Recombinant Human Protein-arginine deiminase type-4 (PADI4)
In Stock-
中文名称:人PADI4重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP890757HU
-
规格:¥1536
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
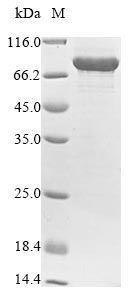
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:PADI4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:EC 3.5.3.15; HL 60 PAD; HL-60 PAD; PAD 4; PAD; PADI 4; PADI 5; PADI H protein; Padi4; PADI4_HUMAN; PADI5; PDI 4; PDI 5; PDI4; PDI5; Peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV; Peptidyl arginine deiminase type V; Peptidylarginine deiminase IV; Protein arginine deiminase; Protein arginine deiminase type 4; Protein arginine deiminase type IV; Protein-arginine deiminase type IV; Protein-arginine deiminase type-4
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:81.1 kDa
-
表达区域:1-663aa
-
氨基酸序列MAQGTLIRVTPEQPTHAVCVLGTLTQLDICSSAPEDCTSFSINASPGVVVDIAHGPPAKKKSTGSSTWPLDPGVEVTLTMKVASGSTGDQKVQISYYGPKTPPVKALLYLTGVEISLCADITRTGKVKPTRAVKDQRTWTWGPCGQGAILLVNCDRDNLESSAMDCEDDEVLDSEDLQDMSLMTLSTKTPKDFFTNHTLVLHVARSEMDKVRVFQATRGKLSSKCSVVLGPKWPSHYLMVPGGKHNMDFYVEALAFPDTDFPGLITLTISLLDTSNLELPEAVVFQDSVVFRVAPWIMTPNTQPPQEVYACSIFENEDFLKSVTTLAMKAKCKLTICPEEENMDDQWMQDEMEIGYIQAPHKTLPVVFDSPRNRGLKEFPIKRVMGPDFGYVTRGPQTGGISGLDSFGNLEVSPPVTVRGKEYPLGRILFGDSCYPSNDSRQMHQALQDFLSAQQVQAPVKLYSDWLSVGHVDEFLSFVPAPDRKGFRLLLASPRSCYKLFQEQQNEGHGEALLFEGIKKKKQQKIKNILSNKTLREHNSFVERCIDWNRELLKRELGLAESDIIDIPQLFKLKEFSKAEAFFPNMVNMLVLGKHLGIPKPFGPVINGRCCLEEKVCSLLEPLGLQCTFINDFFTYHIRHGEVHCGTNVRRKPFSFKWWNMVP
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Catalyzes the citrullination/deimination of arginine residues of proteins such as histones, thereby playing a key role in histone code and regulation of stem cell maintenance. Citrullinates histone H1 at 'Arg-54' (to form H1R54ci), histone H3 at 'Arg-2', 'Arg-8', 'Arg-17' and/or 'Arg-26' (to form H3R2ci, H3R8ci, H3R17ci, H3R26ci, respectively) and histone H4 at 'Arg-3' (to form H4R3ci). Acts as a key regulator of stem cell maintenance by mediating citrullination of histone H1: citrullination of 'Arg-54' of histone H1 (H1R54ci) results in H1 displacement from chromatin and global chromatin decondensation, thereby promoting pluripotency and stem cell maintenance. Promotes profound chromatin decondensation during the innate immune response to infection in neutrophils by mediating formation of H1R54ci. Required for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs); NETs are mainly composed of DNA fibers and are released by neutrophils to bind pathogens during inflammation. Citrullination of histone H3 prevents their methylation by CARM1 and HRMT1L2/PRMT1 and represses transcription. Citrullinates EP300/P300 at 'Arg-2142', which favors its interaction with NCOA2/GRIP1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Molecular interplay between the dimer interface and the substrate-binding site of human PAD4 has been reported. PMID: 28209966
- PADI4 may be closely associated with hypoxiainduced autophagy, and the inhibition of hypoxiainduced autophagy by PADI4 knockdown may contribute to an increase in the apoptosis of RAFLS. PMID: 29393388
- MiRNA-146a rs2910164 and IRAK1 rs3027898 polymorphisms were a risk factor for predisposition to Rheumatoid Arthritis in Egyptian Population in codominant and dominant tested inheritance models, while, the miRNA-499 rs3746444 and PADI4 rs1748033 polymorphisms were a risk factor in codominant and recessive one. PMID: 29734142
- our meta-analysis demonstrated that the PADI4_94 polymorphisms might contribute to RA susceptibility especially in Asian populations but not in Caucasian populations. PMID: 29302826
- Meta-analysis indicated a significantly increased association between PADI -104C/T polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Chinese and Japanese populations (which were the majority of included populations in the analysis). PMID: 29518108
- PADI4 interacted with SYVN1 directly and that overexpression of PADI4 suppressed the ubiquitination of proteins. Thus, a reduction in ER stress induced by PADI4 may abrogate the initiation of chronic RA by suppressing the proliferative signals of RA synoviocytes. PMID: 29039504
- mRNA expression of PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1 is upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis bone marrow CD34+ cells independently of the systemic inflammation or treatment regimen. PMID: 29148420
- this study in a Southern Mexican population suggests that PADI4 individual polymorphisms and the related susceptibility haplotype (GTG) are also genetic risk markers for rheumatoid arthritis PMID: 28551357
- The T allele of PADI4 rs2240340 is associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Asians. PMID: 28653215
- PADI4 contributes to gastric tumorigenesis by upregulating CXCR2, KRT14 and TNF-alpha expression. PMID: 27556695
- In this case-control study with sufficient sample size to detect associations, we observed that PADI4 SNPS rs11203367 and rs874881 do not significantly determine RA susceptibility PMID: 27182695
- SNPs of PADI4 may be a risk factor for airway abnormalities in RA. PMID: 27372294
- this meta-analysis suggested that PADI4 -92C/G polymorphism may be associated with the rheumatoid arthritis incidence in the Chinese population, especially for South China. Further studies conducted on other ethnic groups are required for definite conclusions. PMID: 28832760
- PADI4 contributes to the pathogenesis of RA by protecting FLSs from apoptosis. PADI4 suppresses p21 transcription through altering histone H3 arginine modifications on p21 promoter region. PMID: 28367100
- Proteolysis by granzyme B enhances presentation of autoantigenic PAD4 epitopes in rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 27700100
- No associations were found between clinical subtypes of JIA and PADI4 allele frequency. rs2240337 in the PADI4 gene was significantly associated with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody-positivity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. PMID: 28182665
- The effect of the PADI4-104C/T polymorphism on RA risk in the Chinese population was evaluated in a meta-analysis. The overall analysis indicated a significant association between the PADI4-104C/T polymorphism and RA risk in the Chinese population (T vs C: OR = 1.45, 95%CI = 1.18-1.78; TT vs CC: OR = 1.49, 95%CI = 1.24-1.80; TT vs CC+CT: OR = 1.28, 95%CI = 1.08-1.51; TT+CT vs CC: OR = 1.75, 95%CI = 1.30-2.37). PMID: 27706751
- Overexpression of PAD4 constrains the activity of EMT via suppressing Elk1 expression. PMID: 27176594
- Our study also demonstrated that PADI4 contributes to tumor metastasis by regulating the gene expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and WAS/WASL-interacting protein family member 1 (WIPF1). PMID: 26563365
- PAD4 levels were significantly higher in patients with rheumatoid arthritis than in patients with systemic lupus erythematosis or healthy controls. Anti-PAD4 antibodies were detected in 30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but not in patients with SLE, systemic sclerosis or controls. PMID: 26415740
- the PADI4_94 and PADI_104 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Asians and Caucasians, and the PADI4_92 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to RA in Asians, but not in Caucasians [meta-analysis] PMID: 26474773
- This meta-analysis showed that the PADI4 -94G/A variants may influence RA risk in the Chinese population. PMID: 27051025
- The results highlight an association between PAD4 and DNA hypermethylation in acute promyelocytic leukemia and demonstrate that targeting PAD4 or regulating its downstream effectors may be a promising strategy to control differentiation in the clinic. PMID: 26673819
- Polymorphism in exon-4 of PADI4 gene showed significant association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)and polymorphism in exon-3 exhibited moderate association with RA. PMID: 22976394
- PADI4 rs1748033 gene polymorphism increased the risk of RA in a sample of the Iranian population. PMID: 26546893
- Silencing of PADI4 attenuates the TNF-alpha-induced osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PMID: 26082376
- Data show that peptidylarginine deiminase type 4, mutated citrullinated vimentin and cyclic citrullinated peptides autoantibodies were detected in 24, 61 and 74% of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, respectively. PMID: 26149185
- PAD4 activity was significantly higher in cell-free synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients compared to osteoarthritis patients. PMID: 26245941
- We found that heterozygote genotypes for PADI4_89 were protectively associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. PMID: 25205591
- Data show that peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV (PADI4) polymorphisms and a functional haplotype are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 25562673
- PAD-4 is inhibited by PTPN22. PMID: 26019128
- PADI4-94G/A polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the overall population and in the Asian population. PMID: 26043831
- We propose that the influence of PADI4 on IL6ST transcription plays a role in the control of IL6ST expression during lineage differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. PMID: 24874575
- The prevalence and extent of ILD was markedly higher among RA patients with anti-PAD3/4 cross-reactive antibodies, even after accounting for relevant confounders, particularly among ever smokers. PMID: 24901704
- genetic variants in CDK6 and PADI4 were associated with anti-citrullinated cyclic peptide status in rheumatoid arthritis DRB1*04 negative patients PMID: 25138370
- Data indicate an association between peptidylarginine deiminase PADI4 and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the multiethnic population from South East Asia. PMID: 23164236
- rADI not only reduced NO production but also caused cellular toxicity in nNOS-activated SH-SY5Y cells, suggesting a dual role for rADI in NOS-mediated neurotoxicity. PMID: 25126568
- PADI4 polymorphisms are risk factors contributed to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility, especially for anti-CCP positive disease, and may confer higher risk of radiographic severity in Chinese Han population. PMID: 24564960
- We found that PADI4 polymorphisms are associated with RA susceptibility, regardless of ACPA titers. PMID: 24454473
- results suggest that the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB may play a role in the repression of PAD4 transcription during inflammation PMID: 24140127
- anti-PAD4 autoantibodies (identified by their cross-reactivity with PAD3) markedly increase the catalytic efficiency of PAD4. PMID: 23698378
- PADI4 risk allele and HLA-DRB1 shared epitope are independent genetic risks for radiographic progression in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients PMID: 23577190
- Dysregulation of PAD4-mediated citrullination of nuclear GSK3beta activates TGF-beta signaling and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. PMID: 23818587
- Therefore, our data strongly suggest that the N-terminal Ca(2+) ions play critical roles in the full activation of the PAD4 enzyme. PMID: 23382808
- Data indicate that the declined PADI4 mRNA was significantly associated with Line-1 demethylation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. PMID: 22907585
- Our results suggested that rs2240340 in PADI4 gene is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Yunnan. PMID: 23450494
- This meta-analysis suggests that PADI4 polymorphisms represent a significant risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis, especially in Asians. PMID: 22552437
- The synovial expression of cyclic citrullinated peptide and the generation of anti-CCP antibodies are strongly associated with shared epitope alleles and/or certain PADI4 gene SNPs in rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 22944128
- The relationship between PADI4 and rheumatoid arthritis has been observed among Japanese. PMID: 23214088
- No single point association between genotype and allele frequency was found for rheumatoid arthritis in Tunisia. PMID: 22459419
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic granule.
-
蛋白家族:Protein arginine deiminase family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in eosinophils and neutrophils, not expressed in peripheral monocytes or lymphocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 18368
OMIM: 180300
KEGG: hsa:23569
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000364597
UniGene: Hs.522969
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
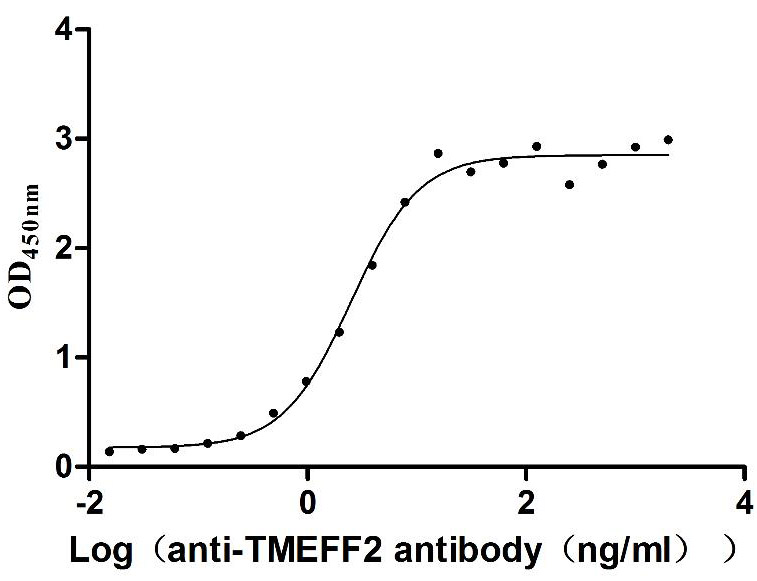
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
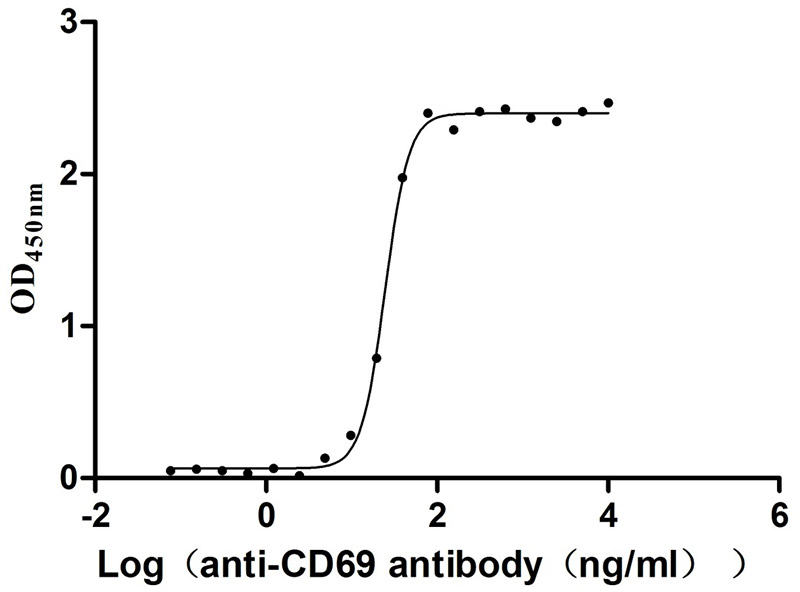
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
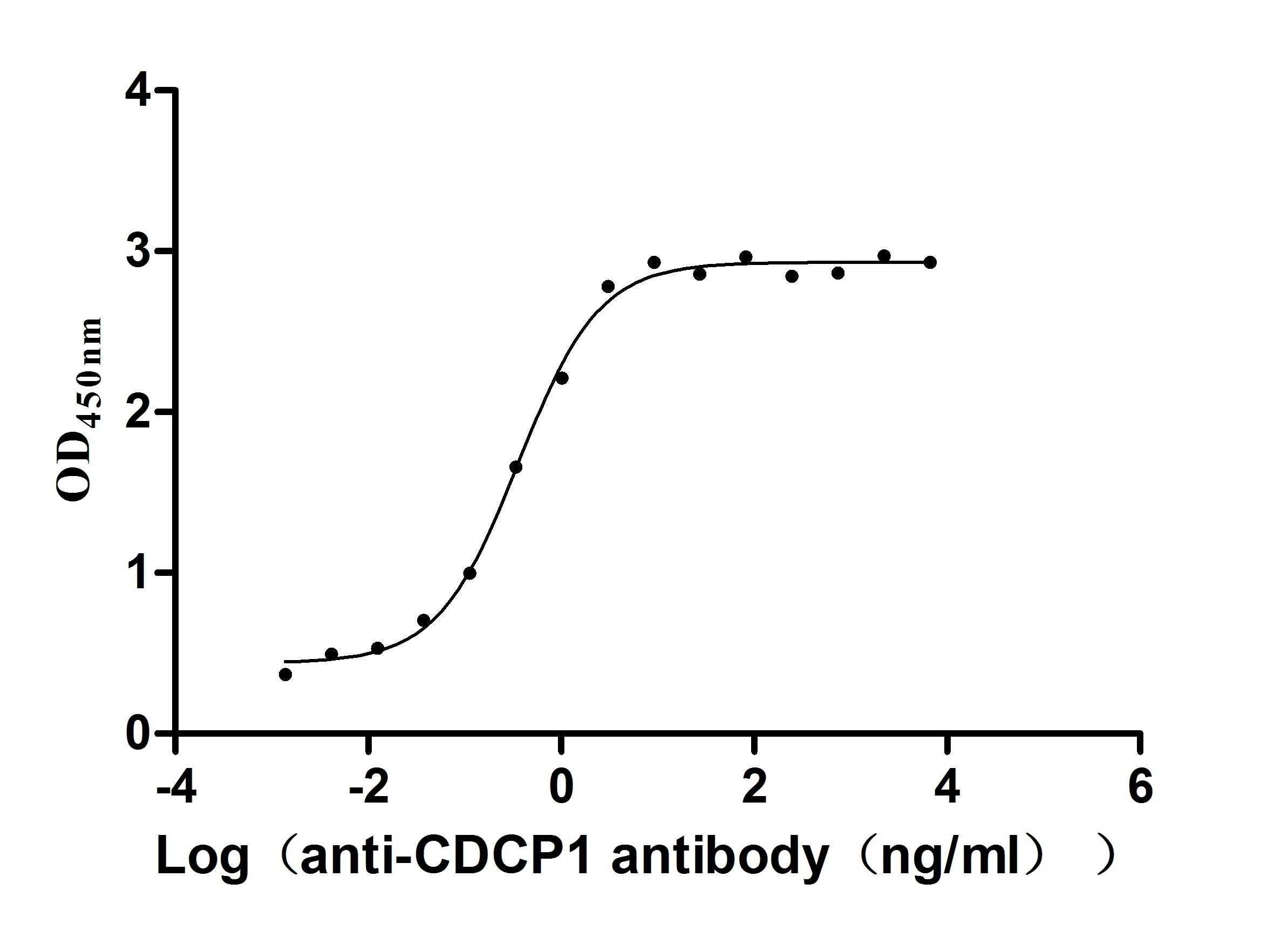
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
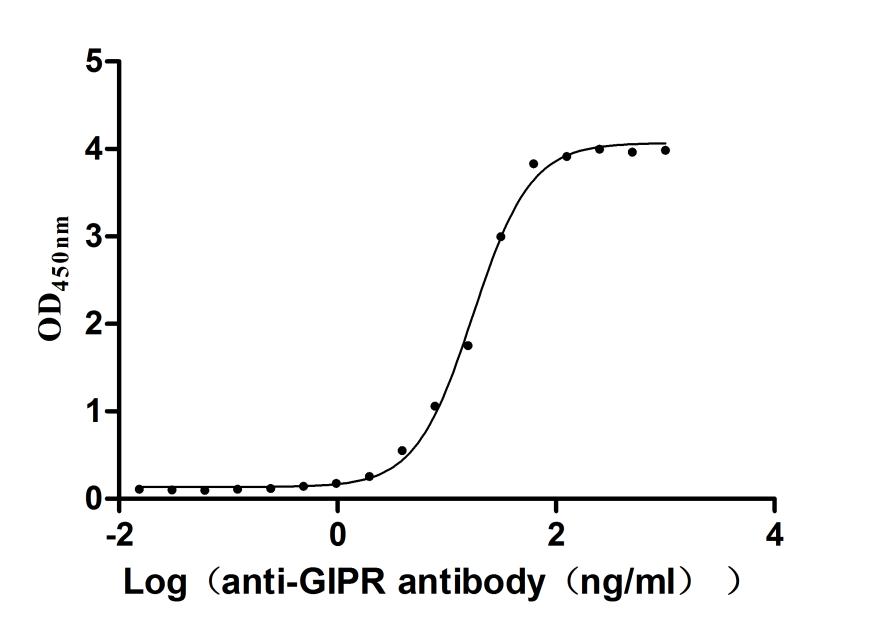
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)