Recombinant Escherichia coli Protein RecA (recA)
-
货号:CSB-YP358971ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP358971ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP358971ENV-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP358971ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP358971ENV
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:recA
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:recA; lexB; recH; rnmB; tif; umuB; zab; b2699; JW2669; Protein RecA; Recombinase A
-
种属:Escherichia coli (strain K12)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-353
-
氨基酸序列AIDENKQKA LAAALGQIEK QFGKGSIMRL GEDRSMDVET ISTGSLSLDI ALGAGGLPMG RIVEIYGPES SGKTTLTLQV IAAAQREGKT CAFIDAEHAL DPIYARKLGV DIDNLLCSQP DTGEQALEIC DALARSGAVD VIVVDSVAAL TPKAEIEGEI GDSHMGLAAR MMSQAMRKLA GNLKQSNTLL IFINQIRMKI GVMFGNPETT TGGNALKFYA SVRLDIRRIG AVKEGENVVG SETRVKVVKN KIAAPFKQAE FQILYGEGIN FYGELVDLGV KEKLIEKAGA WYSYKGEKIG QGKANATAWL KDNPETAKEI EKKVRELLLS NPNSTPDFSV DDSEGVAETN EDF
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Required for homologous recombination and the bypass of mutagenic DNA lesions by the SOS response. Catalyzes ATP-driven homologous pairing and strand exchange of DNA molecules necessary for DNA recombinational repair. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP in the presence of single-stranded DNA, the ATP-dependent uptake of single-stranded DNA by duplex DNA, and the ATP-dependent hybridization of homologous single-stranded DNAs. The SOS response controls an apoptotic-like death (ALD) induced (in the absence of the mazE-mazF toxin-antitoxin module) in response to DNA damaging agents that is mediated by RecA and LexA.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results suggest that an unpaired region acts as a kinetic trap for RecA-based nucleoprotein filaments, impeding the assembly mechanism. PMID: 28112216
- Coupling of helicase and RecA-loading activity during dsDNA-end resection is crucial in avoiding the deleterious effects of a long and stabile 3' tail in E. coli. PMID: 28689072
- RecA-based nucleoprotein filaments were shown to interact with dsDNA in a highly cooperative manner. PMID: 28977583
- The regulation of RecA filament assembly and the mechanism by which RecA quickly and efficiently searches for and identifies a unique homologous sequence among a vast excess of heterologous DNA has been described. (Review) PMID: 27156117
- Intracellular accumulation of d-serine increases RecA production. PMID: 27698085
- models for how sequence imperfections may affect base triplet recognition by Rad51/RecA family members, and we discuss how these models and our results may relate to the different biological roles of RecA, Rad51, and Dmc1. PMID: 28476890
- Rad51 and RecA juxtapose dsDNA ends ready for DNA ligase-catalyzed end-joining under recombinase-suppressive conditions. PMID: 27794044
- These experiments suggest that ATP plays an unanticipated role in promoting the turnover of captured duplex DNA intermediates as RecA attempts to align homologous sequences during the early stages of recombination. PMID: 27587394
- The results indicate that the toxicity of RecA D112R substitution is due to its persistent binding to duplex genomic DNA, creating barriers for other processes in DNA metabolism. PMID: 27124470
- ATP binding is essential for the mutant version of RecA, RecA730, functions while ATP hydrolysis is required only for double-strand break repair. PMID: 27130282
- Data indicate that large recombinase A (RecA)-independent genomic replacements are a novel recombinant class. PMID: 26162088
- membrane acts as a scaffold for nucleating the formation of RecA filament bundles and plays an important role in the SOS response. PMID: 26481664
- Regression of replication forks stalled by leading-strand template damage: regression by RecA is inhibited by SSB. PMID: 25138217
- it is hypothesized that recA4162 suppresses SOS expression best when the ssDNA occurs at a gap and that uvrD303 is able to decrease SOS expression when the ssDNA is either at a gap or when it is generated at a DSB but does so better at a gap PMID: 24084169
- Data shows recA providing tolerance through SOS response network responding to DNA damage caused by geraniol. PMID: 23906844
- Given the opposite effects of RecA on Pol III and TLS replisomes, we propose that RecA acts as a switch to regulate the occupancy of polymerases within a moving replisome. PMID: 23509251
- Using single-molecule microscopy, we directly visualize RecA filament assembly on single molecules of SSB-coated ssDNA, simultaneously measuring nucleation and growth. PMID: 23103864
- Studies characterized the chromosomal replication and degradation patterns during thymine starvation in Rec+ cells, as well as in the recA and recBCD mutants. PMID: 22621921
- The biochemical properties of the [S240N]RecA and [S240K]RecA proteins are described in this report. PMID: 22521886
- MutL has little effect on RecA-ssDNA filament formation, but does down-regulate the ATPase activity of RecA. PMID: 22001225
- These results reveal specific amino acid determinants of the RecA-LexA interaction and suggest that LexA binds RecA and RecAi+6 at a composite site on the RecA filament, which could explain the role of the active filament during LexA cleavage. PMID: 21912525
- DNA strand exchange promoted by RecA is inhibited by M. tuberculosis HupB (MtHupB) even though M. tuberculosis HupB is not homologous with E. coli HU; RecA is unaffected by either N-terminal nor C-terminal domain of MtHupB alone. PMID: 21787377
- These results emphasize the importance of the 5'-3' exonuclease for high constitutive SOS expression in recA730 mutants and show that RecBCD function can further enhance the excellent intrinsic abilities of the RecA730 protein in vivo. PMID: 21764927
- Recombination potential of RecA is structurally suppressed. PMID: 21143322
- new mechanism of the frequency of recombination exchanges increase by improving the synaptase activity of the RecA protein PMID: 20886744
- Uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains defective in regulation of the SOS response mediated by RecA and LexA display attenuated virulence in immunocompetent mice within the first 6 h post infection. PMID: 20435157
- Data show that recA4142, a novel recA(Con) mutant,is additionally dependent on ruvAB, recJ, xonA, and partially dependent on recQ for its high SOS(Con) expression. PMID: 20304994
- RecA filament disassembly plays a major role in, and may be required for, DNA strand exchange PMID: 19910465
- there is a C-terminal point mutation in RecA protein (E343K) that significantly alters the interaction between RecA and RecX proteins PMID: 15466870
- recA mutants, being unable to repair fragmented chromosomes, depend on various strategies designed to avoid chromosomal fragmentation PMID: 15531636
- Data show that UvrD, but not Rep, directly prevents homologous recombination in vivo, and that RecA contributes to toxicity in the rep uvrD mutant. PMID: 15565170
- Nitrogen-containing amino acids are important in locking in the low-DNA affinity, more compact conformation of RecA PMID: 16008358
- Two types of RecA-GFP foci have been defined in E.coli: 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-sensitive foci that are bound to DNA and DAPI-insensitive foci that are DNA-less aggregates/storage structures. PMID: 16091045
- These results suggested that RecA is a constitutive cellular factor that increases translocation of mini-TnMERI1 and may participate in dissemination of TnMERI1-like transposons. PMID: 16243449
- RdgC inhibits RecA in Escherichia coli PMID: 16377615
- Lys248 plays a significant role in ATP hydrolysis in trans across the subunit-subunit interface in the RecA nucleoprotein filament PMID: 16527806
- RecA-catalyzed hydrolysis of a given nucleotide triphosphate or analogue thereof is exquisitely sensitive to certain structural elements of both the base and ribose moieties. Binding of nucleotides by RecA was found to be conformationally selective. PMID: 16584186
- D100R RecA is characterized by inducible reduced activation of SOS response & diminished ability to promote cellular survival after UV irradiation. D100R substitution caused perturbation of RecA-ATP interactions & decrease in affinity of RecA for ssDNA. PMID: 16584187
- Analysis of the single-stranded DNA sequence specificity of Escherichia coli RecA protein. PMID: 16684994
- These findings indicate that the sequence specificity in recombination is achieved by Watson-Crick pairing in the context of base-pair dynamics inherent to the extended DNA structure bound by RecA during strand exchange. PMID: 16756994
- The model is able to reproduce a wide range of observed helix pitches in transitions between compressed and stretched conformations of the RecA filament PMID: 16909421
- trans-stimulation of pol V by RecA bound to ssDNA reflects a distinctive regulatory mechanism of mutation that resolves the paradox of RecA filaments assembled in cis on a damaged template strand obstructing translesion DNA synthesis PMID: 16929290
- mechanisms of RecA-mediated three-strand homologous recombination PMID: 16946710
- overall orientation and also the internal structure of RecA in the active filament are not markedly altered when the bound DNA changes from single- to double-stranded PMID: 16964978
- direct observation of filament assembly on individual double-stranded DNA molecules using fluorescently modified RecA PMID: 16988658
- These results support the proposal that the RecA protein restructures DNA, preparing it for the recognition of a complementary second DNA strand, and that the recognition is due mainly to direct base-base contacts between DNA strands. PMID: 17097680
- These data show that the loading of RecA protein by RecBCD is necessary in vivo, and they show that RecA proteins with enhanced single-stranded DNA-binding capacity can partially bypass the need for RecBCD-mediated loading. PMID: 17141804
- Study showed that the RecA-DNA filament disassembled in the direction from 5' to 3' of ssDNA as dATP hydrolysis proceeded. PMID: 17202195
- in vivo role for UvrD in removing RecA from the DNA PMID: 17259317
- RecA is the first reported cellular factor specifically affecting swarming but not swimming motility in E. coli. PMID: 17391508
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:RecA family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: ecj:JW2669
STRING: 316407.85675524
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
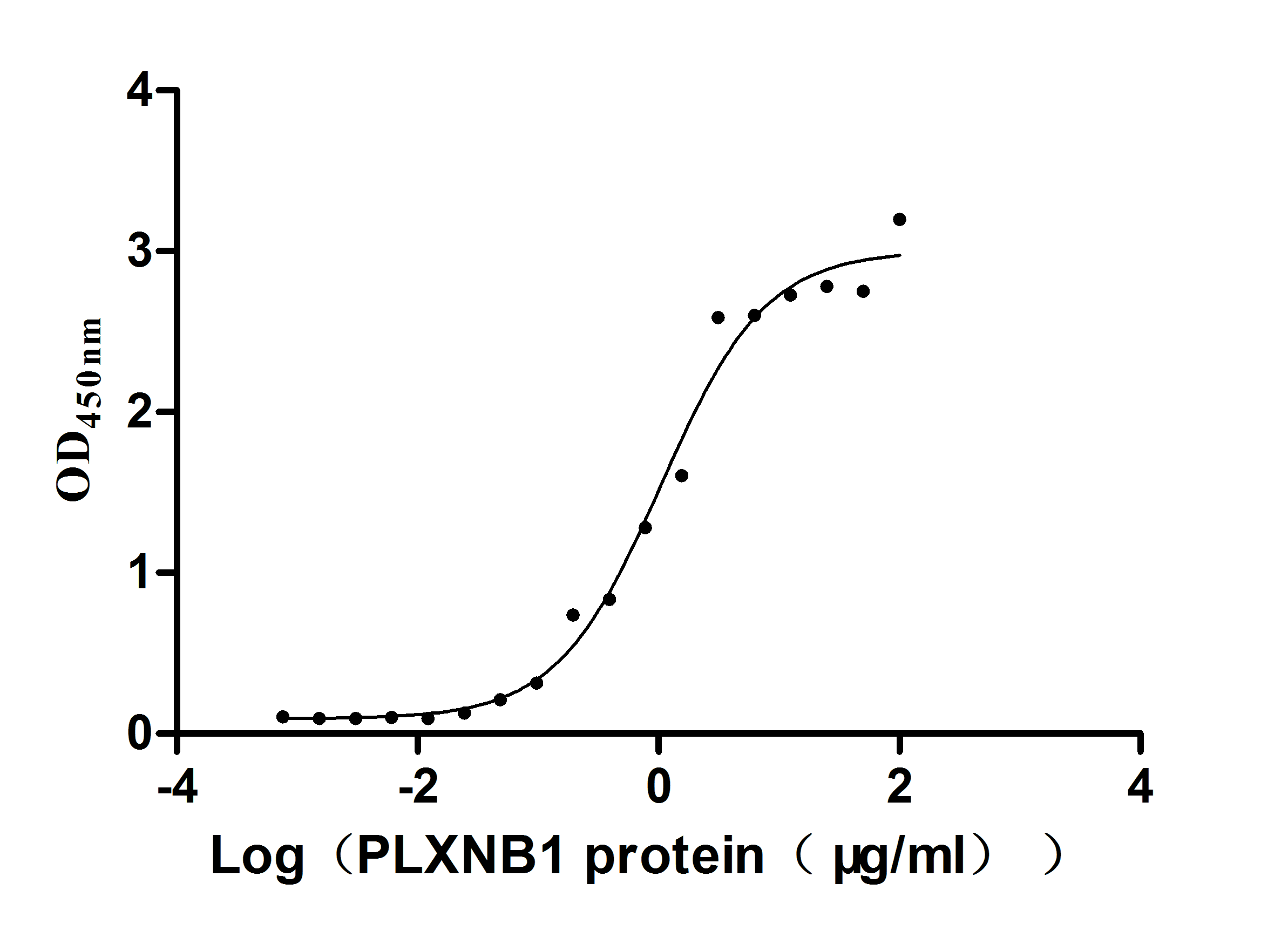
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
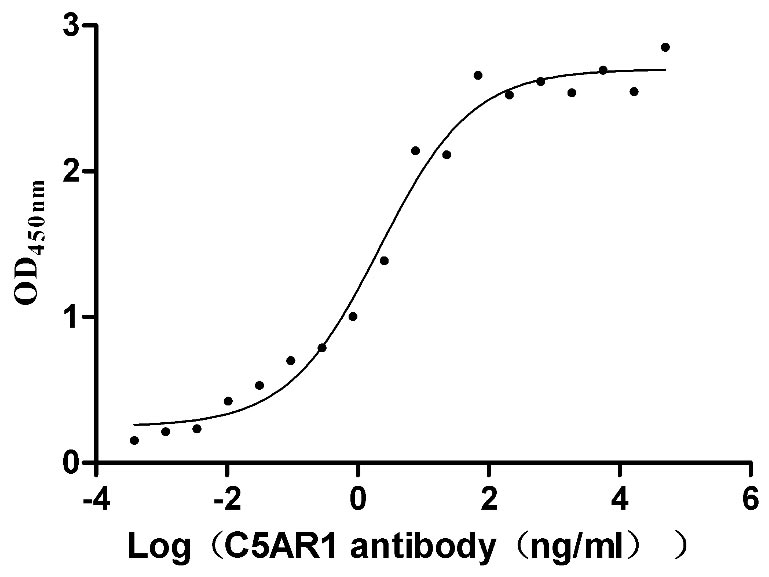
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
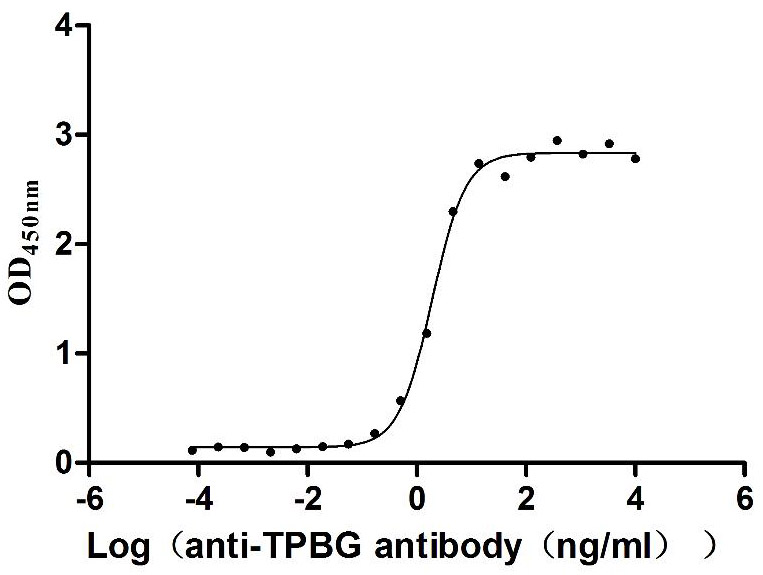
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
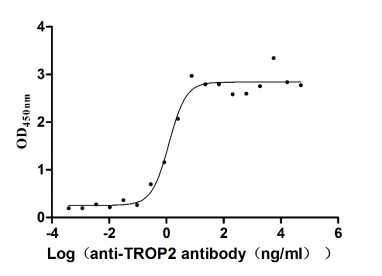
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)