Recombinant Escherichia coli DNA polymerase IV (dinB)
-
中文名称:大肠杆菌dinB重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP675092ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大肠杆菌dinB重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP675092ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大肠杆菌dinB重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP675092ENV-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大肠杆菌dinB重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP675092ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大肠杆菌dinB重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP675092ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:dinB
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:dinB; dinP; b0231; JW0221DNA polymerase IV; Pol IV; EC 2.7.7.7; Translesion synthesis polymerase IV; TSL polymerase IV
-
种属:Escherichia coli (strain K12)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-351
-
氨基酸序列MRKIIHVDMD CFFAAVEMRD NPALRDIPIA IGGSRERRGV ISTANYPARK FGVRSAMPTG MALKLCPHLT LLPGRFDAYK EASNHIREIF SRYTSRIEPL SLDEAYLDVT DSVHCHGSAT LIAQEIRQTI FNELQLTASA GVAPVKFLAK IASDMNKPNG QFVITPAEVP AFLQTLPLAK IPGVGKVSAA KLEAMGLRTC GDVQKCDLVM LLKRFGKFGR ILWERSQGID ERDVNSERLR KSVGVERTMA EDIHHWSECE AIIERLYPEL ERRLAKVKPD LLIARQGVKL KFDDFQQTTQ EHVWPRLNKA DLIATARKTW DERRGGRGVR LVGLHVTLLD PQMERQLVLG L
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Poorly processive, error-prone DNA polymerase involved in translesion repair and untargeted mutagenesis. Copies undamaged DNA at stalled replication forks, which arise in vivo from mismatched or misaligned primer ends. These misaligned primers can be extended by Pol IV. Exhibits no 3'-5' exonuclease (proofreading) activity. Overexpression of Pol IV results in increased frameshift mutagenesis. It is required for stationary-phase adaptive mutation, which provides the bacterium with flexibility in dealing with environmental stress, enhancing long-term survival and evolutionary fitness. Not seen to be involved in translesion snythesis even when stimulated by the beta slding-clamp and clamp-loading complex, which do however increase non-targeted DNA polymerase efficiency 3,000-fold, may be due to targeting to stalled replication forks on nondamaged DNA. Involved in translesional synthesis, in conjunction with the beta clamp from PolIII.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- In an SOS-constitutive mutant that expresses high levels of pol IV, few foci are observed in the absence of damage, indicating that within cells access of pol IV to DNA is dependent on the presence of damage, as opposed to concentration-driven competition for binding sites. PMID: 29351274
- We hypothesize that damaged bases allow the switch to use of Pol IV during MBR by pausing the replicative polymerase to allow polymerase exchange in the replisome. The findings suggest that spontaneous mutation by MBR is regulated by regulation of the intracellular level of ROS PMID: 28727736
- A mathematical model let us define the geometry (infer the structure) of the toxic intermediate as being formed when NER incises a lesion that resides in close proximity of another lesion in the complementary strand. This critical NER intermediate requires Pol IV / Pol II for repair, it is either lethal if left unrepaired or mutation-prone when repaired PMID: 28686598
- although lagging-strand synthesis is still perturbed in holD trkA mutants, the trkA mutation allows HolD-less Pol III HE to resist increased levels of the SOS-induced bypass polymerase DinB PMID: 27280472
- The steric gate is crucial for rNTP discrimination because of its role in specifically promoting a dNTP-induced conformational change and that rNTP discrimination occurs in a relatively closed state of the polymerases. PMID: 25684709
- The structural dynamics of DinB changes upon substrate binding, noncognate DNA damage prevents the formation of the active conformation of DINB. PMID: 25899385
- A DeltadinB mutation that sensitizes Escherichia coli to the lethal effects of UV- and X-radiation. PMID: 24657250
- The study provides evidence that translesion DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase IV can directly restart replication fork stalled at a DNA lesion. PMID: 24957605
- These findings indicate that preferential D-loop extension by Pol IV facilitates error-prone recombination and explain how Pol II reduces such errors in vivo. PMID: 23686288
- The data shows that the Ser42 residue is present at a strategic location to stabilize mismatches in the PolIV active site, and thus facilitate the appearance of transition and transversion mutations. PMID: 23525461
- DinB overexpression generates temporarily viable but non-reproductive cells possessing a fatally depleted chromosomal content. PMID: 23229309
- study of this DinB derivative has revealed a key surface on DinB, which appears to modulate the strength of multiprotein complex binding, and has suggested a binding order of RecA and UmuD to DinB PMID: 23292773
- DinB impedes replication fork progression in a way that does not activate RecA. PMID: 22820381
- The results demonstrate that Pol IV requires the interaction with the C-terminal tail of single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB) to replicate DNA efficiently when the template ssDNA is covered with SSB. PMID: 22447448
- Although it is not a source of enhanced mutagenesis in vivo, the translesion synthesis DNA polymerase IV was critical for the survival of uropathogenic Escherichia coli during urinary tract infection during an active inflammatory assault. PMID: 21597325
- The s demonstrate that Pol IV interacts in vitro with Rep DNA helicase and that this interaction enhances Rep's helicase activity. PMID: 21320186
- Efficient extension of slipped DNA intermediates by DinB is required to escape primer template realignment by DnaQ. PMID: 21421753
- By initiating or participating in double-strand break repair, SbcCD may provide DNA substrates for Pol IV polymerase activity. PMID: 21131491
- Separate DNA Pol II- and Pol IV-dependent pathways of stress-induced mutation during double-strand-break repair in Escherichia coli are controlled by RpoS. PMID: 20639336
- Study shows that the little finger domain of PolIV-beta interaction stabilizes the clamp-polymerase complex in vitro and is necessary for the access of PolIV to ongoing replication forks in vivo. PMID: 19843218
- expression of a variant generated by mutation of an evolutionarily conserved tyrosine (Y79) transforms dinB into a bactericidal drug, resulting in profound toxicity even in a dinB(+) background PMID: 19948952
- REVIEW: properties and functions of Pol IV PMID: 15588845
- levels of Pol IV are positively affected by the heat shock-induced molecular chaperone GroE PMID: 15629916
- Induction of dinB transcription mediated by ceftazidime produces an increase in the reversion of a +1 Lac frameshift mutation. PMID: 15687217
- Ppk is required for the increased rate of growth-dependent mutations produced by Pol IV overexpression; results suggest Ppk is affecting the activity of Pol IV in a manner that is independent of any previously known factors that regulate this polymerase PMID: 16045619
- preferential mutagenesis during lagging strand synthesis from overproduction of DNA polymerase IV PMID: 16166552
- DinB and its orthologues are specialized to catalyse relatively accurate translesion synthesis over some N2-dG adducts that are ubiquitous in nature, and that lesion bypass occurs more efficiently than synthesis on undamaged DNA PMID: 16407906
- data imply that PolIV can also promote mutation in growing cells under genome stress due to excess single-stranded DNA PMID: 16547019
- Study shows that enhanced recombination is dependent on the factors: the RuvA Holliday junction helicase, the RecJ single-strand DNA exonuclease, the RadA/Sms RecA-paralog protein of unknown function and, surprisingly, the DinB translesion polymerase. PMID: 16904387
- while Pol IV contributes to spontaneous mutations within the HSV-tk coding sequence, Pol IV does not play a significant role in spontaneous mutagenesis at [G/C](10), [GT/CA](10), or [TC/AG](11) microsatellite alleles PMID: 17397877
- PolIV performs an error-free bypass of DNA damage that accumulates in the alkA tag genetic background. This result indicates that PolIV is involved in the error-free bypass of cytotoxic alkylating DNA lesions PMID: 17483416
- Data show that an important role is described for Pol IV in producing the mutations and a high fraction of the mutations is dependent on the action of Pol IV in a (dinB) gene dosage-dependent manner. PMID: 18156258
- Observations indicate that proteins like RecA and UmuD(2) may be responsible for managing the mutagenic potential of DinB orthologs throughout evolution. PMID: 18158902
- Overexpression of DinB inhibits DNA replication by targeting DNA polymerase beta, and cell proliferation is also inhibited. PMID: 18761688
- NusA, a modulator of RNA polymerase, interacts with the DNA polymerase DinB. PMID: 18996995
- Elevated DinB expression in Delta(clpP-clpX) cells contributes to elevated mutagenesis. PMID: 19040636
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:DNA polymerase type-Y family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: ecj:JW0221
STRING: 316385.ECDH10B_0213
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
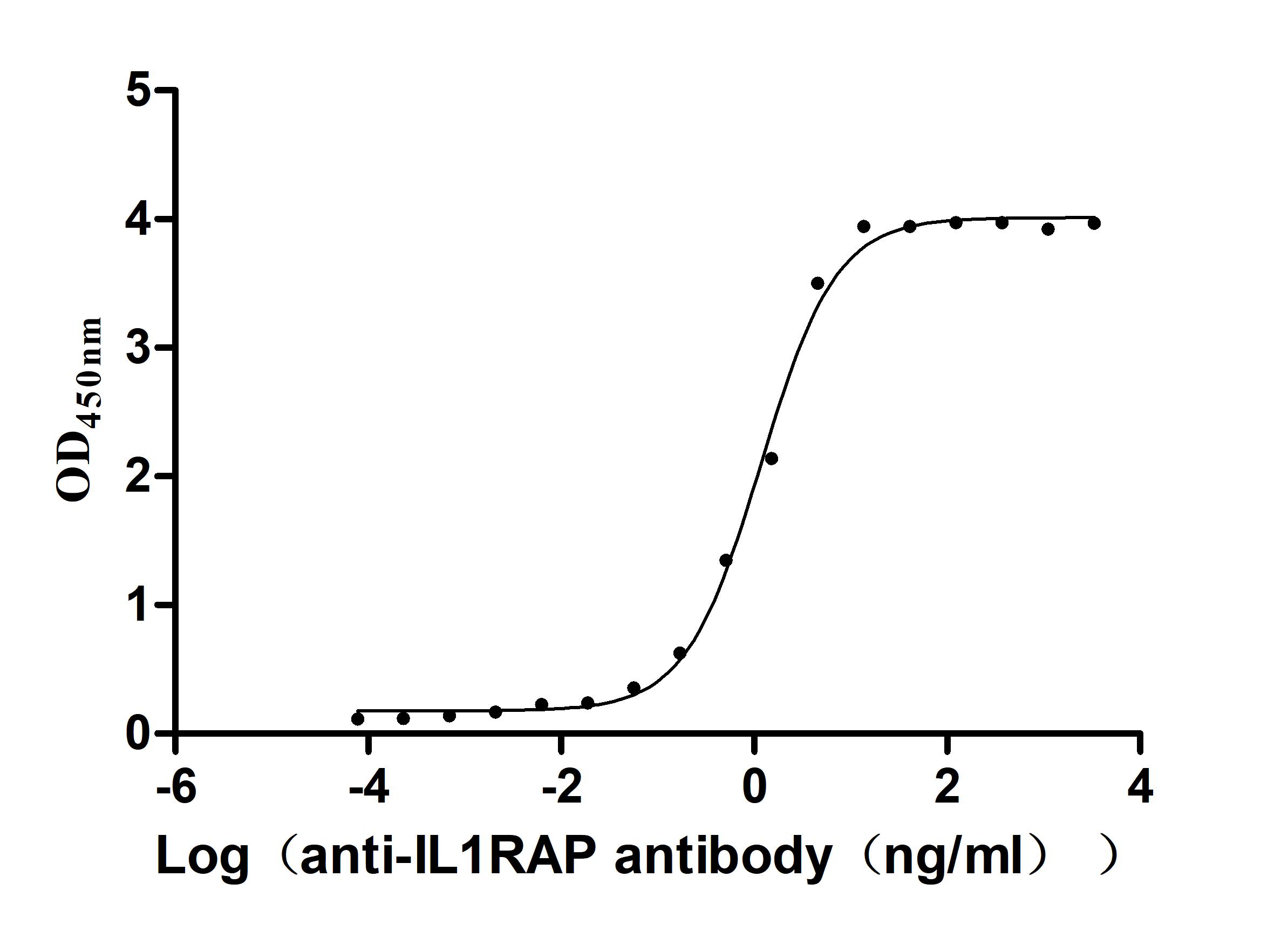
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)