Recombinant Human Atlastin-1 (ATL1), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Atlastin-1(ATL1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP855500HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Atlastin-1(ATL1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP855500HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Atlastin-1(ATL1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP855500HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Atlastin-1(ATL1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP855500HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human Atlastin-1(ATL1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP855500HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:ATL1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ATL1; GBP3; SPG3A; Atlastin-1; Brain-specific GTP-binding protein; GTP-binding protein 3; GBP-3; hGBP3; Guanine nucleotide-binding protein 3; Spastic paraplegia 3 protein A
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:GTPase tethering membranes through formation of trans-homooligomers and mediating homotypic fusion of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Functions in endoplasmic reticulum tubular network biogenesis. May also regulate Golgi biogenesis. May regulate axonal development.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results suggest that SOCE plays an important role in neuronal regeneration, and mutations in ATL1 may cause HSP, partly by undermining SOCE. PMID: 28240257
- Variants in the ATL1 gene are a less frequent cause of hereditary spastic paraplegia among Czech patients than has been previously reported among other populations. PMID: 28736820
- This study demonstrated that ATL1 gene mutation associated with hereditary spastic paraplegias in group of Polish patients PMID: 26671083
- The results suggest that tethering and lipid mixing are catalyzed concurrently by atlastin GTPase hydrolysis but that the energy requirement for lipid mixing exceeds that for tethering, and the full energy released through crossover formation is necessary for fusion. PMID: 28356327
- that Atlastin 1 mutations may cause autosomal recessively inherited paraplegia with an underlying loss-of-function mechanism. Hence, patients with recessive forms of HSP should also be tested for the Atlastin 1 gene. PMID: 26888483
- This study showed that the mutations of were detected in SPG11, ATL1, NIPA1, and ABCD1 in patient with hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 27084228
- We identified two novel mutations and two previously reported mutations in SPAST and ATL1, respectively. The family with the ATL1 c.1204T>G mutation exhibited male-lethality, female infancy-onset, and pseudo- X-linked dominant transmission PMID: 26600529
- Novel splicing pathogenic variants were identified in ATL1 genes of Korean patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 26208798
- a deficit in the membrane fusion activity of atlastin1 may be a key contributor, but is not required, for hereditary spastic paraplegia causation. PMID: 25761634
- purified and reconstituted human ATL1 exhibited no in vitro fusion activity. When the cytosolic segment of human ATL1 was connected to the transmembrane (TM) region and C-terminal tail (CT) of Drosophila ATL PMID: 25407413
- Data showed 3 micro-mutations and 2 exon deletions in SPAST gene and 2 micro-mutations in ATL1 gene in this cohort of Chinese patients with spastic paraplegia. PMID: 25454648
- Our combined findings show that homozygosity for the ATL1 missense variant remains the only plausible cause of Hereditary spastic paraplegias, whereas heterozygous carriers are asymptomatic. PMID: 24473461
- These data suggest that the C-terminal tail of Atlastin locally destabilizes bilayers to facilitate membrane fusion. PMID: 25555915
- The atlastin-mediated fusion of ER membranes is important for LD size regulation. PMID: 23684613
- The hydrophobic domains of protrudin likely adopt hairpin topologies, similar to those in the atlastins, as well as the ER-shaping reticulons and REEPs. Protrudin interacts with these protein families through the hydrophobic segments. PMID: 23969831
- Three novel ATL1 mutations are identified in a cohort of patients with upper motor neuron syndrome. PMID: 23108492
- frontal glucose hypometabolism was associated with frontal cognitive impairment indicating that widespread neuropathology associated with mutations in the SPG3A gene PMID: 23233086
- these results further supports the role of the atlastin-1 of BMP signaling cascade in axonal maintenance and axonal degeneration, which is seen in various types of hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 23079343
- The N355K atlastin 1 mutation is associated with hereditary sensory neuropathy. PMID: 22340599
- The cytoplasmic domain of atlastin acts as a tether and homotypic interactions are timed by GTP binding and hydrolysis. PMID: 23334294
- increasing the distance of atlastin complex formation from the membrane inhibits fusion, suggesting that this distance is crucial for atlastin to promote fusion PMID: 21930898
- previously unreported autosomal dominant mutations in the atlastin gene in hereditary spastic paraplegia PMID: 20718791
- We identified a novel mutation, c.1040T>C (p. M347T), in a family with axonal neuropathy in addition to spastic paraplegia. PMID: 21321493
- experiments also show that membrane fusion is facilitated by the C-terminal cytosolic tails following the two transmembrane segments. Finally, our results show that mutations in ATL1 causing hereditary spastic paraplegia compromise homotypic ER fusion PMID: 21368113
- a model for nucleotide-dependent regulation of atlastin with implications for membrane fusion. This mechanism is affected in several mutants associated with HSP, providing insights into disease pathogenesis. PMID: 21220294
- This study highlights an unexpected major role for atlastin-1 in the function of sensory neurons and identifies hereditary sensory neuropathy type I and Spastic paraplegia 3, autosomal dominant as allelic disorders. PMID: 21194679
- In a large cohort of Spanish patients with spastic paraplegia, SPAST and ATL1 mutations were found in 15% of the cases PMID: 20932283
- Data report a new heterozygous S398F mutation in exon 12 of the SPG3A gene causing a very early-onset spastic paraplegia in association with motor axonal neuropathy resembling diplegic cerebral palsy. PMID: 19735987
- a new mutation in SPG3A in Italian family manifesting a complex phenotype characterized by cerebellar involvement and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like syndrome PMID: 19768483
- Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSP) proteins atlastin-1, spastin, and REEP1 interact within the tubularER membrane in corticospinal neurons to coordinate ER shaping and microtubule dynamics. PMID: 20200447
- study describes two patients with Silver phenotype including one with a novel SPG4 (Spastin) mutation and a second with a known SPG 4 mutation (previously unassociated with this phenotype) and a concomitant previously unreported mutation in SPG3A PMID: 19730024
- This study identified a novel SPG3A mutation (L157W) in the proband and her affected child. PMID: 16533974
- This study reports a novel mutation in the SPG3A gene in a family with spastic paraplegia, further confirming that mutations in this gene cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 12112092
- interaction with NIK/HGK PMID: 12387898
- identification as a multimeric integral membrane GTPase that may be involved in Golgi membrane dynamics or vesicle trafficking PMID: 14506257
- The R239C mutation was found to co-segregate with autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia (ADHSP) in one English ADHSP family confirming a widespread prevalence for this commonly occurring mutation PMID: 14607301
- In a family with autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia, heterozygous substitution in exon 12 exchanges arginine for tryptophan at position 415 (R415W) abolishing an MSP I recognition site (CC'GG). PMID: 15184642
- This paper report a novel mutation in the SPG3A gene in an African American family with an infantile onset of autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 15477516
- Three novel mutations were found in exons 4, 9, and 12 of the atlastin gene and the common R239C mutation located in exon 7 was confirmed in a 7th family of European origin PMID: 15517445
- All mutations of atlastin1 in young-onset autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia patients in France were found in exons 7, 8, 12, and 13. These exons should be given priority when performing molecular diagnoses for SPG3A. PMID: 15596607
- This study report a new atlastin(R495W) mutation causing spastic paraplegia in association with axonal neuropathy in an Italian family. PMID: 15742100
- Spastin and atlastin, two proteins mutated in autosomal-dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia, are binding partners. PMID: 16339213
- Seven families with six different SPG3A mutations were identified among 106 with autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP). PMID: 16401858
- Interaction between atlastin and spastin may define a cellular biological pathway that is important in axon maintenance, the failure of which may be pathogenetically relevant. PMID: 16815977
- Atlastin plays a role in vesicle trafficking in the ER/Golgi interface PMID: 17321752
- This study identified Y469C mutation in SPG3A in Japanese family with hereditary spastic paraplegia. PMID: 17380240
- In a large SPG3A screen of 70 hereditary spastic paraplegia subjects, a novel in-frame deletion, p.del436N, was identified which affects neither the guanosine triphosphatase activity of atlastin nor interactions between atlastin and spastin. PMID: 17427918
- Mutations in SPG3A represent an important cause of patients in the overall hereditary spastic paraplegia population. PMID: 17502470
- identification of one novel and one known SPG3A mutation in screening 20 families and 23 sporadic cases of hereditary spastic paraplegia in Chinese Han population PMID: 17531128
- We describe a severe case of herediatry spastic paraplegia, extending the clinical spectrum of SPG3A mutations to a very severe and very early complicated phenotype. PMID: 18446315
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Spastic paraplegia 3, autosomal dominant (SPG3); Neuropathy, hereditary sensory, 1D (HSN1D)
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, axon.
-
蛋白家族:TRAFAC class dynamin-like GTPase superfamily, GB1/RHD3-type GTPase family, GB1 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed predominantly in the adult and fetal central nervous system. Measurable expression in all tissues examined, although expression in adult brain is at least 50-fold higher than in other tissues. Detected predominantly in pyramidal neurons in the c
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11231
OMIM: 182600
KEGG: hsa:51062
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000351155
UniGene: Hs.584905
Most popular with customers
-
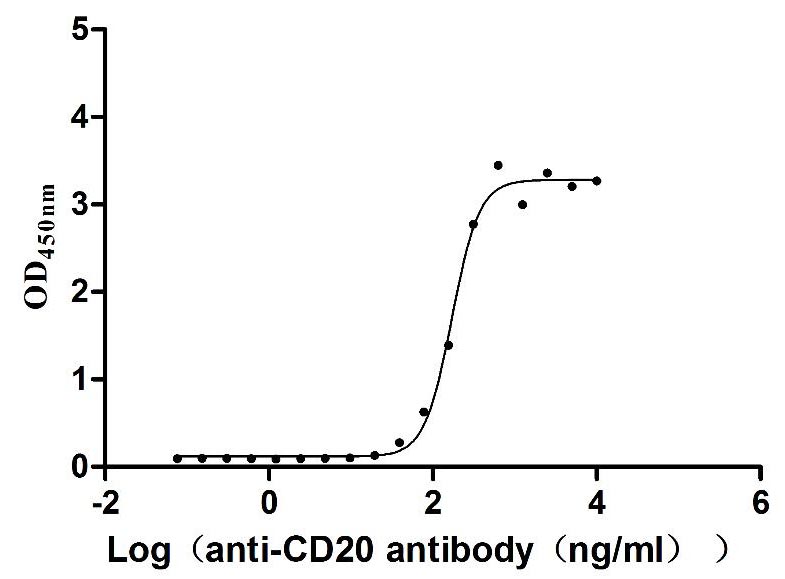
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
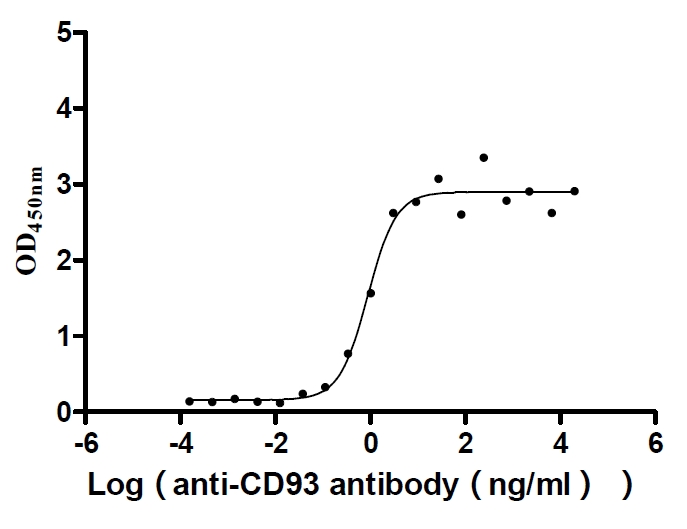
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
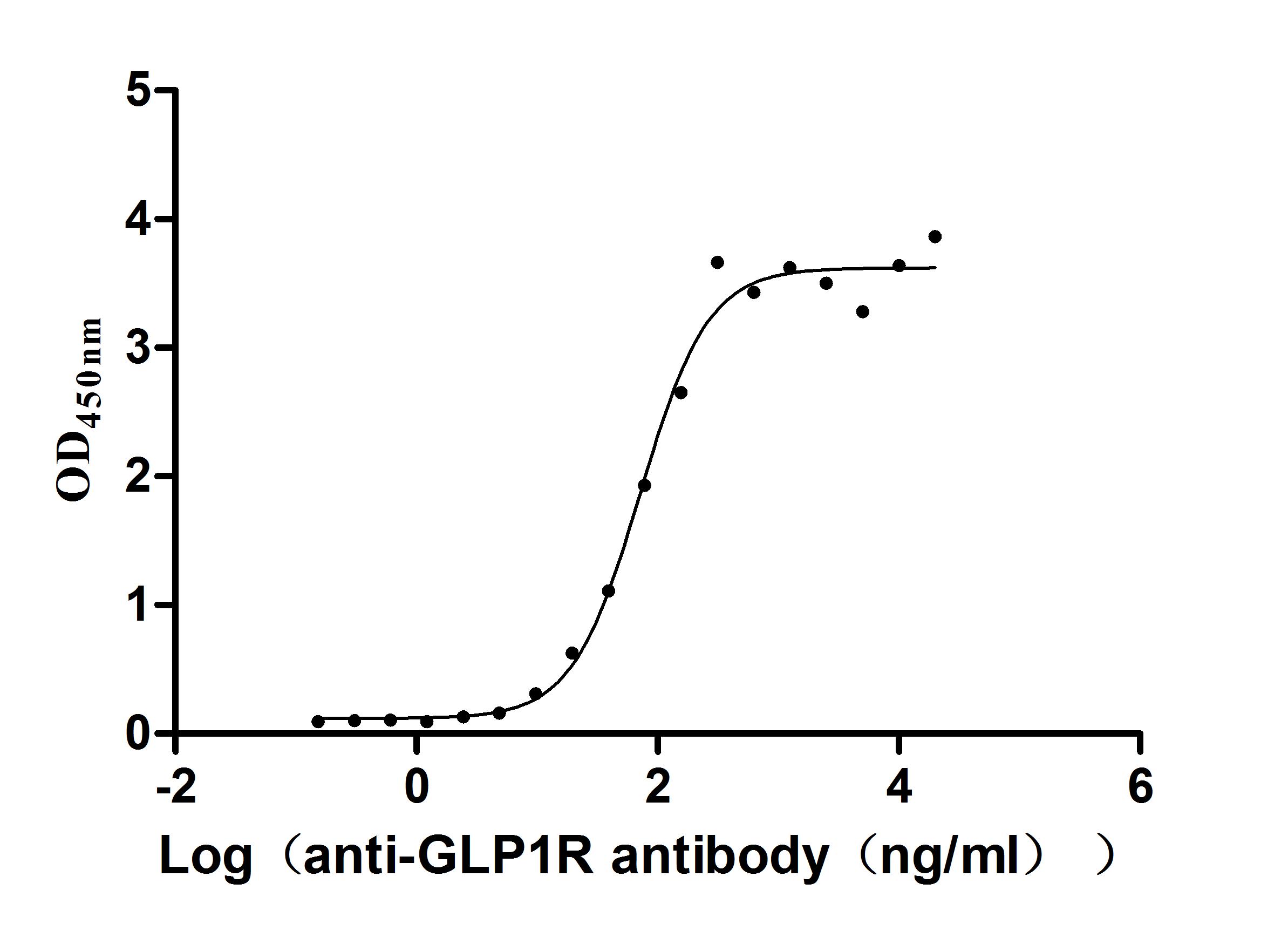
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
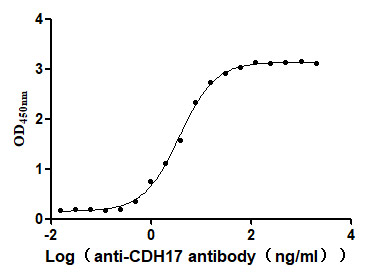
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
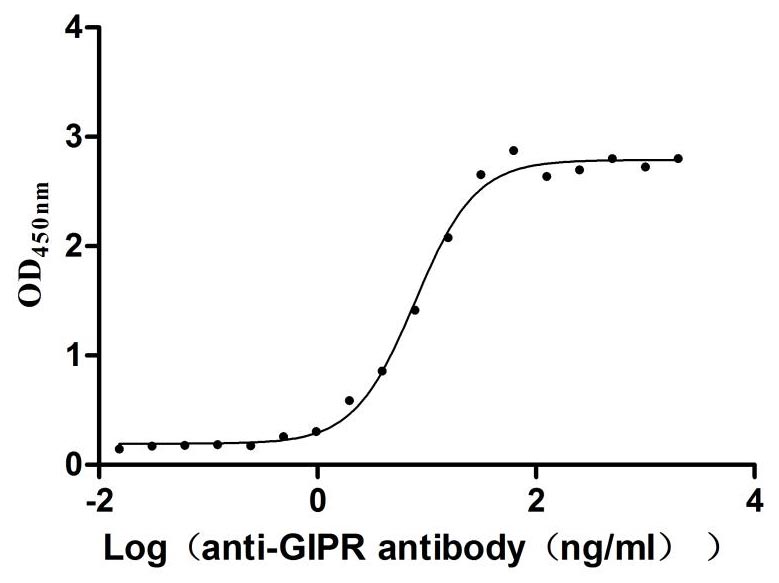
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
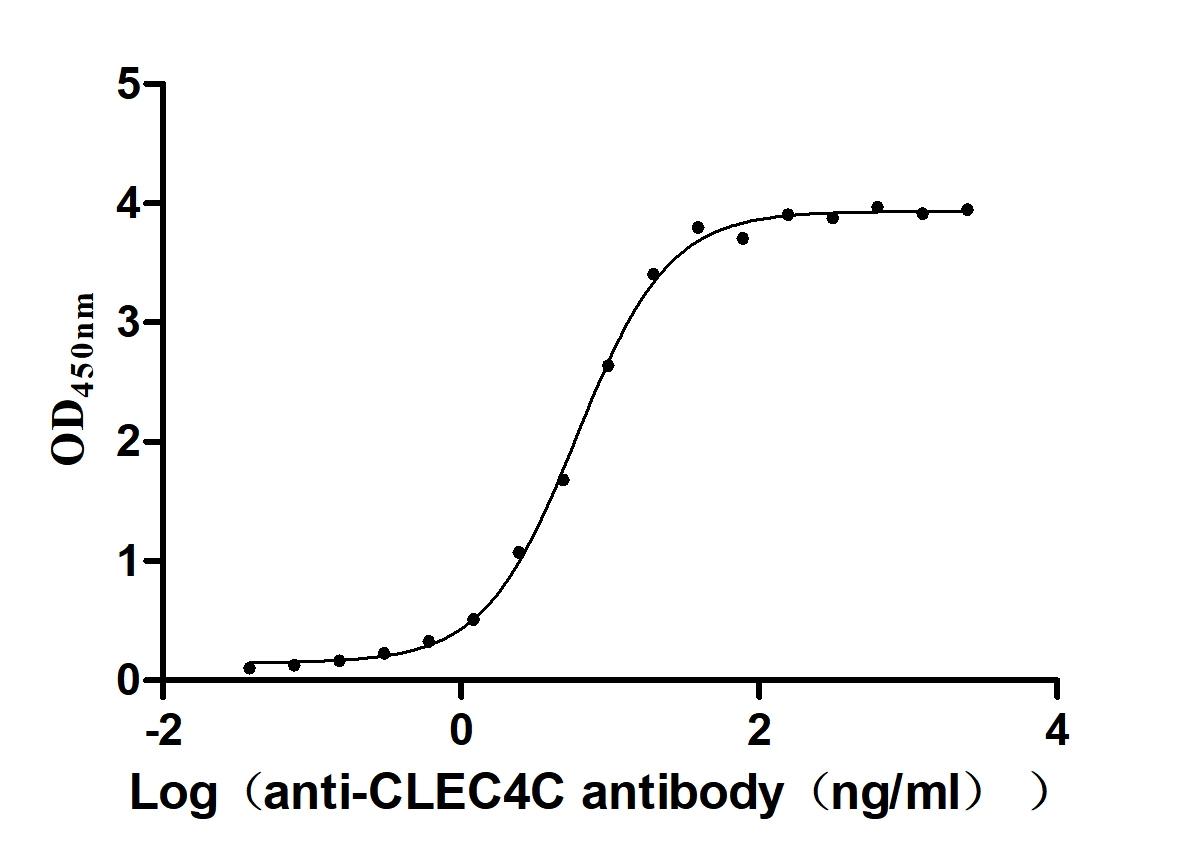
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
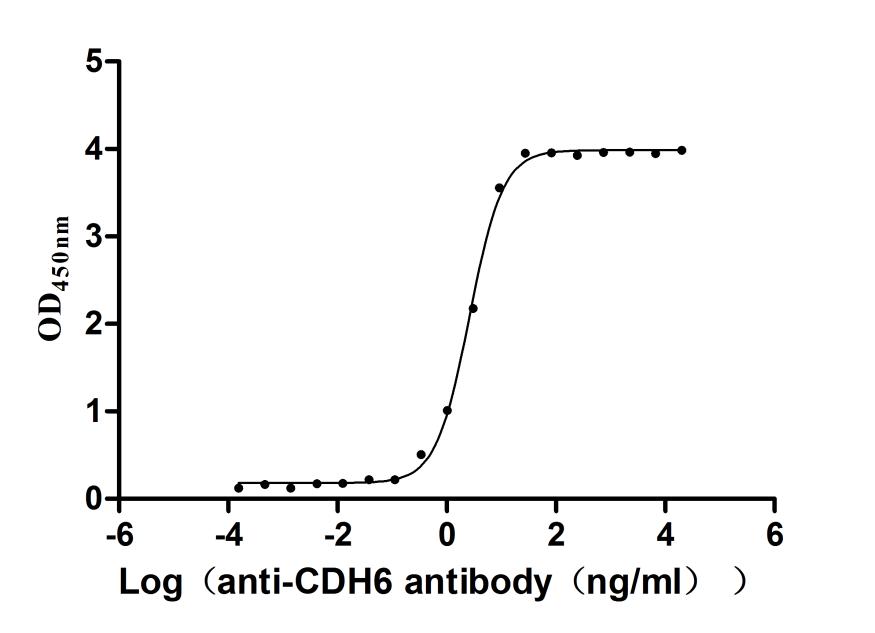
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
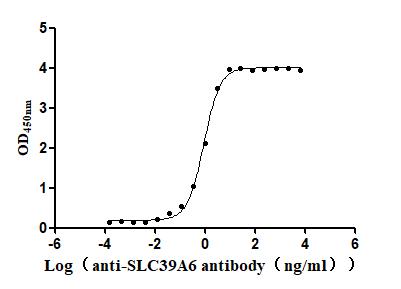
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)