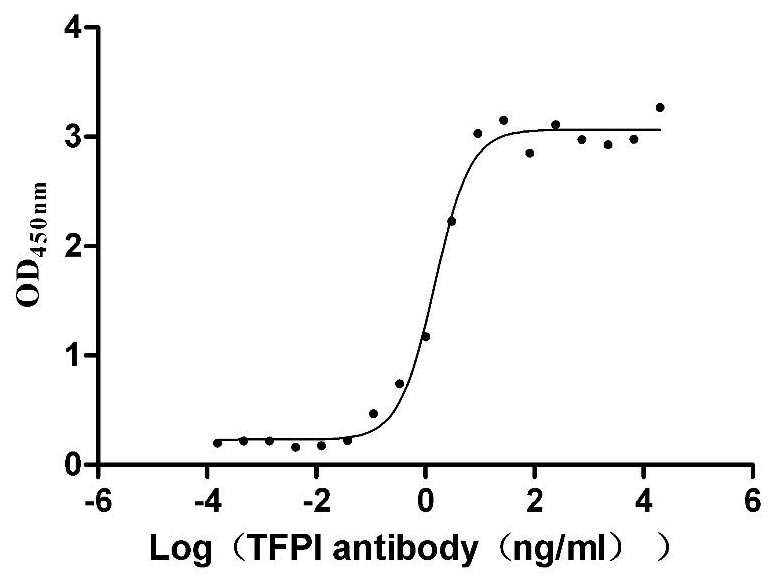
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)