Recombinant Rat Heparanase (Hpse), partial
In Stock Promotion-
中文名称:大鼠Hpse重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP010716RA
-
规格:¥2328
-
促销:

-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
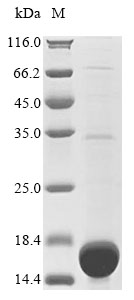
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:Hpse
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Hpse; HepHeparanase; EC 3.2.1.166; Endo-glucoronidase) [Cleaved into: Heparanase 8 kDa subunit; Heparanase 50 kDa subunit]
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:15.8 kDa
-
表达区域:29-102aa
-
氨基酸序列KDVVDLEFYTKRLFQSVSPSFLSITIDASLATDPRFLTFLGSPRLRALARGLSPAYLRFGGTKTDFLIFDPNKE
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Endoglycosidase that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) into heparan sulfate side chains and core proteoglycans. Participates in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and remodeling. Selectively cleaves the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying either a 3-O-sulfo or a 6-O-sulfo group. Can also cleave the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying a 2-O-sulfo group, but not linkages between a glucuronic acid unit and a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid moiety. It is essentially inactive at neutral pH but becomes active under acidic conditions such as during tumor invasion and in inflammatory processes. Facilitates cell migration associated with metastasis, wound healing and inflammation. Enhances shedding of syndecans, and increases endothelial invasion and angiogenesis in myelomas. Acts as procoagulant by increasing the generation of activation factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activation factor VII. Increases cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), independent of its enzymatic activity. Induces AKT1/PKB phosphorylation via lipid rafts increasing cell mobility and invasion. Heparin increases this AKT1/PKB activation. Regulates osteogenesis. Enhances angiogenesis through up-regulation of SRC-mediated activation of VEGF. Implicated in hair follicle inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Heparanase plays an important role in mediating the neuroinflammatory response after subarachnoid hemorrhage. PMID: 28720149
- Endothelial cell-to-cardiomyocyte transfer of heparanase to modulates the cardiomyocyte cell death signature. This mechanism was observed in the acutely diabetic heart, and its interruption following chronic diabetes may contribute towards the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. PMID: 27979811
- the expression of the gene for heparanase was increased in the right and left ventricles after treatment with monocrotaline PMID: 26638897
- Inhibiting heparanase function could offer a new strategy for managing cardiomyopathy observed after diabetes. PMID: 24608441
- Suggest that the heparanase-lipoprotein lipase-VEGF axis amplifies fatty acid delivery, a rapid and adaptive mechanism that is geared to overcome the loss of glucose consumption by the diabetic heart. PMID: 24115032
- active heparanase released lipoprotein lipase from the myocyte surface PMID: 23471235
- Heparanase and TFPI are locally elevated in the process of avascular necrosis and are normalized on treatment. PMID: 23063054
- Heparanase gene is involved in heparan sulfate proteoglycans metabolism. PMID: 22339633
- HPR1 production is increased in endothelial cells from rat models of diabetes, and in macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions of diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Increased HPR1 production may contribute to pathogenesis and progression of atherosclerosis. PMID: 21424539
- Heparanase was upregulated and associated with increased VEGF in streptozotocin diabetic rat retinas. Heparanase may be involved in development of diabetic retinopathy and may be possible novel target for therapeutic intervention. PMID: 20130710
- Characterization of a novel intracellular heparanase that has a FERM domain. PMID: 11988100
- characterization of rat heparanase activity in a parathyroid cell line PMID: 12077130
- heparanase gene transcription is regulated in activated T cells by early growth response 1 PMID: 14522979
- Heparanase plays a role in ovaian tissue remodeling during folliculogenesis and forpus luteum formation and regression. PMID: 15728796
- heparanase contributes to the pathogenesis of proteinuria in a model of anti-GBM disease PMID: 15877677
- Results describe the cellular localization of heparanase and its colocalization with syndecan-3 in spinal cords of adult rats. PMID: 16320243
- These results suggest involvement of radicals and angiotensin II in the modulation of glomerular basement membrane permeability through heparan sulfate and heparanase expression. PMID: 16899518
- HPSE is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in overt diabetic nephropathy by degradation of heparan sulfates PMID: 17051139
- The expression of heparanase by astrocytes may correlate with the time of migration of reactive astrocytes toward the ischemic core, resulting in astrogliosis. This suggests a novel role of heparanase in the pathophysiology of brain ischemia. PMID: 17368723
- Results suggest the involvement of heparanase in the migration or invasion of microglia or brain macrophages across basement membrane around brain vasculature. PMID: 18222122
- results suggest heparanase expression increases after castration & correlates with decreased heparan sulfate; variation in heparanase expression is involved in tissue remodeling & control of regressive pattern after 1 week of androgen deprivation PMID: 18278514
- role for heparanase in the regulation of arterial structure, mechanics, and repair PMID: 19096032
- Following hyperglycemia, translocation of lipoprotein lipase from cardiomyocytes to endothelial cells is dependent on fatty acids to increase endothelial intracellular heparanase followed by secretion of heparanase by glucose. PMID: 19218500
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Secreted. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Glycosyl hydrolase 79 family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:64537
UniGene: Rn.6392
Most popular with customers
-
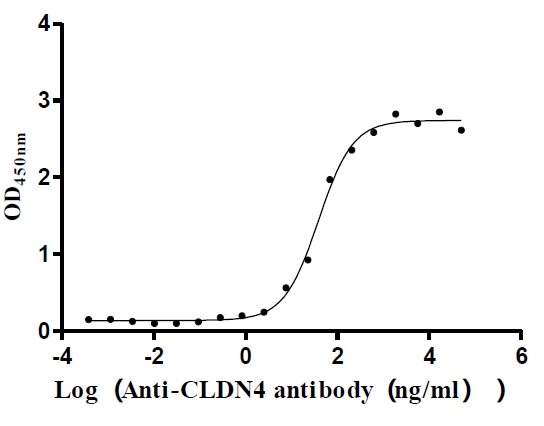
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
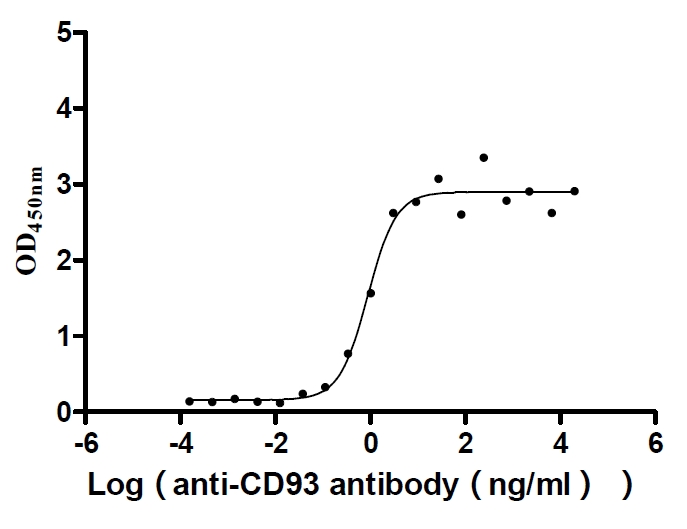
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
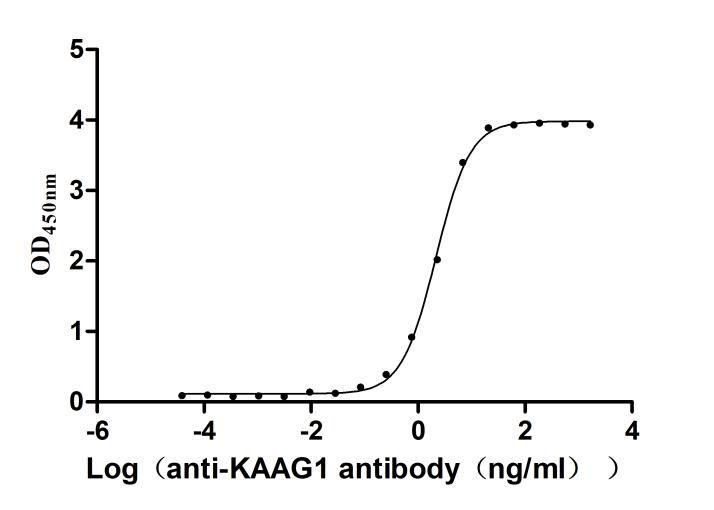
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)