Recombinant Human Egl nine homolog 3 (EGLN3)
-
中文名称:人EGLN3重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP880987HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EGLN3重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP880987HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EGLN3重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP880987HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EGLN3重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP880987HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Egl 9 family hypoxia inducible factor 3; Egl nine homolog 3 (C. elegans); Egl nine homolog 3; Egl nine like protein 3 isoform; EGL9 homolog of C. elegans 3; EGLN3; EGLN3_HUMAN; Factor responsive smooth muscle protein; HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase 3; HIF-PH3; HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3; HIFP4H3; HIFPH3; HPH-1; HPH-3; Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase 3; P4H3; PHD3; Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain Containing Protein 3; Prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 3; SM20
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-239
-
氨基酸序列MPLGHIMRLD LEKIALEYIV PCLHEVGFCY LDNFLGEVVG DCVLERVKQL HCTGALRDGQ LAGPRAGVSK RHLRGDQITW IGGNEEGCEA ISFLLSLIDR LVLYCGSRLG KYYVKERSKA MVACYPGNGT GYVRHVDNPN GDGRCITCIY YLNKNWDAKL HGGILRIFPE GKSFIADVEP IFDRLLFFWS DRRNPHEVQP SYATRYAMTV WYFDAEERAE AKKKFRNLTR KTESALTED
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Prolyl hydroxylase that mediates hydroxylation of proline residues in target proteins, such as PKM, TELO2, ATF4 and HIF1A. Target proteins are preferentially recognized via a LXXLAP motif. Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A. Also hydroxylates HIF2A. Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF2A. Hydroxylation on the NODD site by EGLN3 appears to require prior hydroxylation on the CODD site. Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex. Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes. ELGN3 is the most important isozyme in limiting physiological activation of HIFs (particularly HIF2A) in hypoxia. Also hydroxylates PKM in hypoxia, limiting glycolysis. Under normoxia, hydroxylates and regulates the stability of ADRB2. Regulator of cardiomyocyte and neuronal apoptosis. In cardiomyocytes, inhibits the anti-apoptotic effect of BCL2 by disrupting the BAX-BCL2 complex. In neurons, has a NGF-induced proapoptotic effect, probably through regulating CASP3 activity. Also essential for hypoxic regulation of neutrophilic inflammation. Plays a crucial role in DNA damage response (DDR) by hydroxylating TELO2, promoting its interaction with ATR which is required for activation of the ATR/CHK1/p53 pathway. Also mediates hydroxylation of ATF4, leading to decreased protein stability of ATF4.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- PHD3 overexpression may reduce the migratory and invasive capacity of gastric cancer cells, and inhibit the formation of tumor vasculature via negatively regulating HIF1A, which has been revealed to control VEGF transcription. PMID: 28901473
- provides a rationale for targeting the PHD3-mediated regulation of the adaptive cellular hypoxic response in MM and suggests that targeting the O2-sensing pathway, alone or in combination with other anti-myeloma chemotherapeutics, may have clinical efficacy PMID: 29206844
- These results indicate that the immunohistochemistry analysis of the protein expression of PDK1, PHD3, and HIF-1alpha defines the hypoxic status of Neuroblastoma tumors. PMID: 29117193
- These findings indicate that downregulation of PHD3 and FIH in HCC is associated with more aggressive tumor behavior and a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma PMID: 28099905
- PHD3 loss in cancer enables metabolic reliance on fatty acid oxidation via deactivation of ACC2. PMID: 27635760
- demonstrate that downregulation of PHD3 augments metastatic spread in human colorectal cancer and identify MCL-1 as a novel downstream effector of oxygen sensing PMID: 26921340
- In pancreatic Beta cells, knock-down of PHD3 inhibited glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. PMID: 26997627
- Loss of PHD3 expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 26372732
- The selective efficacy of PZ was further demonstrated at the cellular level by observing inhibition of the PHD3-dependent DNA damage response pathway without stabilization of HIF-1alpha. PMID: 26940742
- The enhanced expression of PHD3 might likely contribute to the poor neovascularization and affect the biological characterization in PDAC cancer cells PMID: 25542265
- The data demonstrates that PHD3 can drive cell cycle entry at the G1/S transition through decreasing the half-life of p27 that occurs by attenuating p27S10 phosphorylation. PMID: 26223520
- PHD3 controls EGFR activity by acting as a scaffolding protein that associates with the endocytic adaptor Eps15 and promotes the internalization of EGFR. PMID: 25420589
- PHD3 loss sustains cell proliferation through the control of EGFR. PMID: 25420773
- PHD3 SUMOylation occurs at a cluster of four lysines at the C-terminal end of the protein. Furthermore, PHD3 SUMOylation by SUMO2 or SUMO3 contributes to PHD3-mediated repression of HIF1-dependent transcriptional activity. PMID: 25380826
- HIFPH3 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer lesions is significantly higher than that in para-cancerous and normal lung tissues and is positively associated with lymph node metastasis and microvessel density. PMID: 25081707
- A novel role for PHD3 as a negative regulator of cell motility through posttranslational modification of nonmuscle actins. PMID: 25079693
- LOw expression of PHD3 is associated with gastric cancer. PMID: 23533015
- PHD3 depletion did not affect the expression of the PDH-E1alpha, E1beta, and E2 subunits, or the phosphorylation status of E1alpha, but destabilized the PDH complex (PDC), resulting in less functional PDC. PMID: 25088999
- the relationship between PHD3 expression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition PMID: 24367580
- reduced PHD3 expression in cancerous tissue was accompanied by methylation of the CpG rich region located within the first exon and intron of the PHD3 gene. PMID: 24195777
- PHD3 has an antiproliferative function independent of HIF protein status in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), indicating a novel expression mechanism and function of PHD3. PMID: 24477694
- Studies suggest that hypoxia, HIF-1 alpha, PHD3 and pVHL could be considered as potential therapeutic targets for lung cancer pathogenesis and progression. PMID: 23601303
- PHD-3 mediates specific HIF1-alpha proline 567 hydroxylation, which can function as a new player in the VHL/HIF-1alpha interactions. PMID: 23886708
- The data demonstrate p62 is a critical regulator of the hypoxia response and PHD3 activity, by inducing PHD3 aggregation and degradation under normoxia. PMID: 23345396
- EGLN3 inhibits cIAP1-mediated IKK-gamma ubiquitination by interfering with the interaction between IKK-gamma and cIAP1. PMID: 23732909
- Overexpression of PHD3 is a favorable prognosticator for gastric cancer. PMID: 22290580
- Our study has provided preliminary materials and data for further investigation of the effect of PHD3 on HepG2 cells PMID: 22898032
- Prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) modulates catabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) on cells of the nucleus pulposus through co-activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)/p65 signaling. PMID: 22948157
- Egln3 suppresses glioma progression PMID: 22905089
- identification of HCLK2 as a substrate of PHD3 reveals the mechanism through which hypoxia inhibits the DDR, suggesting hydroxylation of HCLK2 is a potential therapeutic target for regulating the ATR/CHK1/p53 pathway PMID: 22797300
- These results indicate that EGLN3 gene expression in macrophages is dependent on activin A PMID: 22778395
- PHD3 may be an important regulator of apoptosis and it is mainly found in tumors with good prognosis. PMID: 21877141
- a block in G1 to S transition in carcinoma cells under PHD3 inhibition PMID: 22087251
- High tumor cell expression of PHD3 (P= 0.058) and FIH (P= 0.15) did not, however, reach statistical significance PMID: 21887331
- The oxygen sensor PHD3 limits glycolysis under hypoxia via direct binding to pyruvate kinase PMID: 21483450
- these results suggest that PHD3 targets Pax2 for destruction. PMID: 21575608
- Interaction of PKM2 with prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) enhances PKM2 binding to HIF-1alpha and PKM2 coactivator function; PKM2 participates in a positive feedback loop that promotes HIF-1 transactivation and reprograms glucose metabolism in cancer cells. PMID: 21620138
- PHD3 expression is silenced by aberrant CpG methylation in a subset of human carcinoma cell lines of diverse origin and this aberrant cytosine methylation status is the mechanism by which these cancer cell lines fail to upregulate PHD3 mRNA PMID: 21297970
- Prolyl hydroxylases (PHD3) regulate the transcriptional activity of HIF-1alpha. This could be potentially inhibited by polynitrogen compounds. PMID: 21421125
- PHD3 has a role in regulating neutrophil survival in hypoxia PMID: 21317538
- Essential functions of PHD3 in pncreatic tumour growth, apoptosis and angiogenesis. PMID: 20978507
- hPRP19 interacts with PHD3 to suppress the cell death under hypoxic conditions by limiting the function of PHD3 which leads to caspase activation PMID: 20599946
- The CpG island of EGLN3 is frequently methylated in plasma cell dyscrasias and B-cell lymphomas. loss of EGLN3 is an important epigenetic event not only in plasma cell neoplasias but also in B-cell neoplasias. PMID: 19737309
- PHD3 appears to be a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer cells that inhibits IKKbeta/NF-kappaB signaling, independent of its hydroxylase activity. PMID: 19786027
- siRNA targeted degradation of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha results in decreased hypoxia-induced PHD3 expression PMID: 15156561
- results indicate that PHD3 is a TRiC substrate, providing another step at which PHD3 activity may be regulated PMID: 15251459
- EglN3 acts downstream of c-Jun and is specifically required among the three EglN family members for neuronal apoptosis. PMID: 16098468
- Mechanism underlying the regulation of PHD3 availability and activity in hypoxia by the E3 ligase Siah2. PMID: 16958618
- The role of Siah2 phosphorylation in the regulation of its activity toward PHD3 is reported. PMID: 17003045
- PHD-dependent oxygen-sensing recruits both the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) and ATF-4 systems. PMID: 17684156
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed at low levels. Expressed at higher levels in adult heart (cardiac myocytes, aortic endothelial cells and coronary artery smooth muscle), lung and placenta, and in fetal spleen, heart and skeletal muscle. Also expressed in pancreas. Locali
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 14661
OMIM: 606426
KEGG: hsa:112399
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000250457
UniGene: Hs.135507
Most popular with customers
-
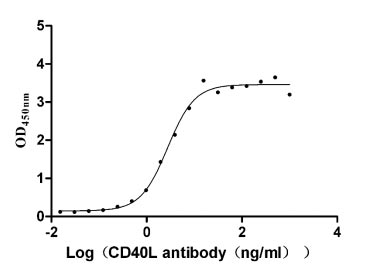
Recombinant Human CD40 ligand (CD40LG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
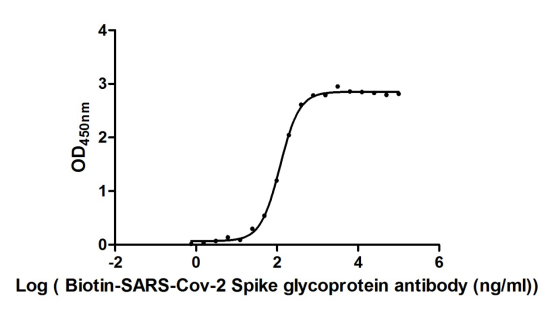
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (2019-nCoV) (SARS-CoV-2)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
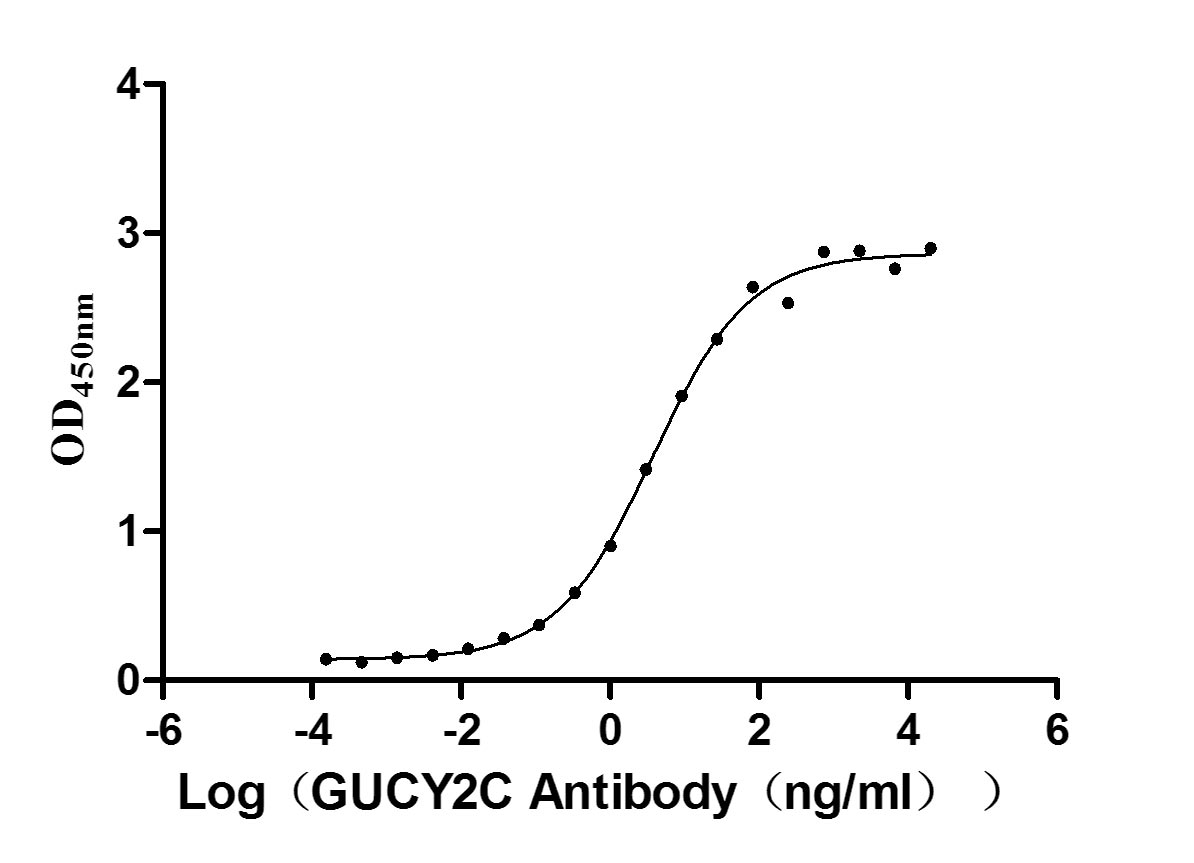
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)