Recombinant Human Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein B (SFTPB)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-BP021173HU
-
规格:¥3168
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
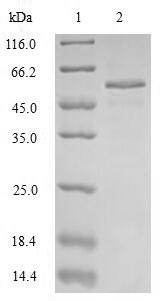
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:SFTPB
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:SFTPB; SFTP3; Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein B; SP-B; 18 kDa pulmonary-surfactant protein; 6 kDa protein; Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Phe
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
分子量:50.7 kDa
-
表达区域:201-279aa
-
氨基酸序列FPIPLPYCWLCRALIKRIQAMIPKGALAVAVAQVCRVVPLVAGGICQCLAERYSVILLDTLLGRMLPQLVCRLVLRCSM
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal MBP-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins promote alveolar stability by lowering the surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the peripheral air spaces. SP-B increases the collapse pressure of palmitic acid to nearly 70 millinewtons per meter.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- rs7316 polymorphism associated with respiratory distress syndrome in Iranian premature newborns PMID: 28738720
- TGF beta markedly decreased expression of SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, fatty acid synthase, and the phospholipid transporter ABCA3. However, TGF beta increased protein levels of SP-D with little change in mRNA levels. PMID: 29621540
- Surfactant protein B suppresses lung cancer progression by inhibiting secretory phospholipase A2 activity and arachidonic acid production. PMID: 28743125
- Data show that the thermal transitions observed in N-terminal propeptide of proSP-B (SP-BN) may correspond to the unfolding of certain protein domains or subdomains and/or to oligomers dissociation whereas the overall protein shows resistance to temperature-induced unfolding up to ~ 86 degrees C. PMID: 27380171
- SP-A (+186A/G) and SP-B (1580C/T) polymorphisms are strongly associated with the risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in preterm infants. Notably, reduced serum SP-A levels were correlated with a high risk of RDS and may serve as novel biomarkers for RDS detection and monitoring. PMID: 28011976
- Differences were found regarding SPA and pro-SPB expression in the vast majority of subjects: in some lungs, SPA was more expressed whereas in others pro-SPB showed an higher degree of immunoreactivity. The expression of both surfactant proteins was not strictly correlated with gestational age. PMID: 27734990
- There is no significant association between the gene polymorphism of the R236C site in exon 7 of SP-B gene and the incidence ofneonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) in Han populations in that region. PMID: 27655533
- Rare mutations in surfactant-associated genes contribute to neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. The frequency of mutations in these genes in the Chinese population is unknown. We resequenced all exons of the surfactant protein-B (SFTPB) and we did not find any rare mutations in SFTPB PMID: 26547207
- mice with SP-B-C allele are more susceptible to S. aureus pneumonia than mice with SP-B-T allele, and that CMC2.24 attenuates lung injury thus reducing mortality. PMID: 26863117
- In term newborns with pneumonia, SP-B increases with respect to total phospholipids, and disaturated-phosphatidylcholine and is turned over at a faster rate. PMID: 26107393
- SP-B -18C/A and 1580C/T polymorphisms are associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia PMID: 26045806
- These results demonstrate for the first time that human SP-B C allele is more susceptible to bacterial pneumonia than SP-B T allele in vivo. PMID: 26620227
- Significant differences in frequency of occurrence of unfavorable genotypes CC rs1965708, AA rs1059046 of SFTPA2 gene and CC rs1130866 of SFTPB gene in influenza patients in comparison with individuals of the control group were not detected. PMID: 26950992
- Investigated the relationship between SP-A2 and SP-B gene polymorphisms and respiratory distress syndrome in preterm neonates. PMID: 26061924
- Given these fact SP-B deficiency may be considered as a further field for research on regenerative therapy i. e. stem cell administration in models of postnatal SP-B deficiency. PMID: 25565191
- Results support a critical role of SP-B for promoting pulmonary surface film formation. PMID: 25360829
- SFTPB variants are associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility and lung function in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 25299874
- Surfactant protein B gene polymorphism is associated with severe influenza. PMID: 24337193
- data support the hypothesis that proSP-B glycosylation due to Ile131Thr variation may have a causal role in genetic susceptibility to acute respiratory distress PMID: 24002332
- It was concluded that the polymorphisms of SP-B intron 4 and C/A-18 could be associated with BPD in Chinese Han infants, and the del allele of intron 4 and A allele of C/A-18 might be used as markers of susceptibility in the disease. PMID: 23771654
- there was no evidence for any association between common polymorphisms in the SP-B and SP-D genes and COPD risk (all p>0.05). PMID: 24093802
- Glucocorticoids mediated surfactant protein B production, maturation, and release is amplified by caffeine. PMID: 24163141
- macrophages participate in the repression of SFTPB expression by LPS, and that macrophage-released cytokines (including TNF) regulate the transcription factor CEBPB PMID: 23590297
- D2S388-5 microsatellite polymorphism of surfactant protein B may be associated with susceptibility to COPD in Xinjiang Kazakhs. PMID: 23088317
- elevated expression in nasal mucosa in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps PMID: 23406594
- Mutations in exon 4 of the surfactant protein B gene demonstrate an association between homozygous mutations with C/C genotype in SP-B gene and neonatal respiratory distress. PMID: 23330012
- caffeine is able to induce the expression of SP-transcription factors and affects the signaling pathways of glucocorticoids, amplifying their effects PMID: 23272120
- The results indicate that tryptophan oxidation causes substantial disruptions in helical structure and lipid interactions. PMID: 21128671
- review focuses on published association studies of surfactant proteins A and D genetic polymorphisms with respiratory, and non-respiratory diseases in adults, children, and newborns [review] PMID: 22201752
- The present study demonstrated that the AG genotype of AG 9306 polymorphism was a protective factor against the development of respiratory distress syndrome, other polymorphisms studied (G/C at 8714, C/T at 1580, A/C at -18) were not associated with RDS. PMID: 21180884
- In patients undergoing major vascular abdominal surgery, SP-B values increase progressively during mechanical ventilation stages compared to advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) kinetics. PMID: 21736957
- SP-B 1580C/T polymorphism contributes to the etiology of respiratory distress syndrome. PMID: 22289747
- Circulating levels of SP-B increase with greater smoking burden and independently associate with abdominal abdominal aortic plaque among current smokers. PMID: 21817103
- Genetic variations in the gene coding for surfactant protein B are associated with more severe lung injury as indicated by the association of specific single nucleotide polymorphism genotypes and haplotypes PMID: 21283003
- Surfactant protein B and RAGE increases in the plasma during cardiopulmonary bypass PMID: 20650982
- Surfactant protein B polymorphisms have a role in pulmonary function and COPD PMID: 20693256
- Disaturated-phosphatidylcholine and surfactant protein-B have a different turnover both in healthy and diseased lungs. PMID: 21429235
- Absence of this protein resulted in Congenital pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in two newborn children PMID: 20005435
- Surfactant protein-B 121ins2 heterozygosity is associated with reduced lung function and increased risk for COPD among smokers PMID: 19833825
- review of lipid-protein interactions of hydrophobic proteins SP-B and SP-C in lung surfactant assembly and dynamics PMID: 11699574
- Data suggest that SMAD3 interactions with the positive regulators NKX2.1 and HNF-3 underlie the molecular basis for TGF-beta-induced repression of surfactant protein B gene transcription. PMID: 12161428
- role of Differences in N-linked glycosylation between human surfactant protein-B variants of the C or T allele at the single-nucleotide polymorphism at position 1580 in disease PMID: 12356334
- suggest that polymorphisms in intron 4 of the surfactant protein B gene independently modify the course of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome PMID: 12424586
- An association between SP-B polymorphism and RDS was found in premature, first-born twins. In particular, the threonine allele was associated with an increased risk of RDS. PMID: 12483294
- dimeric SP-B(1-25) is more efficient in restoring lung function in neonatal RDS and ARDS than monomeric SP-B(1-25) surfactant. PMID: 12490037
- surfactant protein B expression is regulated by an enhancer region which binds to thyroid transcription factor-1, retinoic acid receptor, signal transducers and activators of transcription 3, nuclear receptor coactivators (SRC-1, ACTR, TIF2, and CBP/p300 PMID: 12573987
- Mutataions and Polymorphisms in SFTPB is associated with severe unexplained respiratory distress PMID: 12784301
- SP-B expression is regulated by PPARgamma in the lung PMID: 12829715
- Reduced SP-B expression due to elevated nitric oxide levels can contribute to lung injury. PMID: 12896877
- In human lungs, mature SP-B is involved in the structural organization of lamellar bodies and tubular myelin by the formation of core particles. PMID: 12972403
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Pulmonary surfactant metabolism dysfunction 1 (SMDP1); Respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants (RDS)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, surface film.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10801
OMIM: 178640
KEGG: hsa:6439
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000377409
UniGene: Hs.512690
Most popular with customers
-
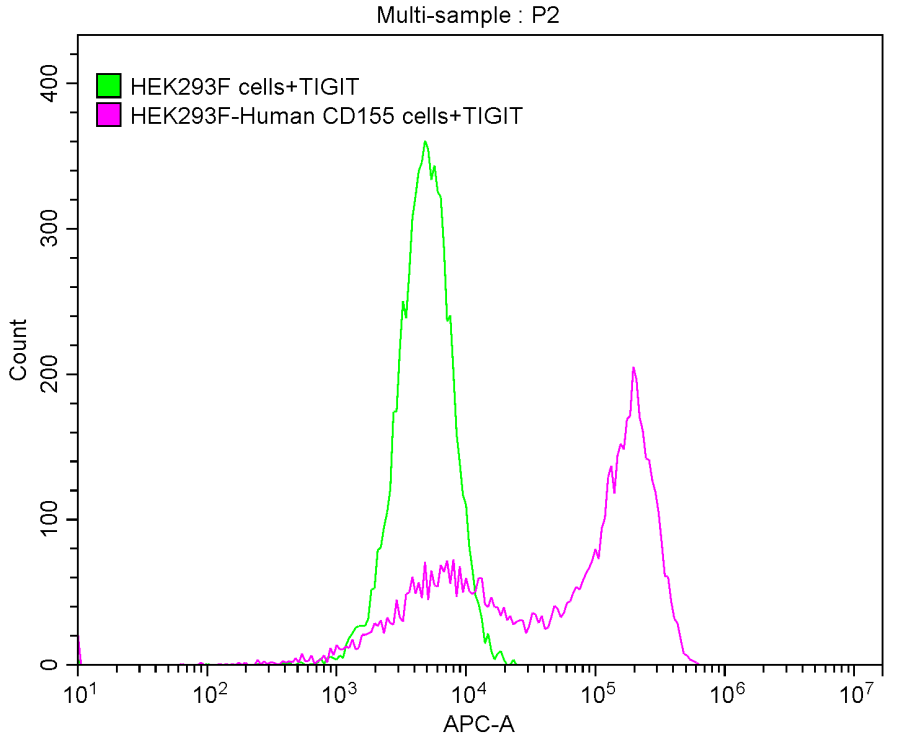
Recombinant Human T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
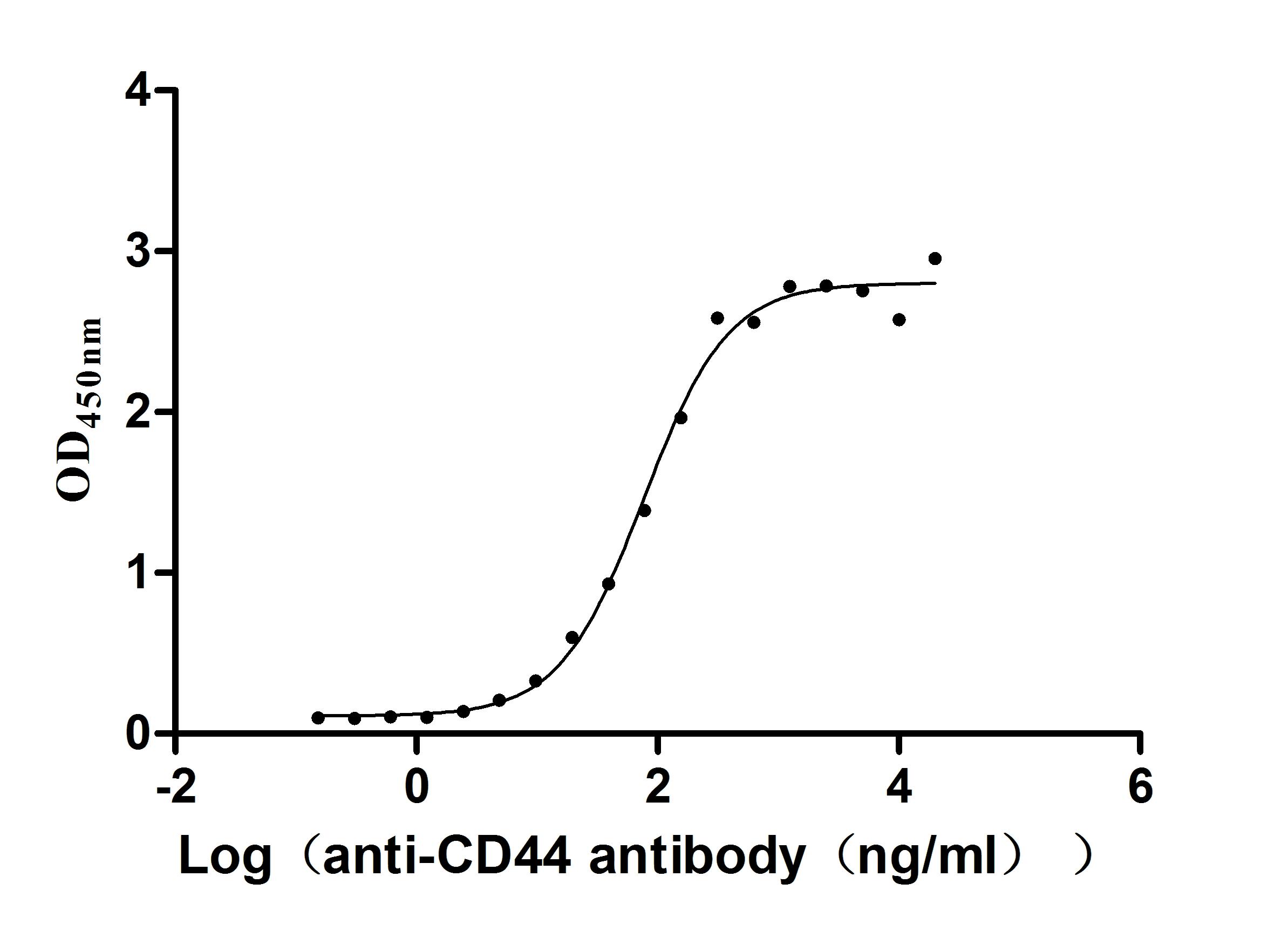
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
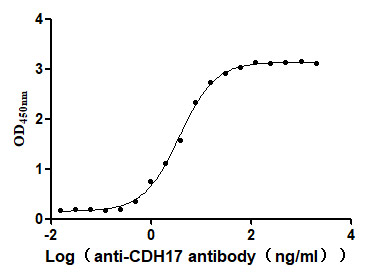
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
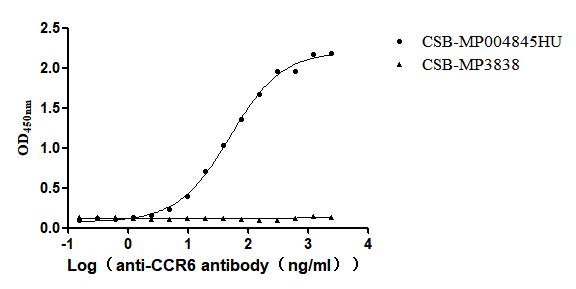
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
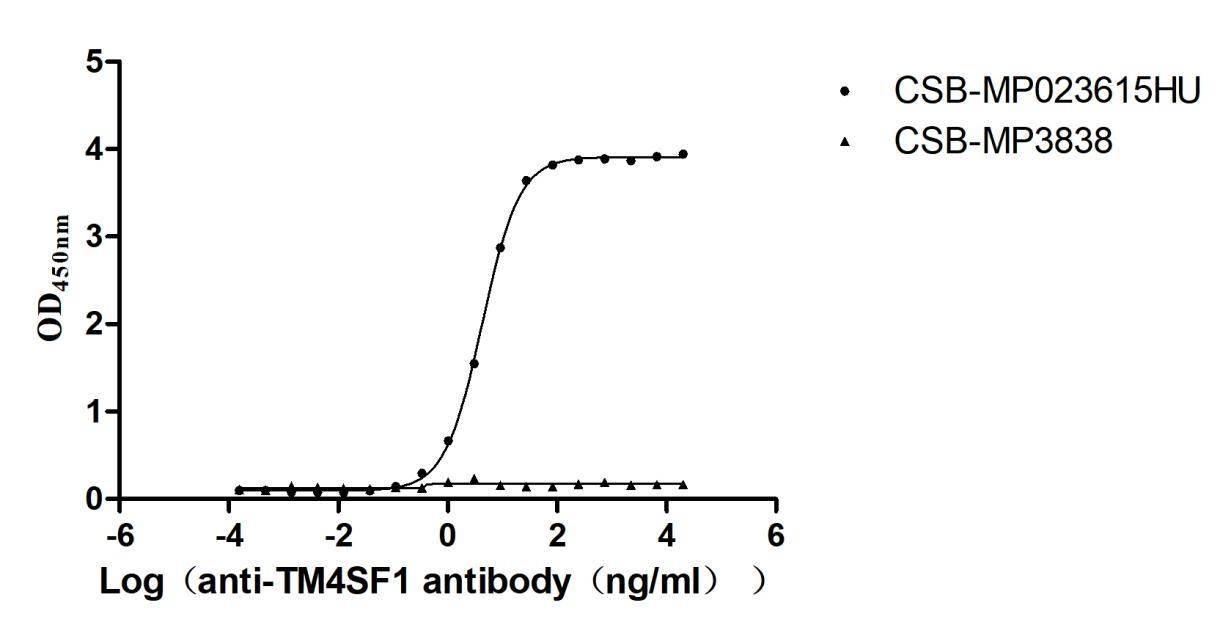
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)