Recombinant Rat Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 2 (Kcna2), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP012007RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP012007RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP012007RA1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP012007RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP012007RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Kcna2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Kcna2; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 2; RAK; RBK2; RCK5; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.2
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain and the central nervous system, but also in the cardiovascular system. Prevents aberrant action potential firing and regulates neuronal output. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane. Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6, KCNA7, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel. Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation of delayed rectifier potassium channels. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to a particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA2 forms a delayed-rectifier potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by slow spontaneous channel closure. In contrast, a heteromultimer formed by KCNA2 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation. Response to toxins that are selective for KCNA1, respectively for KCNA2, suggests that heteromeric potassium channels composed of both KCNA1 and KCNA2 play a role in pacemaking and regulate the output of deep cerebellar nuclear neurons. KCNA2-containing channels play a presynaptic role and prevent hyperexcitability and aberrant action potential firing. Response to toxins that are selective for KCNA2-containing potassium channels suggests that in Purkinje cells, dendritic subthreshold KCNA2-containing potassium channels prevent random spontaneous calcium spikes, suppressing dendritic hyperexcitability without hindering the generation of somatic action potentials, and thereby play an important role in motor coordination. Plays a role in the induction of long-term potentiation of neuron excitability in the CA3 layer of the hippocampus. May function as down-stream effector for G protein-coupled receptors and inhibit GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons. May contribute to the regulation of neurotransmitter release, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Contributes to the regulation of the axonal release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Reduced KCNA2 expression plays a role in the perception of neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury, but not acute pain. Plays a role in the regulation of the time spent in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- indings suggest that increased dorsal horn DNMT3a contributes to bone cancer pain through silencing dorsal horn Kv1.2 expression PMID: 29056068
- Ventricular Kcna2 AS expression increases in rats with CHF and contributes to reduced IKs, prolonged APs, and the occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias by silencing Kcna2. PMID: 29263036
- Data indicate that in cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) images of the relatively small Kv1.2 channel complex, the protein particle's contribution is quite weak compared to the membrane density. PMID: 26835990
- the dynamics of the ion conduction processes in the Kv1.2 pore domain PMID: 26950215
- Kv1.2 mediates heterosynaptic modulation of direct cortical synaptic inputs in CA3 pyramidal cells PMID: 26047212
- An R300C mutation creates a large cavity in the voltage sensing domain. PMID: 25588216
- Data suggest that exercise training reverses the pathological expression of the Kv1.2, Kv1.5, and BKCa channels in aortic myocytes from spontaneously hypertensive rats. PMID: 25661478
- a majority of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons were positive for Kv channel alpha subunit Kv1.2. PMID: 24472174
- The alpha subunit of Kv1.2 channels determines the pharmacological characteristics of potassium channel blockers by their position in the channel. PMID: 23725331
- Cell-surface Kv1.2 alpha-subunit levels are controlled by secretin-regulated Kv1.2 endocytic trafficking. PMID: 22764231
- myelin regulates both trafficking and activity of Kv1 channels along hippocampal axons through TAG-1 PMID: 21602278
- Kv1.1 or 1.2 homomers and their concatenated forms between the pairs of adjacently and diagonally arranged heterotetramers show differential sensitivity to tetraethylammonium. PMID: 20805574
- proper amounts of Kv1 channels and their associated proteins are required for efficient transport of Kv1 channel proteins along axons PMID: 20694152
- Results indicate that the extreme C-terminal end of the S6 inner helix plays an important regulatory role in the activation of the C-terminal-truncated Kv1.2 channel. PMID: 19947938
- analysis of full-length Shaker potassium channel Kv1.2 structure by normal-mode-based X-ray crystallographic refinement PMID: 20534430
- atomic-resolution observations of permeation and gating in a K(+) channel, based on molecular dynamics simulations of the Kv1.2 pore domain PMID: 20231479
- Kv1.2 channels have general presynaptic function in suppressing terminal hyperexcitability during depolarising after-potential PMID: 12777451
- crystal structure, at a resolution of 2.9 angstroms PMID: 16002581
- Kv 1.2 was found in cochlear nucleus neuronal cell bodies at birth and postnatal day 21 through adulthood, labeling for potassium channel was in axonal processes, whereas the no cell bodies labeled for Kv 1.2. PMID: 16122713
- study shows that activation of presynaptic mu opioid receptors primarily attenuates GABAergic synaptic inputs to central nucleus of the amygdala-projecting neurons in the basolateral amygdala through a signaling mechanism involving Kv1.1 & Kv1.2 channels PMID: 16306173
- Results suggest that amino acids in the pore region help regulate ion permeability or cellular trafficking by affecting glycosylation of Kv1.2. PMID: 16770729
- Enhanced nitrosative stress in diabetes mellitus contributes to Kcna2 channel dysfunction in the coronary microcirculation, which may be restored by ebselen. PMID: 17675568
- Data show that in the KcsA potassium channel, the number and strength of hydrogen bonds between residues in the selectivity filter and pore helix determine the rate and extent of C-type inactivation, which can also be engineered in Kv1.2 channels. PMID: 17922012
- impairment of cAMP-mediated endothelium independent vasodilation of rat small coronary artery by STZ-induced diabetes was resulted from decrease of mRNA and protein expressions of Kv channels, and which leads to a reduced current from Kv channels PMID: 17982915
- cluster of cytoplasmic C-terminal phosphorylation sites regulates Kv1.2 trafficking PMID: 18056633
- Expression of Kv1.2, Kv1.5, and Kv2.1 was higher in mesenteric arteries but was not different in aortas of SHR rats as compared to WKY rats PMID: 18174882
- R294H, A351H mutagenesis and also in combination with D352G, E353S mutations (oocytes expression)show intersubunit histidine metallic bridges formed between the first arginine of S4 (R294) and residues A351 or D352 of the pore domain PMID: 18504314
- We conclude that Kv1.2 in microglia modulates IL-1beta and TNF-alpha expression and ROS production probably by regulating the intracellular potassium concentration. PMID: 18627436
- The Kv1.2 channel exhibits functional properties that are distinct from Kv1.2 channels reported in the literature. PMID: 18638484
- the dynamic interaction of the C-terminus with the S4-S5 linker from a neighboring subunit of the Kv1.2 channel provides a mechanism for its C-terminus to regulate the channel activation PMID: 19247844
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane. Cell projection, axon. Cell junction, synapse. Cell junction, synapse, synaptosome. Cell junction, synapse, presynaptic cell membrane. Cell projection, dendrite. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane. Endosome. Perikaryon. Cell junction, paranodal septate junction.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, A (Shaker) (TC 1.A.1.2) subfamily, Kv1.2/KCNA2 sub-subfamily
-
组织特异性:Detected in neurons in dorsal root ganglion. Detected in hippocampus neurons. Detected on neurons of the anteroventral cochlear nucleus. Detected in renal arteries. Detected in neurons of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Detected in neurons in th
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:25468
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000042653
UniGene: Rn.10298
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
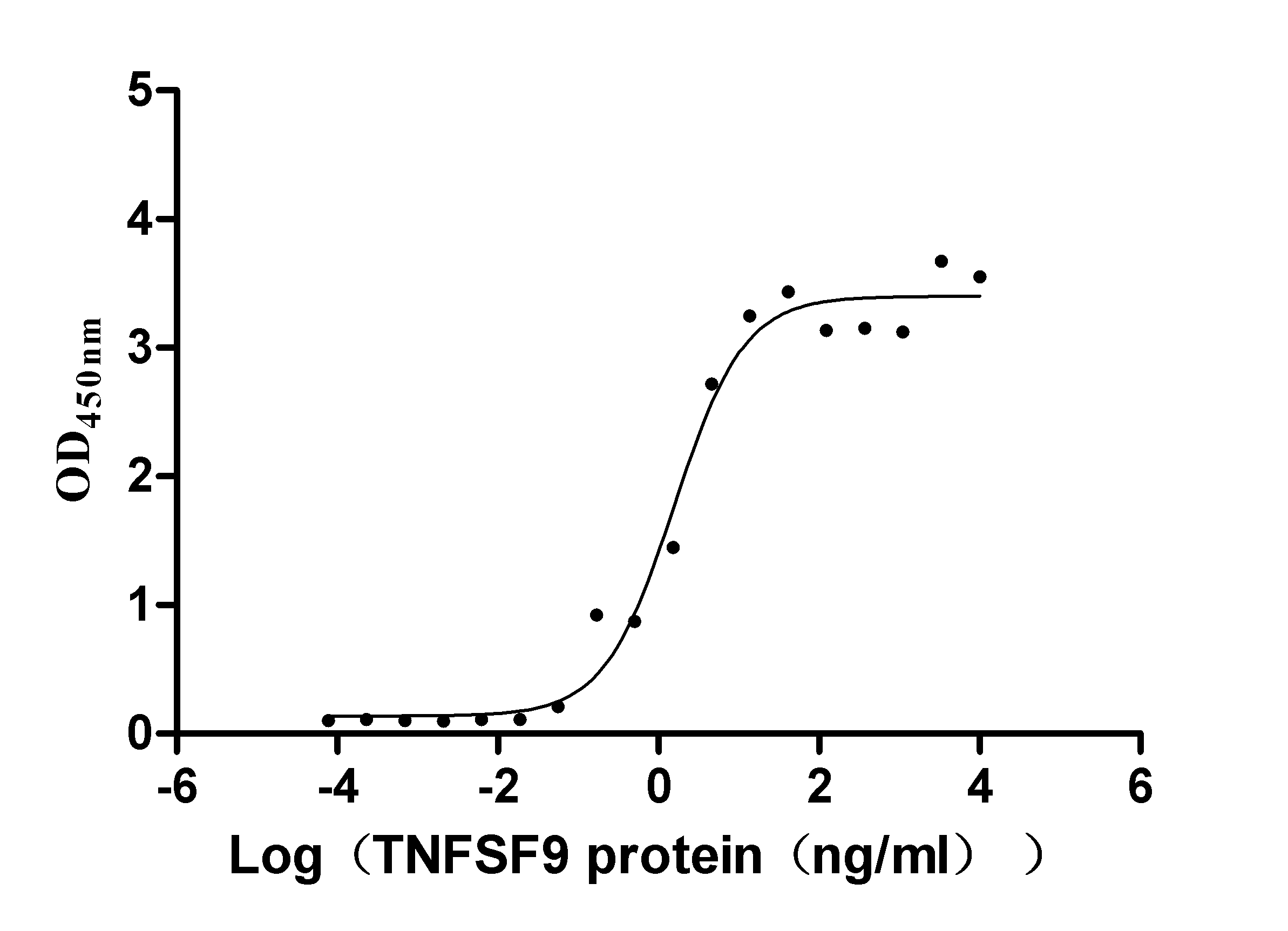
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
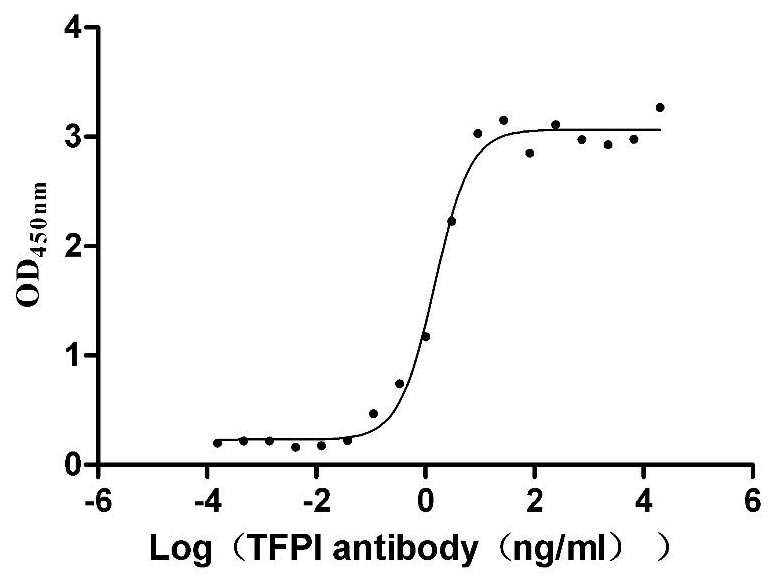
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
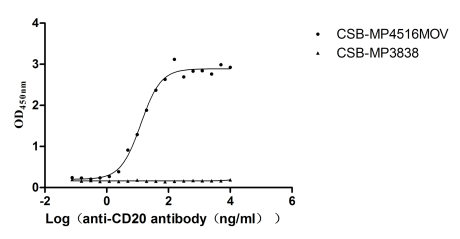
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
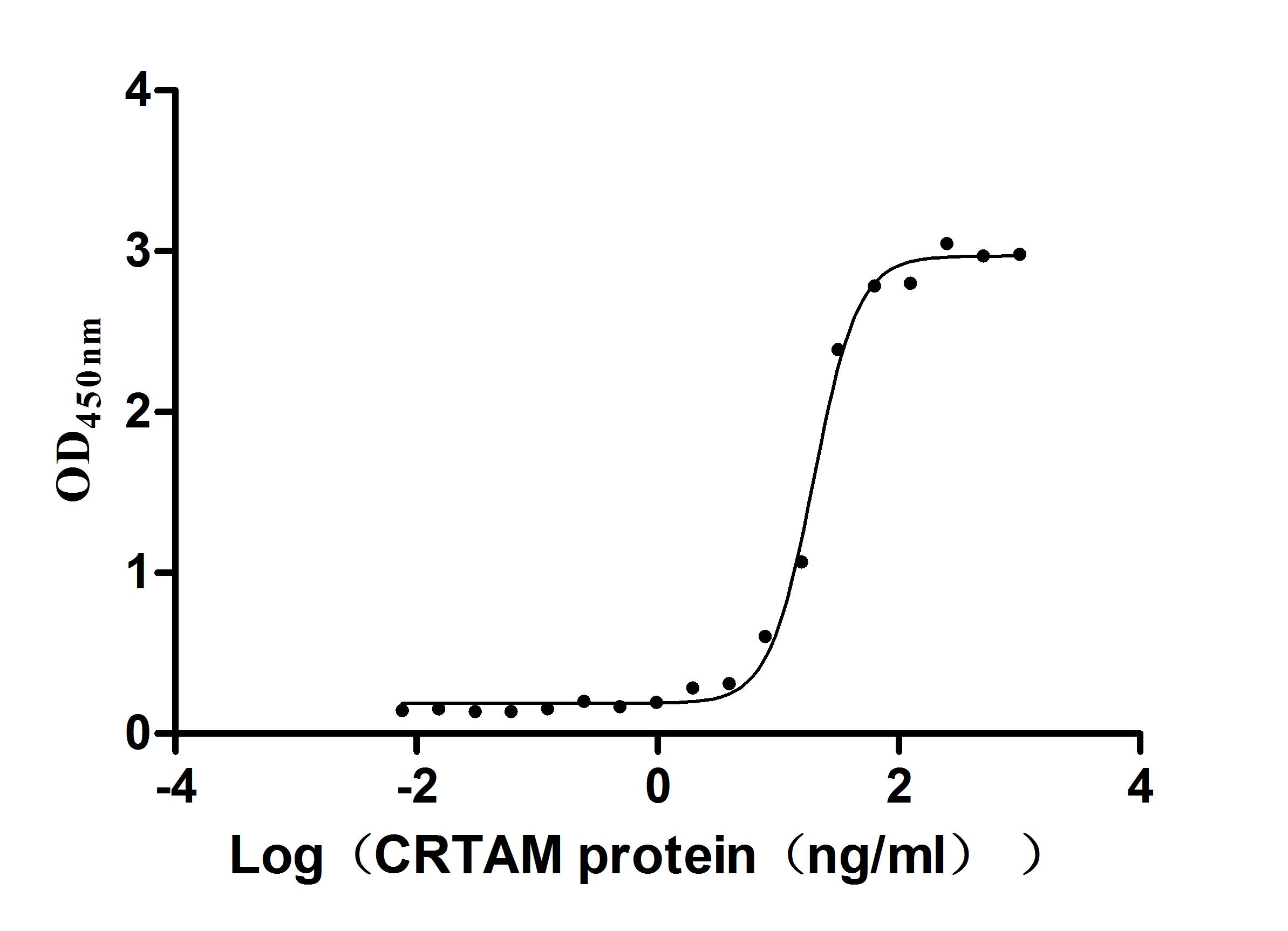
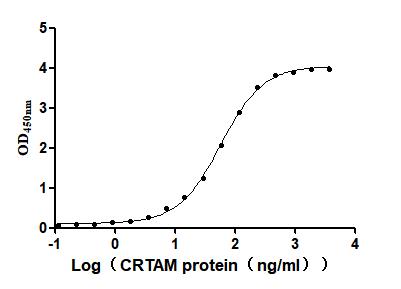
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
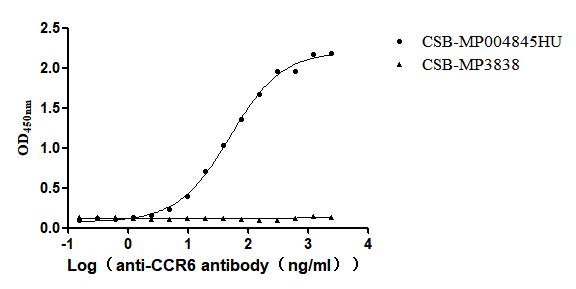
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)