Recombinant Human Kinesin-like protein KIF2C (KIF2C)
-
中文名称:人KIF2C重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP860347HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KIF2C重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP860347HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KIF2C重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP860347HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KIF2C重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP860347HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人KIF2C重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP860347HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:KIF2C
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:4930402F02Rik; CT139; ESTM5; KIF 2C; kif2c; KIF2C_HUMAN; Kinesein Family Member 2C; Kinesin family member 2C; kinesin like 6 (mitotic centromere associated kinesin) ; Kinesin like 6; Kinesin like protein 6; Kinesin like protein KIF2C; Kinesin-like protein 6; Kinesin-like protein KIF2C; KNS L6; KNSL 6; KNSL6; MCAK; MGC11883; Mitotic centromere associated kinesin; Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin; OTTHUMP00000010066; X83316
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-725
-
氨基酸序列AMDSSLQAR LFPGLAIKIQ RSNGLIHSAN VRTVNLEKSC VSVEWAEGGA TKGKEIDFDD VAAINPELLQ LLPLHPKDNL PLQENVTIQK QKRRSVNSKI PAPKESLRSR STRMSTVSEL RITAQENDME VELPAAANSR KQFSVPPAPT RPSCPAVAEI PLRMVSEEME EQVHSIRGSS SANPVNSVRR KSCLVKEVEK MKNKREEKKA QNSEMRMKRA QEYDSSFPNW EFARMIKEFR ATLECHPLTM TDPIEEHRIC VCVRKRPLNK QELAKKEIDV ISIPSKCLLL VHEPKLKVDL TKYLENQAFC FDFAFDETAS NEVVYRFTAR PLVQTIFEGG KATCFAYGQT GSGKTHTMGG DLSGKAQNAS KGIYAMASRD VFLLKNQPCY RKLGLEVYVT FFEIYNGKLF DLLNKKAKLR VLEDGKQQVQ VVGLQEHLVN SADDVIKMID MGSACRTSGQ TFANSNSSRS HACFQIILRA KGRMHGKFSL VDLAGNERGA DTSSADRQTR MEGAEINKSL LALKECIRAL GQNKAHTPFR ESKLTQVLRD SFIGENSRTC MIATISPGIS SCEYTLNTLR YADRVKELSP HSGPSGEQLI QMETEEMEAC SNGALIPGNL SKEEEELSSQ MSSFNEAMTQ IRELEEKAME ELKEIIQQGP DWLELSEMTE QPDYDLETFV NKAESALAQQ AKHFSALRDV IKALRLAMQL EEQASRQISS KKRPQ
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:In complex with KIF18B, constitutes the major microtubule plus-end depolymerizing activity in mitotic cells. Regulates the turnover of microtubules at the kinetochore and functions in chromosome segregation during mitosis. Plays a role in chromosome congression and is required for the lateral to end-on conversion of the chromosome-microtubule attachment.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- KIF-2C expression in tumor tissues may serve as an independent prognostic marker for male, but not female, patients with operable esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. PMID: 27563815
- these findings demonstrate that p53 can repress MCAK promoter activity indirectly via down-regulation of Sp1 expression level, and suggest that MCAK elevation in human tumor cells might be due to p53 mutation PMID: 29244835
- Results show that three residues (K524, E525 and R528), which are located in the C-terminal half of the a4-helix, play a crucial role in the ability of MCAK to distinguish between the microtubule lattice and the microtubule end. PMID: 27733589
- s find that 3D ECM engagement uncouples MCAK-mediated regulation of MT growth persistence from myosin-II-mediated regulation of growth persistence specifically within EC branched protrusions. PMID: 28298485
- REVIEW: Conformation changes in MCAK related to its depolymerization activity and function are described. A model of its regulation by multiple mitotic kinases is proposed and its potential involvement in oncogenesis and drug resistance its highlighted. PMID: 27146484
- GTSE1 inhibition of MCAK activity regulates the balance of MT stability that determines the fidelity of chromosome alignment, segregation, and chromosomal stability. PMID: 27881713
- MCAC role in microtubule assembly PMID: 26912793
- Our results reveal an underlying mechanism by which NuSAP controls kinetochore microtubule dynamics spatially and temporally by modulating the depolymerisation function of MCAK in an Aurora B kinase-dependent manner. PMID: 26733216
- MCAK is involved in directional migration and invasion of tumor cells. PMID: 26148251
- the Aurora B-PLK1 signaling at the kinetochore orchestrates MCAK activity, which is essential for timely correction of aberrant kinetochore attachment to ensure accurate chromosome segregation during mitosis. PMID: 26206521
- MCAK activity is modulated by Plk1 phosphorylation on S632/S633 in mitosis. PMID: 25504441
- These results demonstrate that the structural change of Kif2C-ATP upon binding to microtubule ends is sufficient for tubulin release, whereas ATP hydrolysis is not required PMID: 26055718
- Ras regulates KIF2C to control cell migration pathways in transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. PMID: 24240690
- A dynamic interaction of MCAK-TIP150 orchestrated by Aurora A-mediated phosphorylation governs entosis via regulating microtubule plus-end dynamics and cell rigidity. PMID: 24847103
- this study suggests a new mechanism by which Plk1 regulates MCAK: by regulating its degradation and hence controlling its turnover in mitosis. PMID: 24931513
- up-regulation of KIF2C and KIF2A by ERK1/2 caused aberrant lysosomal positioning and mTORC1 activity in a mutant K-Ras-dependent cancer and cancer model. PMID: 25002494
- A Rac1-Aurora A-MCAK signaling pathway mediates endothelial cell polarization and directional migration by promoting regional differences in microtubule dynamics. PMID: 25002679
- result suggested E403K mutation in mitotic centromere-associated kinesin protein as highly damaging and showed strong concordance to the previously observed colorectal cancer mutations aggregation tendency and energy value changes PMID: 23564489
- A CENP-E mediated wall-tethering event and a MCAK-mediated wall-removing event show that human chromosome-microtubule attachment is achieved through a set of deterministic sequential events rather than stochastic direct capture of microtubule ends. PMID: 23891108
- expression has no effect on the level of the TRAIL receptors DR4 and DR5. These findings might have clinical implications since the combination of TRAIL therapy with administration of Pgp modulators might sensitize TRAIL resistant tumors. PMID: 23830822
- PAK1 phosphorylates MCAK and regulates both its localization and function. PMID: 23055517
- Results suggest that MCAK/Kif2C plays an important role in the regulation of cellular senescence through a p53-dependent pathway and might contribute to tissue/organism aging and protection of cellular transformation. PMID: 23098759
- a mechanism in which, in the first step, the specificity of ATP-bound Kif2C for soluble tubulin causes it to stabilize a curved conformation of tubulin heterodimers at the ends of microtubules. PMID: 22403406
- The mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK) was identified as a novel mitosis-phase target in prostate cancer that was overexpressed in multiple castration-resistant prostate cancer gene-expression datasets. PMID: 22363599
- study identifed and defined a mitotic function specific to the microtubule tip-associated population of MCAK: negative regulation of microtubule length within the assembling bipolar spindle. PMID: 22492725
- Abeta impairs the assembly and maintenance of the mitotic spindle. Mechanistically, these defects result from Abeta's inhibition of mitotic motor kinesins, including Eg5, KIF4A and MCAK. PMID: 21566458
- Results uncover a novel role for Aurora A/B kinases in regulating spindle MT dynamics through Kif18b-MCAK and suggest that the Kif18b-MCAK complex constitutes the major MT plus-end depolymerizing activity in mitotic cells. PMID: 21820309
- Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK)has the ability to stimulate microtubule depolymerization. PMID: 21471284
- Results provide a simple model for the generation of driving force and the regulation of chromosome segregation by the activity of MCAK at both kinetochores and spindle poles through a 'side-sliding, end-catching' mechanism. PMID: 21602793
- MCAK and CENP-E are involved in DDA3-mediated chromosome congression PMID: 21426902
- The identification of the MCAK/HLA-A*0201 and *2402 peptides suggests the possibility of designing peptide-based immunotherapeutic approaches that might prove effective in treating patients with MCAK-positive cancer. PMID: 21165574
- dynamic regulation of MCAK phosphorylation by PLK1 is required to orchestrate faithful cell division PMID: 21078677
- MCAK appears to possess a unique distribution and function in oocyte maturation. PMID: 20406800
- identified the phosphorylation of hSgo2 by Aurora B at the N-terminal coiled-coil region and the middle region, and showed that these phosphorylations separately promote binding of hSgo2 to PP2A and MCAK PMID: 20889715
- Data show that Cdk1 regulates the localization and activity of mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK) in mitosis by directly phosphorylating the catalytic core domain of MCAK. PMID: 20368358
- Mitotic cells deficient in MCAK fail to maintain spindle bipolarity in the absence of Eg5 activity. PMID: 19931454
- identification as a candidate gene for the testis-specific KRPs and its specific expression in the testis was correlated with spermatogenesis and may be correlated with male infertility PMID: 12383881
- MCAK has a role in bipolar spindle assembly along with Kif2a PMID: 15302853
- MCAK is a microtubule-catastrophe promoting factor in vitro, and may serve as a catastrophe-promoting factor in cells. PMID: 15304328
- We propose that tip tracking is a mechanism by which MCAK is preferentially localized to regions of the cell that modulate the plus ends of MTs. PMID: 15883193
- Spindles in human mitotic cells depleted of the kinesin-13 proteins Kif2a and MCAK lack detectable flux and that such cells frequently fail to segregate all chromosomes appropriately at anaphase. PMID: 16243029
- MCAK moves along the microtubule lattice in a one-dimensional (1D) random walk PMID: 16672973
- These data demonstrate that Kif2b function is required for spindle assembly and chromosome movement and that the microtubule depolymerase activities of Kif2a, Kif2b, and MCAK fulfill distinct functions during mitosis in human cells. PMID: 17538014
- Elevated expression of MCAK may be associated with lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. PMID: 17653072
- KIF2C/MCAK expression was significantly suppressed by ectopic introduction of p53. Findings suggest that overexpression of KIF2C/MCAK might be involved in breast carcinogenesis PMID: 17944972
- MCAK is held in an inactive conformation when associated with EB1 PMID: 17968321
- Sp1-binding to the GC-motifs was crucial for promoter activation, but the E2F1-binding to the E2F-motif was crucial for promoter repression. PMID: 18440323
- MCAK expression was higher in colorectal cancer tissue than in corresponding normal tissue; elevated expression level was markedly associated with factors such as lymph node metastasis, venous invasion, peritoneal dissemination & Dukes' classification PMID: 18506187
- A novel function of Aurora-A, the regulation of ch-TOG and MCAK localization, in a common pathway in control of spindle pole integrity. PMID: 18663358
- ch-Tog has at least two distinct roles in spindle formation: it protects kinetochore microtubules from depolymerization by MCAK, and ch-Tog plays an essential role in centrosomal microtubule assembly, a function independent of MCAK activity. PMID: 18809577
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus. Chromosome, centromere. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore.
-
蛋白家族:TRAFAC class myosin-kinesin ATPase superfamily, Kinesin family, MCAK/KIF2 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed at high levels in thymus and testis, at low levels in small intestine, the mucosal lining of colon, and placenta, and at very low levels in spleen and ovary; expression is not detected in prostate, peripheral blood Leukocytes, heart, brain, lung
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6393
OMIM: 604538
KEGG: hsa:11004
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000361298
UniGene: Hs.720061
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
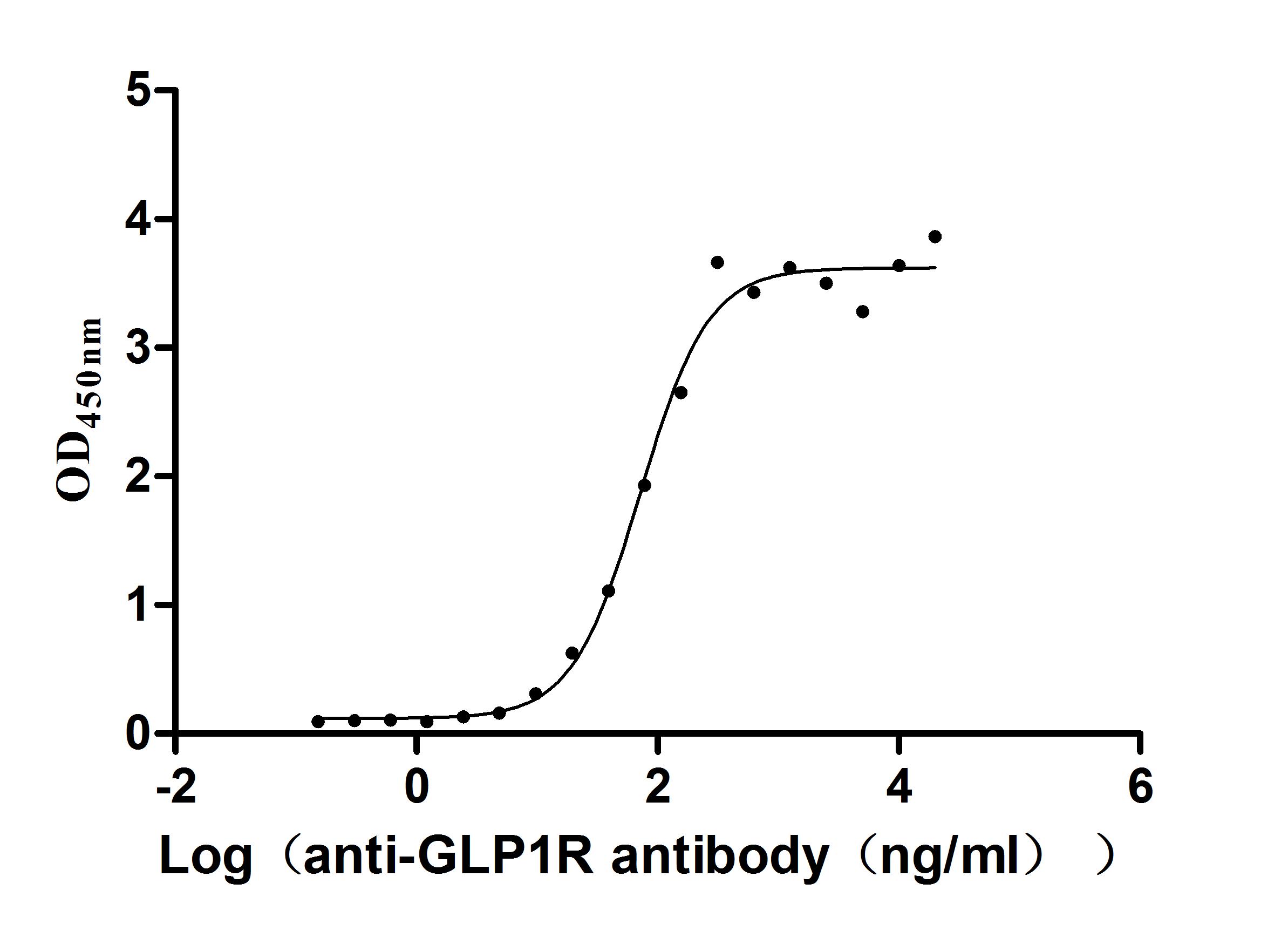
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
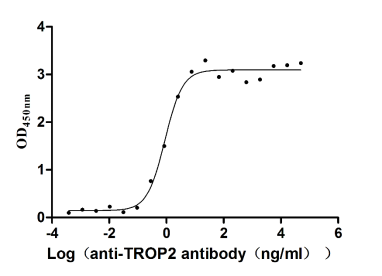
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
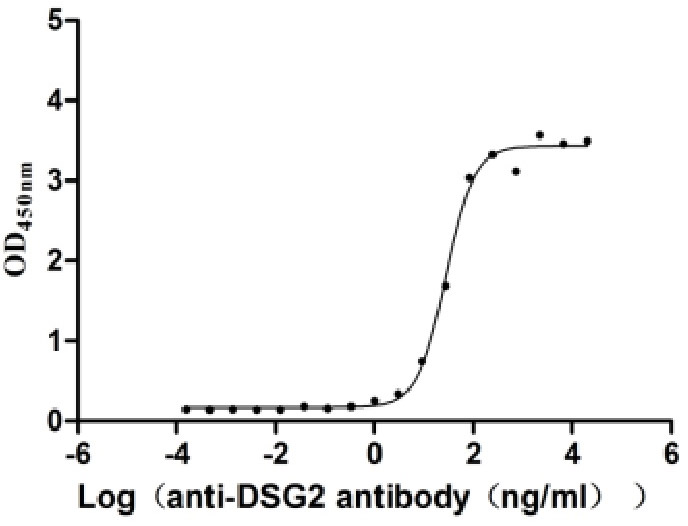
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
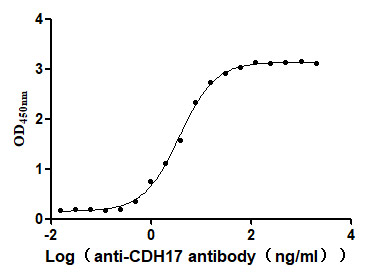
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



f4-AC1.jpg)