Recombinant Human Bifunctional polynucleotide phosphatase/kinase (PNKP)
-
中文名称:人PNKP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP857031HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人PNKP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP857031HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人PNKP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP857031HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人PNKP重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP857031HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PNKP
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:2''(3'')-polynucleotidase; 2'(3')-polynucleotidase; Bifunctional polynucleotide phosphatase/kinase; DEM 1; DEM1; DNA 5' kinase/3' phosphatase; DNA 5''-kinase/3''-phosphatase; EIEE10; Homo sapiens polynucleotide kinase 3' phosphatase (PNKP); MCSZ; PNK 1; PNK1; Pnkp; PNKP DNA kinase; PNKP_HUMAN; Polynucleotide 3'-phosphatase; Polynucleotide 5' hydroxyl kinase; Polynucleotide 5''-hydroxyl-kinase; Polynucleotide kinase 3 prime phosphatase; Polynucleotide kinase 3' phosphatase; Polynucleotide Kinase; Polynucleotide kinase-3''-phosphatase
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-521
-
氨基酸序列MGEVEAPGRL WLESPPGGAP PIFLPSDGQA LVLGRGPLTQ VTDRKCSRTQ VELVADPETR TVAVKQLGVN PSTTGTQELK PGLEGSLGVG DTLYLVNGLH PLTLRWEETR TPESQPDTPP GTPLVSQDEK RDAELPKKRM RKSNPGWENL EKLLVFTAAG VKPQGKVAGF DLDGTLITTR SGKVFPTGPS DWRILYPEIP RKLRELEAEG YKLVIFTNQM SIGRGKLPAE EFKAKVEAVV EKLGVPFQVL VATHAGLYRK PVTGMWDHLQ EQANDGTPIS IGDSIFVGDA AGRPANWAPG RKKKDFSCAD RLFALNLGLP FATPEEFFLK WPAAGFELPA FDPRTVSRSG PLCLPESRAL LSASPEVVVA VGFPGAGKST FLKKHLVSAG YVHVNRDTLG SWQRCVTTCE TALKQGKRVA IDNTNPDAAS RARYVQCARA AGVPCRCFLF TATLEQARHN NRFREMTDSS HIPVSDMVMY GYRKQFEAPT LAEGFSAILE IPFRLWVEPR LGRLYCQFSE G
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays a key role in the repair of DNA damage, functioning as part of both the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) and base excision repair (BER) pathways. Through its two catalytic activities, PNK ensures that DNA termini are compatible with extension and ligation by either removing 3'-phosphates from, or by phosphorylating 5'-hydroxyl groups on, the ribose sugar of the DNA backbone.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Despite presence of an alternative 3'-phosphatase, loss of PNKP significantly sensitizes cells to 3'-phosphate-terminated DSBs, due to a 3'-dephosphorylation defect. PMID: 29807321
- PNKP mutation in two siblings is associated with progressive ataxia, abnormal saccades, sensorimotor neuropathy and dystonia consistent with ataxia with oculomotor apraxia disorders. PMID: 28552035
- we have identified a mutation in PNKP, leading to a phenotype of microcephaly with primordial dwarfism. PMID: 27232581
- XRCC1 and PNKP interact via a high-affinity phosphorylation-dependent interaction site in XRCC1 and a forkhead-associated domain in PNKP. Data suggest a second PNKP interaction site in XRCC1 that binds PNKP with lower affinity and independently of XRCC1 phosphorylation. (XRCC1 = X-ray repair cross complementing protein 1; PNKP = polynucleotide kinase 3'-phosphatase) PMID: 28821613
- In a recombinant PNKP-XRCC4-LigIV complex, stable binding of PNKP requires XRCC4 phosphorylation. Only one PNKP protomer binds per XRCC4 dimer. Both the PNKP FHA and catalytic domains contact the XRCC4 coiled-coil and LigIV BRCT repeats. A surface on the PNKP phosphatase domain may contact XRCC4-LigIV. A mutation on this surface (E326K) impairs PNKP recruitment to damaged DNA and causes microcephaly with seizures. PMID: 28453785
- Mutations in TDP1 and APTX have been linked to Spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy (SCAN1) and Ataxia-ocular motor apraxia 1 (AOA1), respectively, while mutations in PNKP are considered to be responsible for Microcephaly with seizures (MCSZ) and Ataxia-ocular motor apraxia 4 (AOA4). PMID: 27470939
- the role for PNKP in maintaining brain function and how perturbation in its activity can account for the varied pathology of neurodegeneration or microcephaly present in microcephaly with seizures and ataxia with oculomotor apraxia 4 respectively. PMID: 27125728
- In 11 Portuguese patients, PNKP mutations cause ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 4. PMID: 26970421
- Here we report that purified wild-type (WT) ATXN3 stimulates, and by contrast the mutant form specifically inhibits, PNKP's 3' phosphatase activity in vitro. ATXN3-deficient cells also show decreased PNKP activity PMID: 25633985
- We now report that the mutant ATXN3 protein interacts with and inactivates PNKP (polynucleotide kinase 3'-phosphatase), an essential DNA strand break repair enzyme PMID: 25590633
- We identified homozygous or compound-heterozygous PNKP mutations in eight of the nine Portuguese families we studied, suggesting that, in Portugal, mutations in PNKP are the most frequent cause of ataxia with oculomotor apraxia. PMID: 25728773
- we show that modest inhibition of PNKP in a PTEN knockout background enhances cellular radiosensitivity, suggesting that such a "synthetic sickness" approach involving the combination of PNKP inhibition with radiotherapy PMID: 23883586
- Mutations in PNKP have previously been associated with a syndrome of microcephaly, seizures and developmental delay (MIM 613402), and is now associated with a neurodegenerative disorder. PMID: 23224214
- the interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 has roles in the retention of XRCC1 at DNA damage sites and in DNA alkylation damage repair PMID: 22992732
- The data suggest that all four known mutations associated with microcephaly, seizures and developmental delay reduce the cellular stability and level of PNKP protein, with three mutations likely ablating cellular DNA 5'-kinase activity and all of the mutations greatly reducing cellular DNA 3'-phosphatase activity. PMID: 22508754
- the critical role of NEIL2 and PNKP in maintenance of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. PMID: 22130663
- PNKP distorts target DNA structures to access damaged substrate DNA ends, thus providing a molecular mechanism for the involvement of PNKP in the repair of both single- and double-strand breaks. PMID: 22171004
- Results reveal that ionizing radiation-induced phosphorylation of PNKP by ATM and DNA-PK regulates PNKP function at DNA double strand breaks. PMID: 21824916
- Studies indicate that PNKP serves a crucial role in the repair of DNA strand breaks through interactions with other DNA repair proteins, notably XRCC1 and XRCC4. PMID: 21353781
- CK2-mediated phosphorylation of XRCC4 can have different effects on PNKP activity. PMID: 20852255
- The neurological abnormalities in individuals with microcephaly, early onset, intractable seizures and develomental delays may reflect a role for PNKP in several DNA repair pathways. PMID: 20118933
- Involvement of human polynucleotide kinase in double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining PMID: 12032095
- First direct physical evidence for ternary complex formation involving a polynucleotide kinase, AMP-PNP, and an oligonucleotide, supports a reaction mechanism in which ATP and DNA bind simultaneously to the enzyme. PMID: 14556639
- Data show that polynucleotide kinase is associated with the PARP-1-dependent end-joining pathway, and show functional parallels between the PARP-1 and DNA-PK-dependent end-joining processes. PMID: 16364363
- polynucleotide kinase participates in repair of DNA double-strand breaks by nonhomologous end joining but not homologous recombination PMID: 17638872
- XRCC1 enhances the capacity of hPNK to discriminate between strand breaks with 5'-OH termini and those with 5'-phosphate termini; and XRCC1 stimulates hPNK activity by displacing hPNK from the phosphorylated DNA product PMID: 17650498
- The PNKP T5644G variant does not seem to be involved in adenoma recurrence in the Polyp Prevention Trial. PMID: 18414202
- the FHA domain of PNK binds specifically, and with high affinity to a multiply phosphorylated motif in XRCC1 containing a pSer-pThr dipeptide, and forms a 2:1 PNK:XRCC1 complex. PMID: 19155274
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Microcephaly, seizures, and developmental delay (MCSZ); Ataxia-oculomotor apraxia 4 (AOA4)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome.
-
蛋白家族:DNA 3' phosphatase family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in many tissues with highest expression in spleen and testis, and lowest expression in small intestine. Expressed in higher amount in pancreas, heart and kidney and at lower levels in brain, lung and liver.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 9154
OMIM: 605610
KEGG: hsa:11284
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000323511
UniGene: Hs.78016
Most popular with customers
-
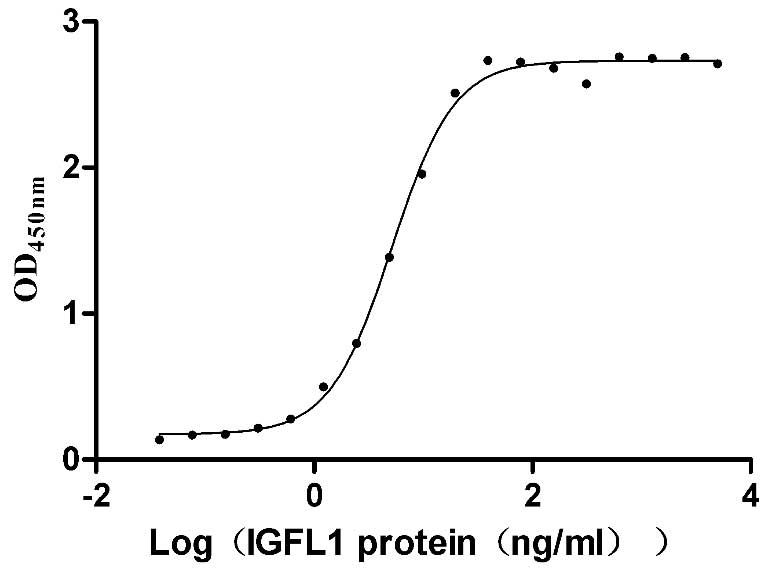
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
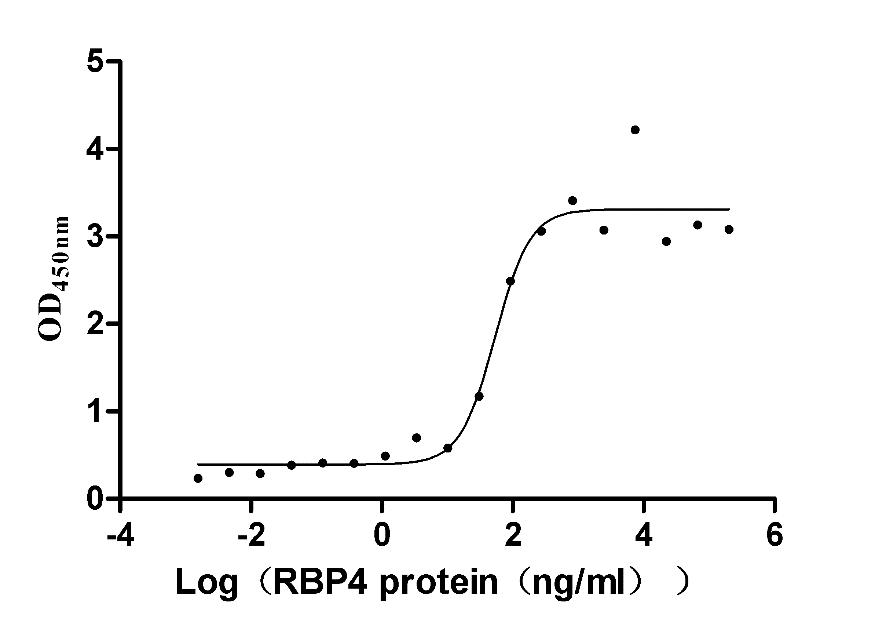
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
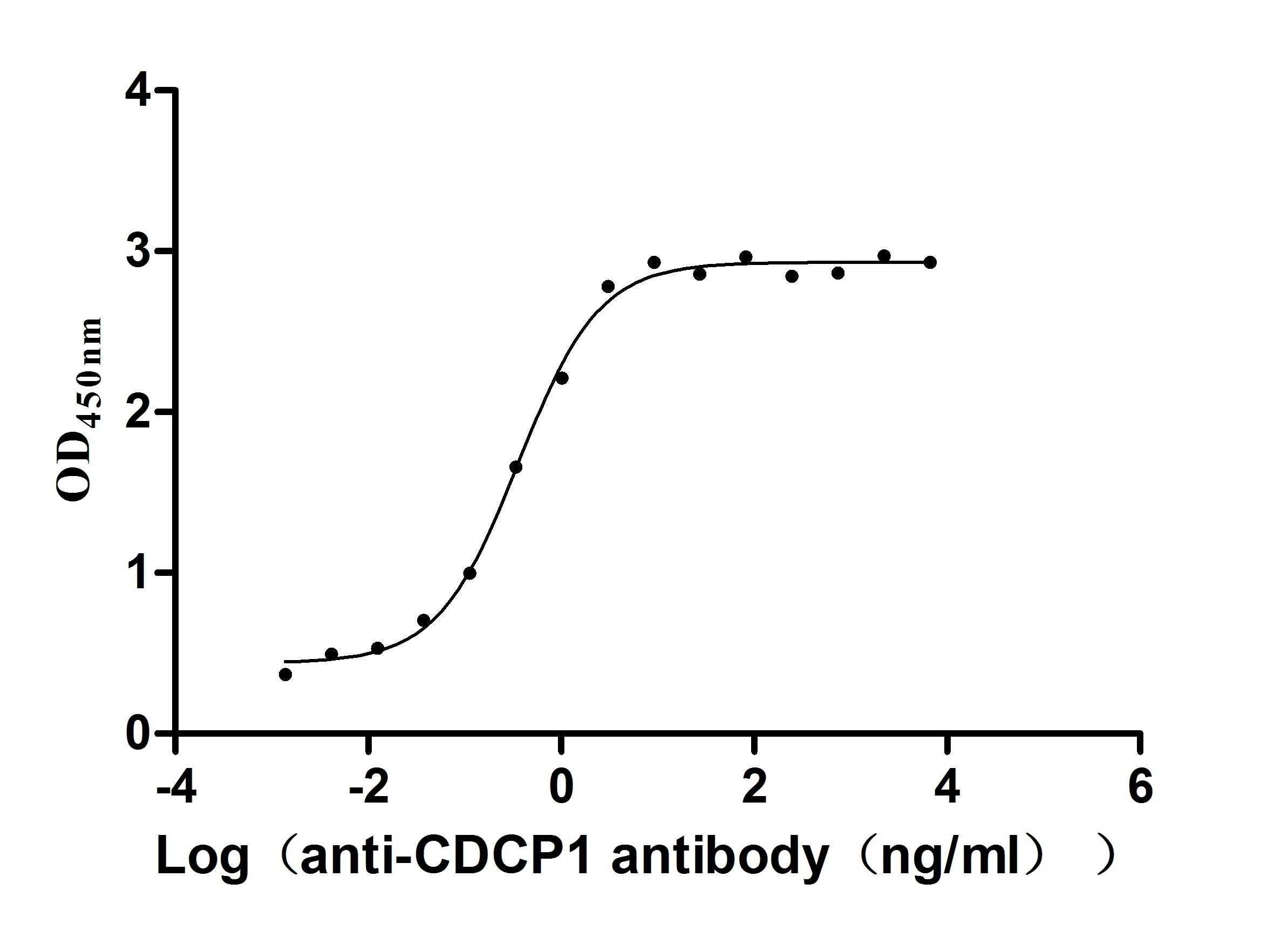
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
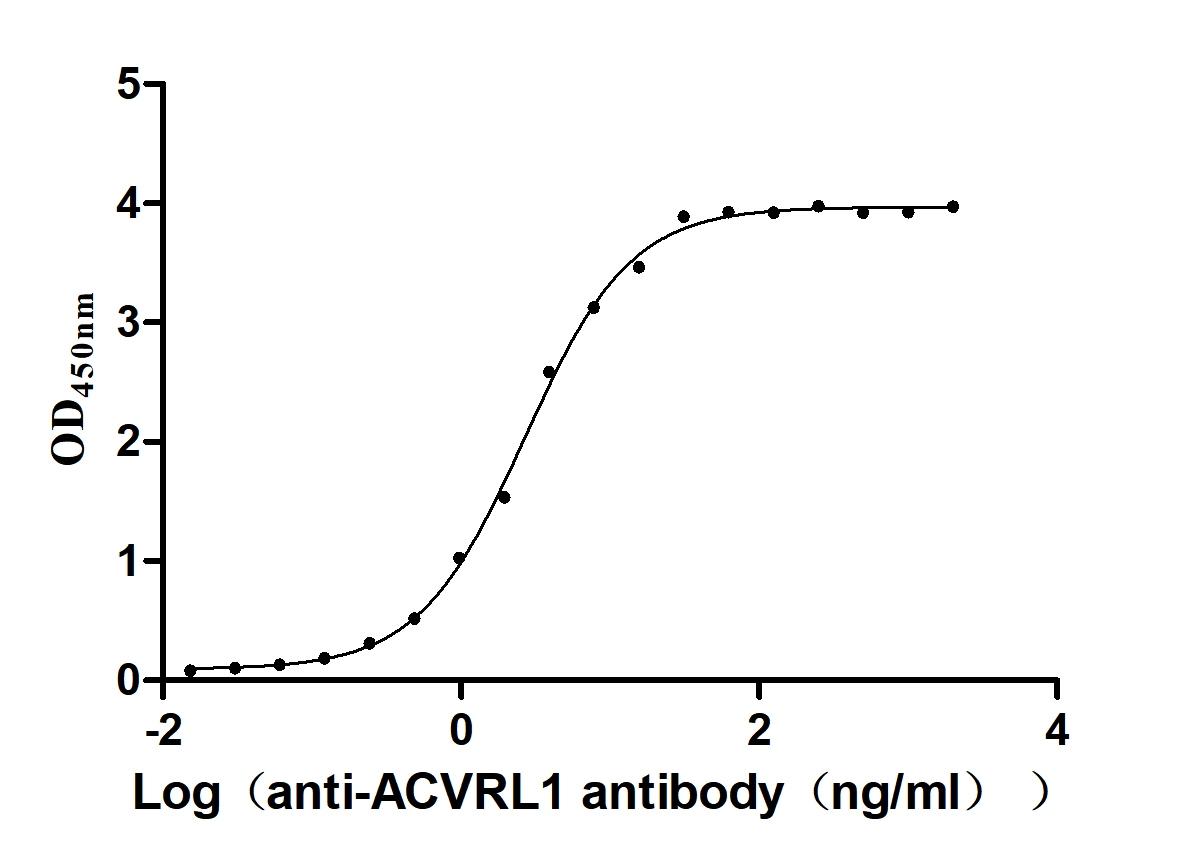
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
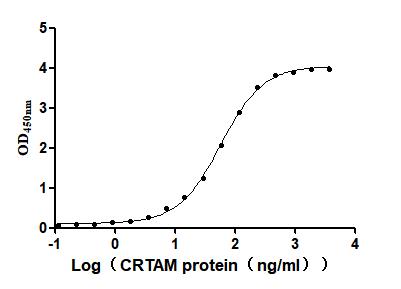
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)


-AC1.jpg)