Recombinant Human Double homeobox protein 4 (DUX4), partial
-
中文名称:人DUX4重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP890667HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DUX4重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP890667HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DUX4重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP890667HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DUX4重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP890667HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:DUX4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:DUX4; DUX10Double homeobox protein 4; Double homeobox protein 10
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
表达区域:327-424aa
-
氨基酸序列AGAAPPPQPAPPDASASARQGQMQGIPAPSQALQEPAPWSALPCGLLLDELLASPEFLQQAQPLLETEAPGELEASEEAASLEAPLSEEEYRALLEEL
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor that is selectively and transiently expressed in cleavage-stage embryos. Binds to double-stranded DNA elements with the consensus sequence 5'-TAATCTAATCA-3'. Binds to chromatin containing histone H3 acetylated at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac) and promotes deacetylation of H3K27ac. In parallel, binds to chromatin that lacks histone H3 acetylation at 'Lys-27' (H3K27ac) and recruits EP300 and CREBBP to promote acetylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-27' at new sites. Involved in transcriptional regulation of numerous genes, primarily as transcriptional activator, but mediates also repression of a set of target genes. Promotes expression of ZSCAN4 and KDM4E, two proteins with essential roles during early embryogenesis. Heterologous expression in cultured embryonic stem cells mediates also transcription of HERVL retrotransposons and transcripts derived from ACRO1 and HSATII satellite repeats. May activate expression of PITX1. May regulate microRNA (miRNA) expression. Inappropriate expression can inhibit myogenesis and promote apoptosis.; Probably inactive as a transcriptional activator, due to the absence of the C-terminal region that is important for transcriptional activation. Can inhibit transcriptional activation mediated by isoform 1. Heterologous expression of isoform 2 has no deleterious effect on cell survival.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Sporadic DUX4 expression seen in FSHD myocytes is due to the incomplete repression by the PRC2 complex. PMID: 30122154
- Biallelic DUX4 expression lowers the threshold for disease presentation and is a modifier for disease severity in FSHD2. PMID: 29162933
- recurrent IGH-DUX4 or ERG-DUX4 fusions, ETV6-RUNX1-like gene-expression profile in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, is reported. PMID: 27265895
- The recent identification of aberrant activation of DUX4 transcription in Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. PMID: 29478599
- Case Report: t(10;19) CIC-DUX4 undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma of the abdominal wall. PMID: 28645808
- The DUX4 homeodomains mediate inhibition of myogenesis and are functionally exchangeable with the Pax7 homeodomain. PMID: 28935672
- selective loss of H3K9me3 from the DUX4 locus is associated with expression of DUX4 in late-phase squamous differentiation of human keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 26872601
- We discuss the involvement of this rearrangement in Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy (FSHD), since all mutations in SMCHD1 are not associated with D4Z4 hypomethylation and do not always segregate with the disease PMID: 28744936
- The study describes a model system for inducible DUX4 expression that enables reproducible and synchronized experiments and validates the fidelity and facioscapulohumeral dystrophy (FSHD) relevance of multiple distinct models of DUX4 expression. PMID: 28171552
- DUX4 and Dux may regulate some common pathways, and despite diverging from a common progenitor under different selective pressures for millions of years, the two genes maintain partial functional homology. PMID: 28173143
- We propose that DUX4 controls the cellular migration of mesenchymal stem cells through the CXCR4 receptor. PMID: 27556182
- These novel inhibitors of DUX4 transcriptional activity may thus act on pathways or cofactors needed by DUX4 for transcriptional activation in these cells. PMID: 27245141
- It has been proposed that the induction of DNA damage is a novel function of the DUX4 protein affecting myogenic differentiation of facioscapulohumeral dystrophy myoblasts. PMID: 27519269
- results underscore the complexity of the region immediately downstream of the D4Z4 and uncover a previously unknown function for the beta-satellite region in Dux4 cleavage and polyadenylation. PMID: 28540412
- Gene silencing of CIC-DUX4 as well as Ccnd2, Ret, and Bcl2 effectively inhibited CDS tumor growth in vitro PMID: 28404587
- Estrogens antagonize DUX4 transcriptional activity and its differentiation inhibitory function and support the protective role of these hormones toward facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy myoblast in in vitro differentiation. PMID: 28263188
- Findings show CIC-DUX4 sarcomas occur mostly in young adults within the somatic soft tissues, having a wide spectrum of morphology including round, epithelioid and spindle cells, and associated with an aggressive clinical course, with an inferior survival compared with Ewing sarcoma. Results support classification of CIC-rearranged tumors as an independent molecular and clinical subset of small blue round cell tumors. PMID: 28346326
- DUX4 activate genes associated with a cleavage-stage embryos in muscle cells. PMID: 28459454
- DUX4 role in activating cleavage-stage genes and MERVL/HERVL retrotransposons. PMID: 28459457
- DUX4 rearrangement and overexpression is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 27776115
- Targeted next-generation sequencing of CIC-DUX4 soft tissue sarcomas demonstrates low mutational burden and recurrent chromosome 1p loss. PMID: 27664537
- Transcriptomic analysis showed that DUX4 operates through both target gene activation and repression to orchestrate a transcriptome characteristic of a less-differentiated cell state. PMID: 27744317
- MYC, DUX4, and EIF4A3 might contribute to facioscapulohumeral dystrophy pathophysiology PMID: 28273136
- data shows that DUX4 can become an oncogenic driver as a result of somatic chromosomal rearrangements and that acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and young adults may be a clinical entity distinct from ALL at other ages PMID: 27019113
- We show that a DUX4 minigene, bearing only the homeodomains and C-terminus, is transcriptionally functional and cytotoxic, and that overexpression of a nuclear targeted C-terminus impairs the ability of WT DUX4 to interact with p300 and to regulate target genes. PMID: 26951377
- The aim of this study was to describe seven cases of CIC-DUX4 fusion-positive sarcomas, including the first reported example arising primarily in bone. Our series confirms that CIC-DUX4 fusion-positive sarcomas are aggressive tumours with an adverse prognosis PMID: 27079694
- CIC-DUX4 gene fusion is associated with Round cell sarcoma. PMID: 26800124
- Report DNA-binding sequence preferences of DUX4. PMID: 26823969
- Recent studies indicate that a combination of genetic and epigenetic factors that act on the D4Z4 repeat array determine the probability of DUX4 expression in skeletal muscle and disease penetrance and progression PMID: 26356006
- DUX4 mRNAs were induced during the differentiation of hMSCs into osteoblasts and that this process involved DUX4 and new longer protein forms. PMID: 26192274
- Endogenous DUX4 expression in FSHD myotubes is sufficient to cause cell death and disrupts RNA splicing and cell migration pathways. PMID: 26246499
- Interactions between DUX4 and DUX4c with cytoplasmic proteins play a major role during muscle differentiation. PMID: 26816005
- Loss of D4Z4 repression in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy is observed as hypomethylation of the array accompanied by loss of repressive chromatin marks. [Review] PMID: 26113644
- Our results demonstrate that FRG1 is a direct DUX4 transcriptional target uncovering a novel regulatory circuit contributing to Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. PMID: 25326393
- This feedback loop illustrates an unexpected mode of autoregulatory behavior of a transcription factor, is consistent with 'bursts' of DUX4 expression in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy muscle. PMID: 25564732
- These findings demonstrate that the expression of DUX4 accounts for the majority of the gene expression changes in facioscapulohumeral dystrophy skeletal muscle together with an immune cell infiltration. PMID: 24861551
- There is a special role of the 4q/10q D4Z4 chromatin and the DUX4 open reading frame in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. PMID: 24838473
- The distinct gene signature and immunoprofile of CIC-DUX4 sarcomas suggest a distinct pathogenesis from Ewing sarcoma. PMID: 24723486
- Results show that both DUX4-FL isoforms are expressed in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) myotubes; DUX4-FL expression level is much lower in trapezius than in quadriceps myotubes, which is confirmed by the level of expression of DUX4 downstream genes PMID: 23966205
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy 1 (FSHD1)
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Nucleus.; [Isoform 2]: Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Paired homeobox family
-
组织特异性:Isoform 1: Does not seem to be expressed in normal muscle, but is detected in muscle of individuals with FSHD, and also in testis (at protein level). Isoform 1: Does not seem to be expressed in normal muscle, but in muscle of individuals with FSHD, where
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 50800
OMIM: 158900
KEGG: hsa:100288687
UniGene: Hs.728749
Most popular with customers
-
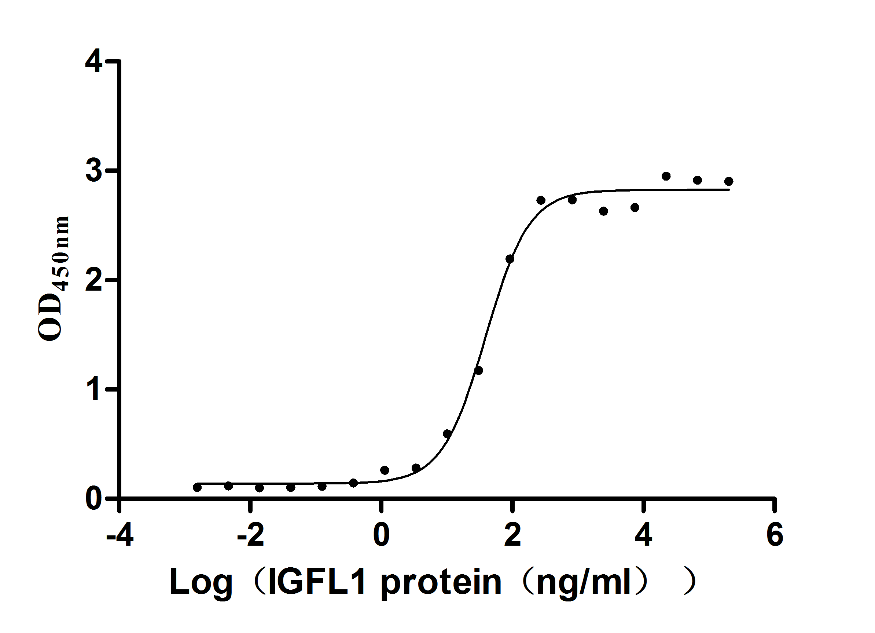
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
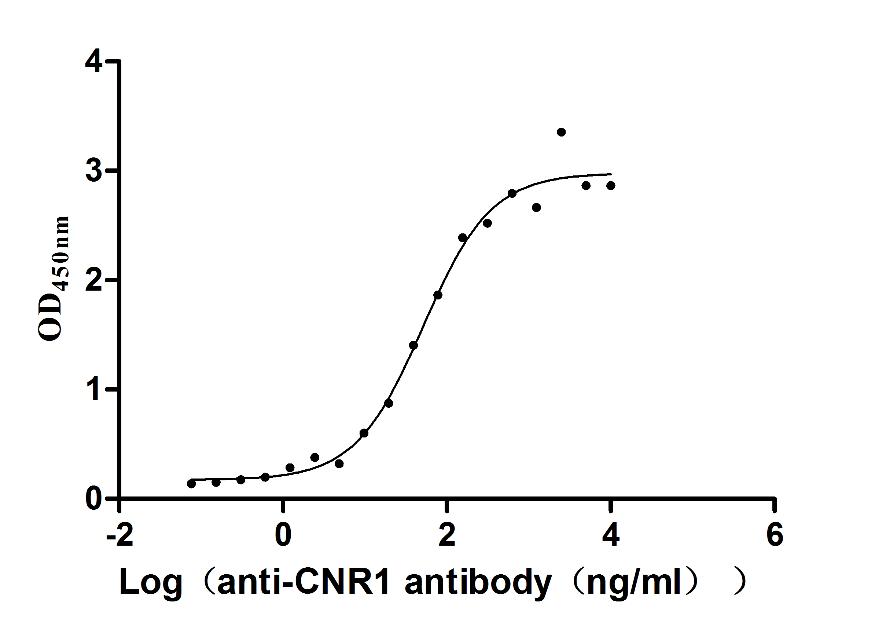
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
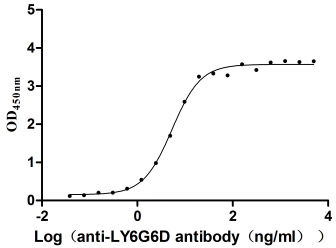
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


f4-AC1.jpg)